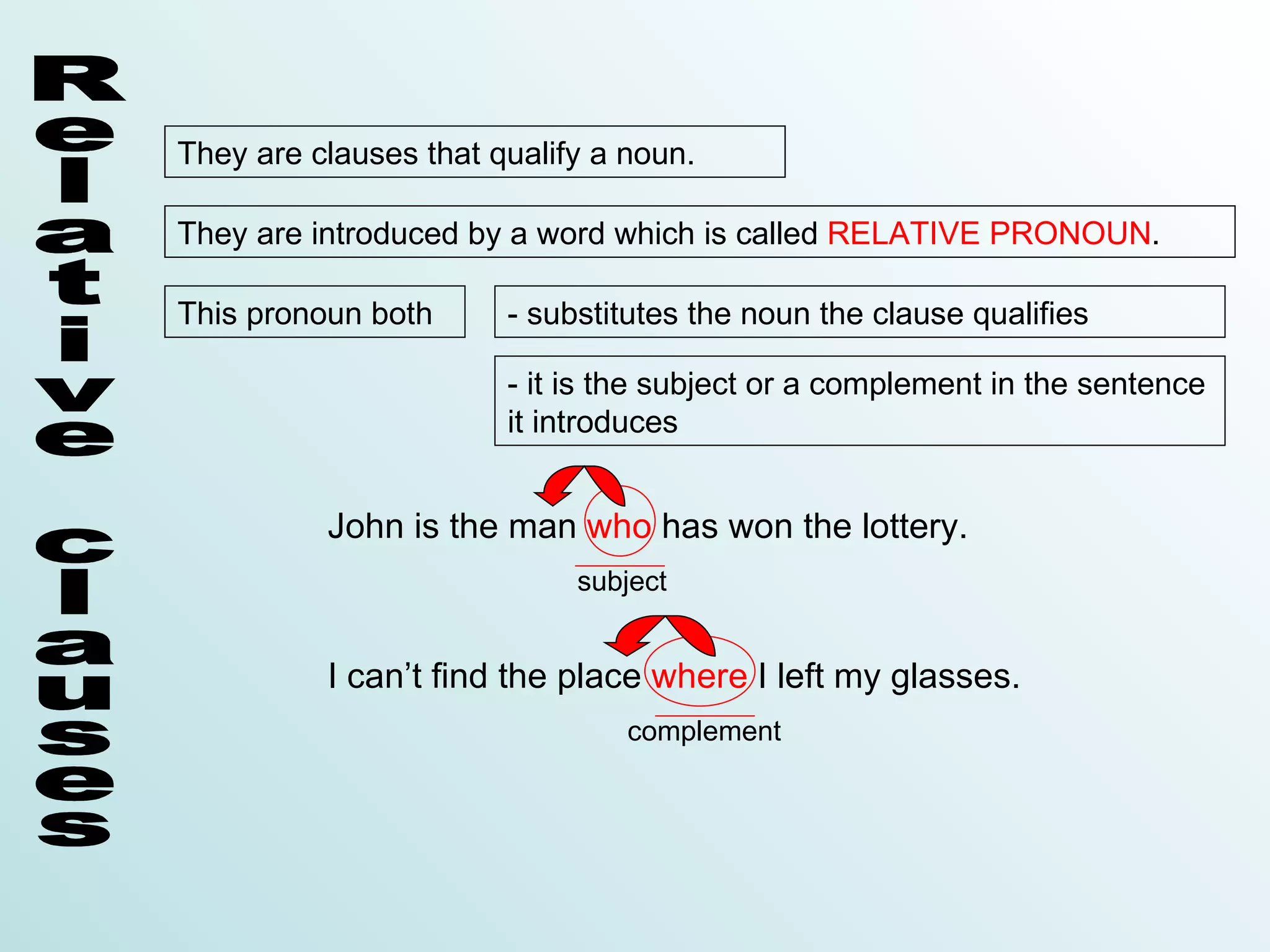
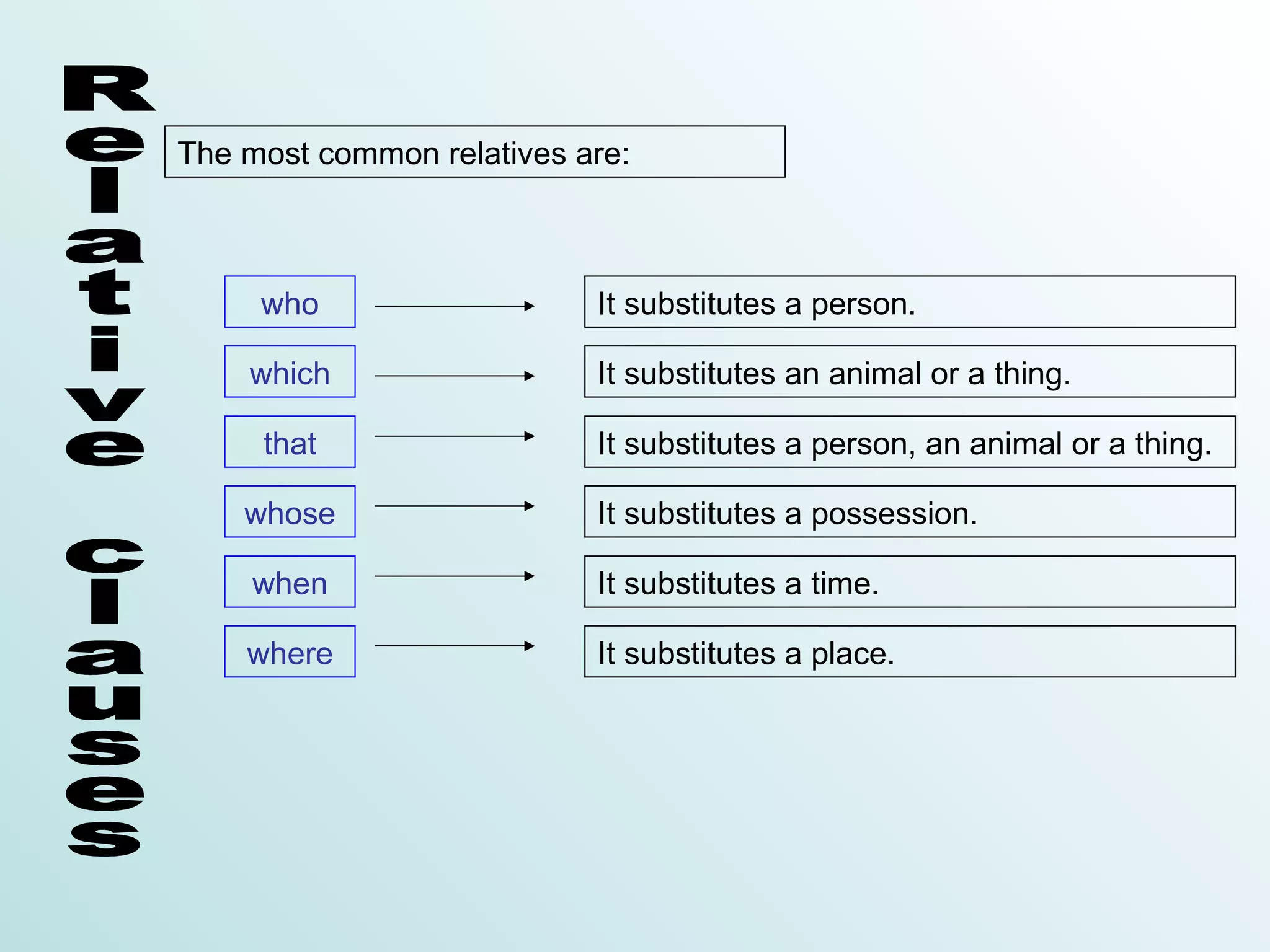
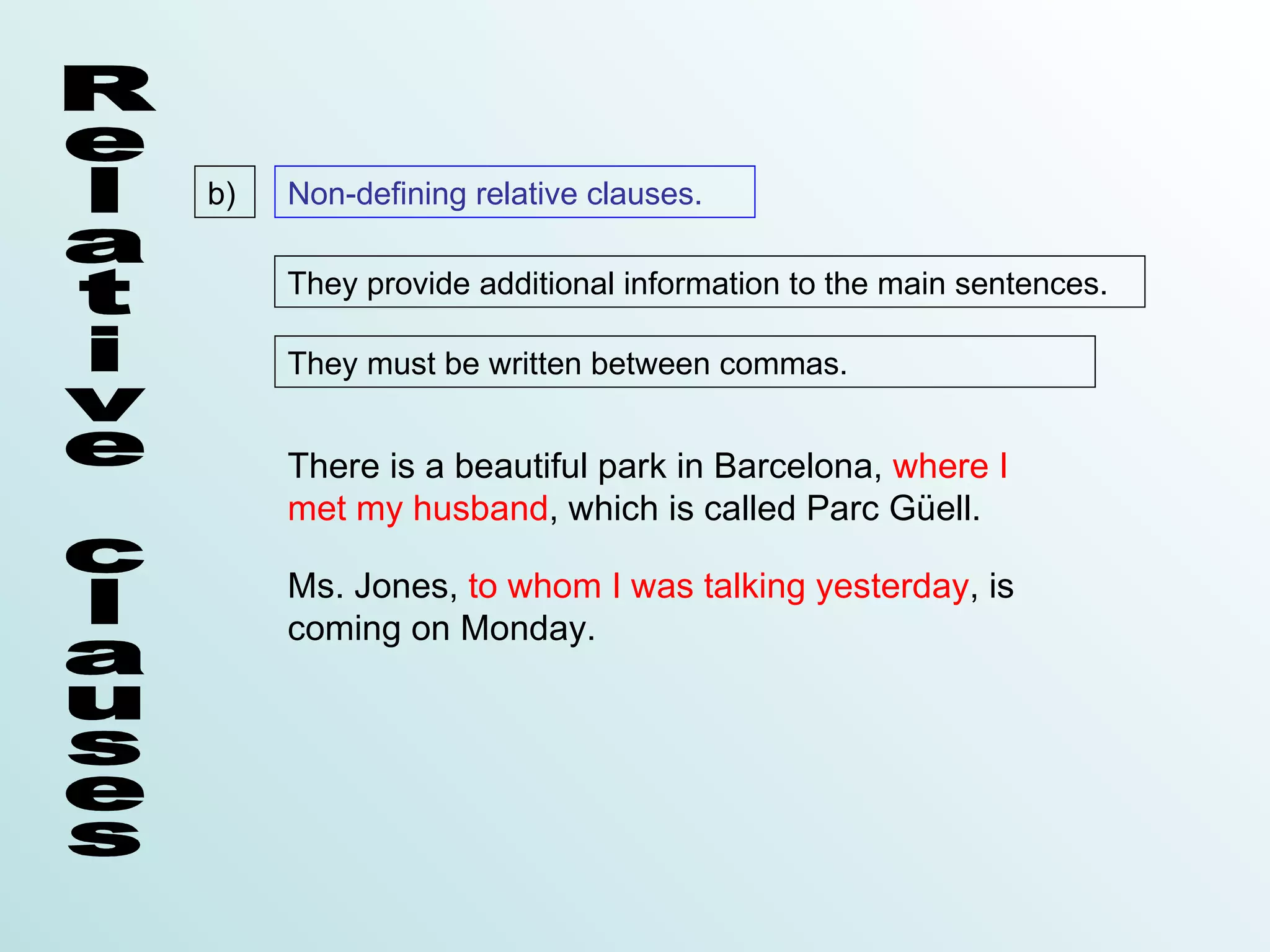
Relative clauses are clauses that qualify a noun. They are introduced by a relative pronoun such as who, which, that, whose, when, or where. The relative pronoun substitutes the noun and acts as the subject or complement in the relative clause. There are two types of relative clauses - defining clauses that provide essential information, and non-defining clauses that provide additional, non-essential information enclosed in commas. The relative pronoun can sometimes be omitted depending on whether it is the subject or preceded by a preposition.