FRENCH RENAISSANCE
Geographical : France was united with its capital at Paris lead to the spread of Renaissance to all the parts of France. Due to the proximity of France from Italy, it took 50 years for Renaissance to spread.
Religious : As the number of gothic churches was adequate for population only few churches were built in 15th CE. Later in 16th CE under Jesuit orders churches were built for preaching to large congregations.
Social : The eminence in art and literature in Paris lead to the adoption of a national architectural style that emanated from the Parisian schools. Louis XIV was a great patron of the later renaissance in France & the palaces of Louvre and Versailles are monuments to his lavish expenditure on architecture & the decorative arts.
Historical : The main factor that resulted in the unification of France was the expulsion of the English in 1453 by Joan of Arc. The new national feeling gave great impetus to architecture & resulted in the building of many fine monuments.
Geological : Paris is considered to be the city of stone and building materials were available in abundance.
Climatic: Dissimilar to Italy, the climatic conditions had lead to large windows, high pitched roof, and lofty chimneys.
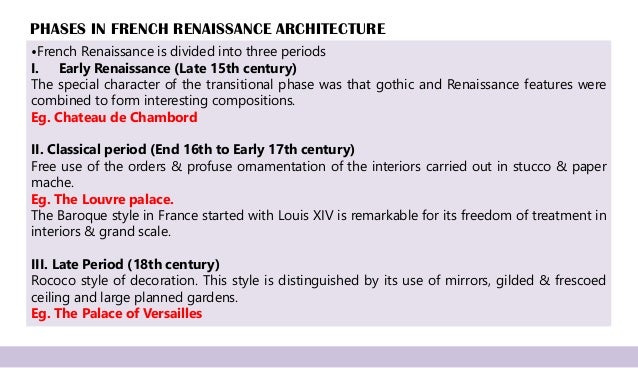
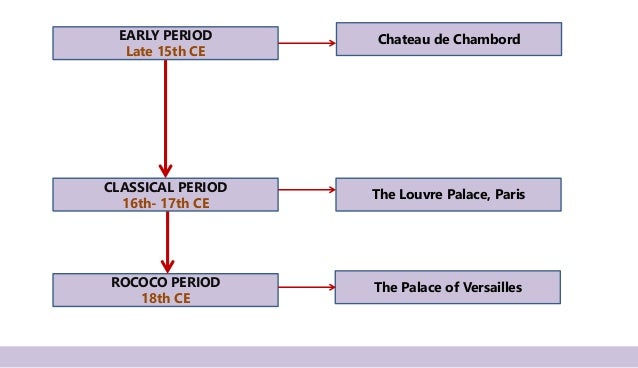
⦁French Renaissance is divided into three periods
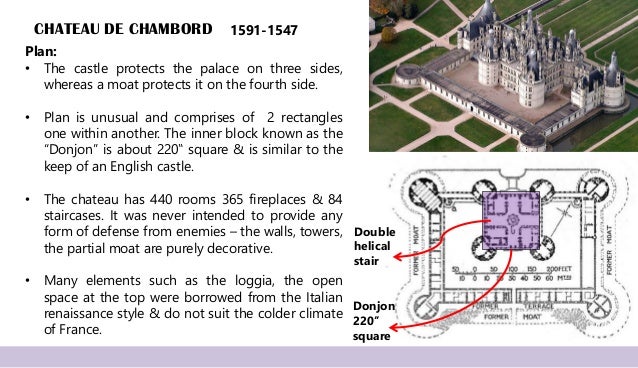
Early Renaissance (Late 15th century)
The special character of the transitional phase was that gothic and Renaissance features were combined to form interesting compositions.
Eg. Chateau de Chambord
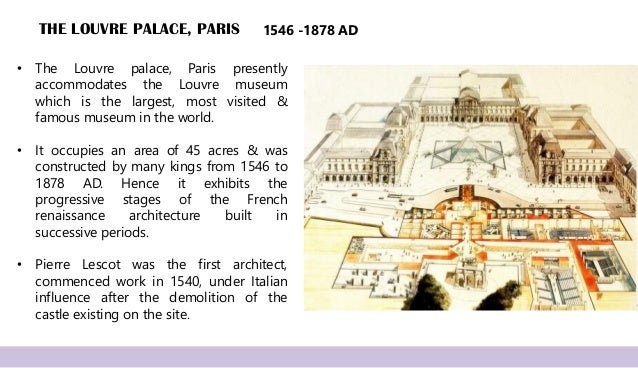
II. Classical period (End 16th to Early 17th century)
Free use of the orders & profuse ornamentation of the interiors carried out in stucco & paper mache.
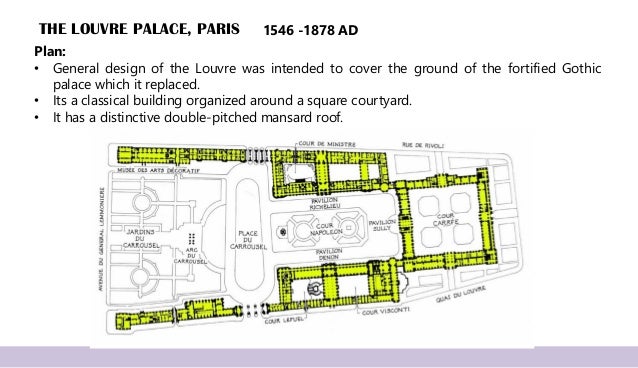
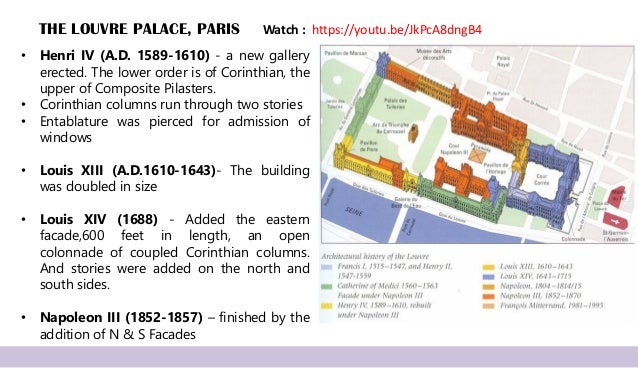
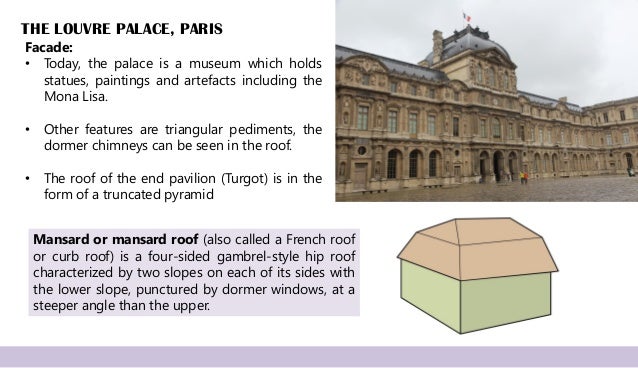
Eg. The Louvre palace.
The Baroque style in France started with Louis XIV is remarkable for its freedom of treatment in interiors & grand scale.
III. Late Period (18th century)
Rococo style of decoration. This style is distinguished by its use of mirrors, gilded & frescoed ceiling and large planned gardens.
Eg. The Palace of Versailles
ROCOCO STYLE
The Rococo style began in France in the 1730s as a reaction against the more formal and geometric Louis XIV style.
Rococo or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colors, sculpted molding, and trompe-l’oeil frescoes to create surprise and the illusion of motion and drama. It is often described as the final expression of the Baroque movement.