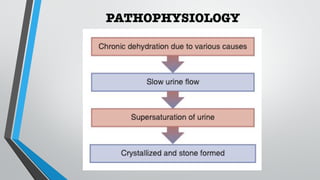
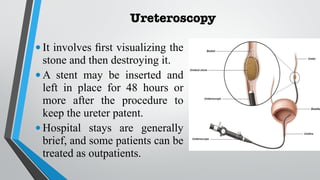
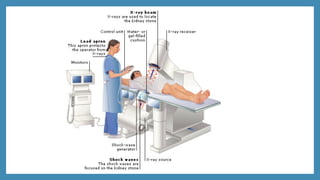
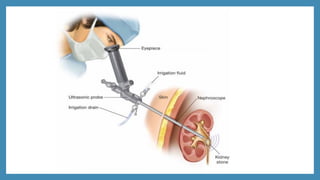
This document discusses renal calculi (kidney stones), including their incidence, causes, risk factors, types, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management. It provides an overview of the different types of kidney stones such as calcium, struvite, uric acid and cystine stones. Diagnostic tests including imaging, blood tests and urine analysis are used to identify stones and determine their composition. Treatment involves pain relief, increasing fluid intake, preventing infections, and sometimes surgical procedures if stones do not pass spontaneously. Nursing care focuses on relieving pain, ensuring adequate hydration and output, and educating patients on preventing future stone recurrences.