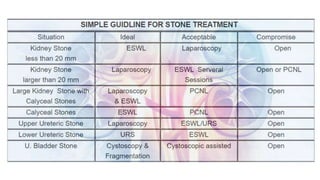
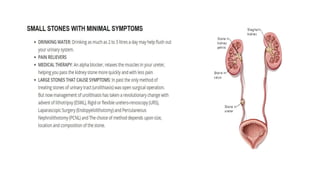
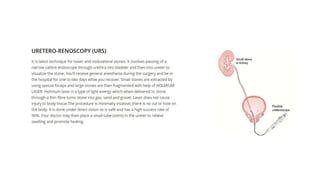
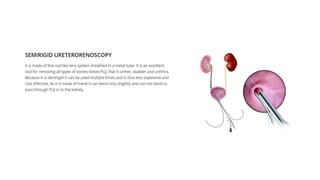
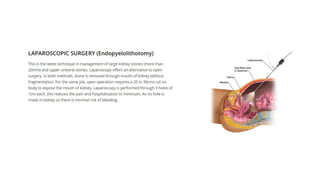
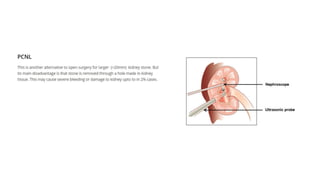
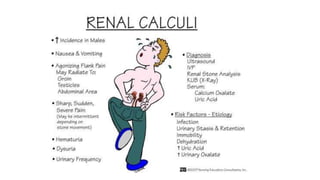
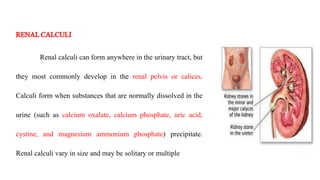
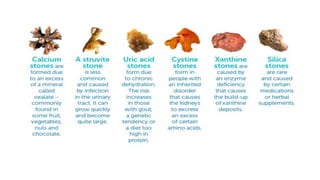
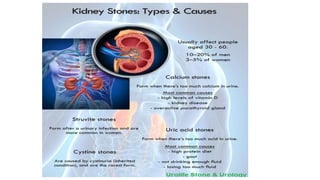
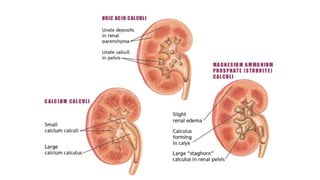
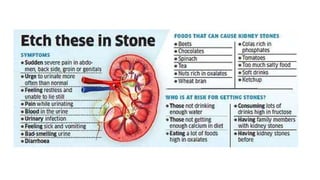
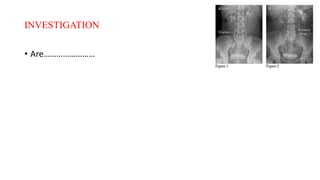
Renal calculi, or kidney stones, form when substances normally dissolved in urine precipitate. Risk factors include dehydration, urinary tract infections, abnormal urine pH, immobilization, and certain metabolic disorders. Symptoms include severe flank pain radiating to the groin (renal colic), nausea, vomiting, fever and hematuria. Treatment involves vigorous hydration, antibiotics, pain medications, and procedures to remove or break up stones depending on size. Nursing care focuses on monitoring fluid intake and output, administering medications, and educating patients on preventative diet and lifestyle changes.






![Treatment
Vigorous hydration (more than 3 qt [3 L]/24 hr) to encourage natural passage of small calculi
Antimicrobial agents (for infection, varying with the cultured organism)
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ketorolac (proven effective for renal coli
pain)Analgesics, such as morphine (for pain)
Diuretics to prevent urinary stasis and further calculus formation (thiazides decrease calcium
excretion into the urine)
Methenamine mandelate to suppress calculus formation (for infection)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/renalcakculi-210515050400/85/Renal-cakculi-13-320.jpg)