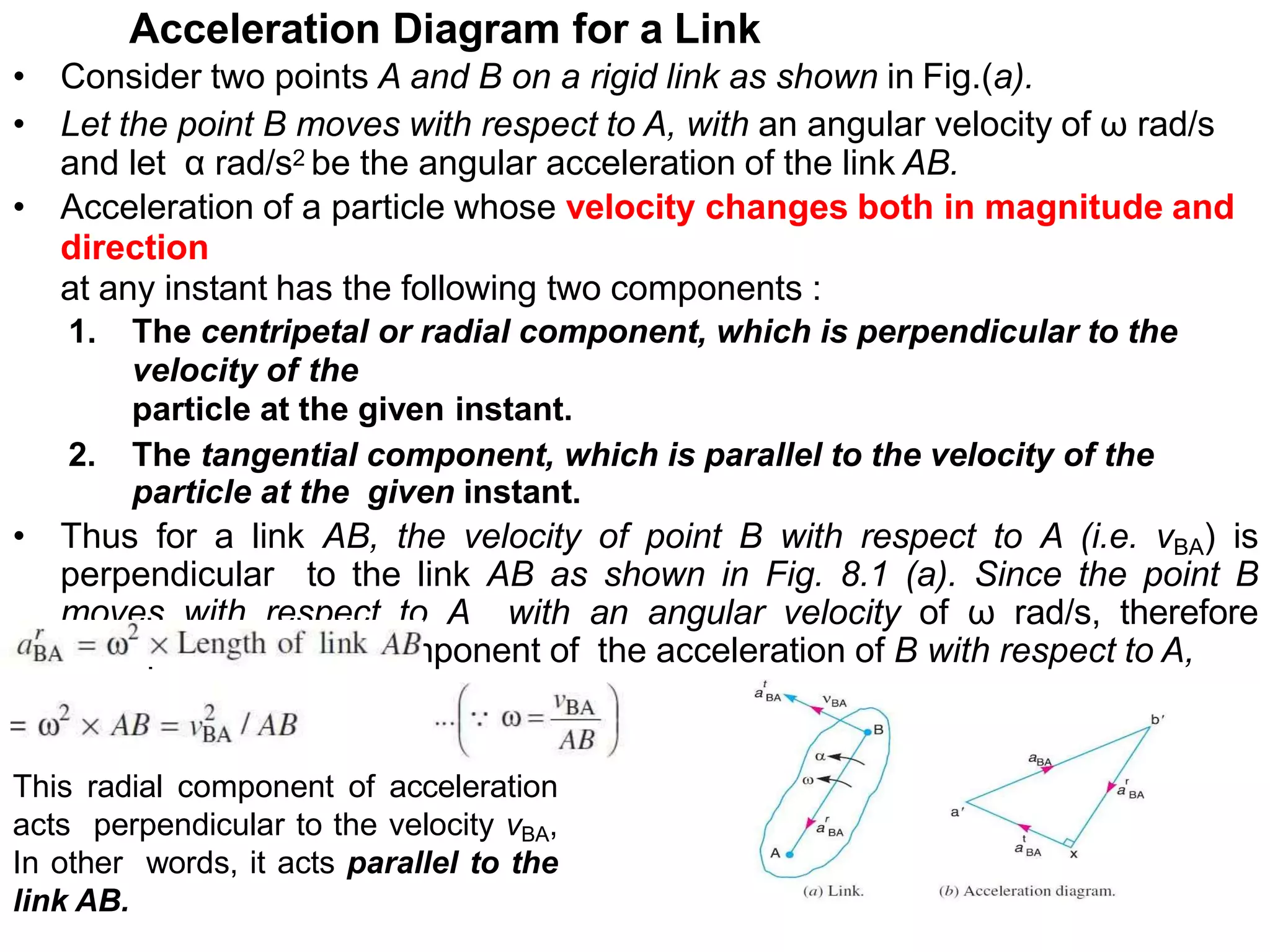
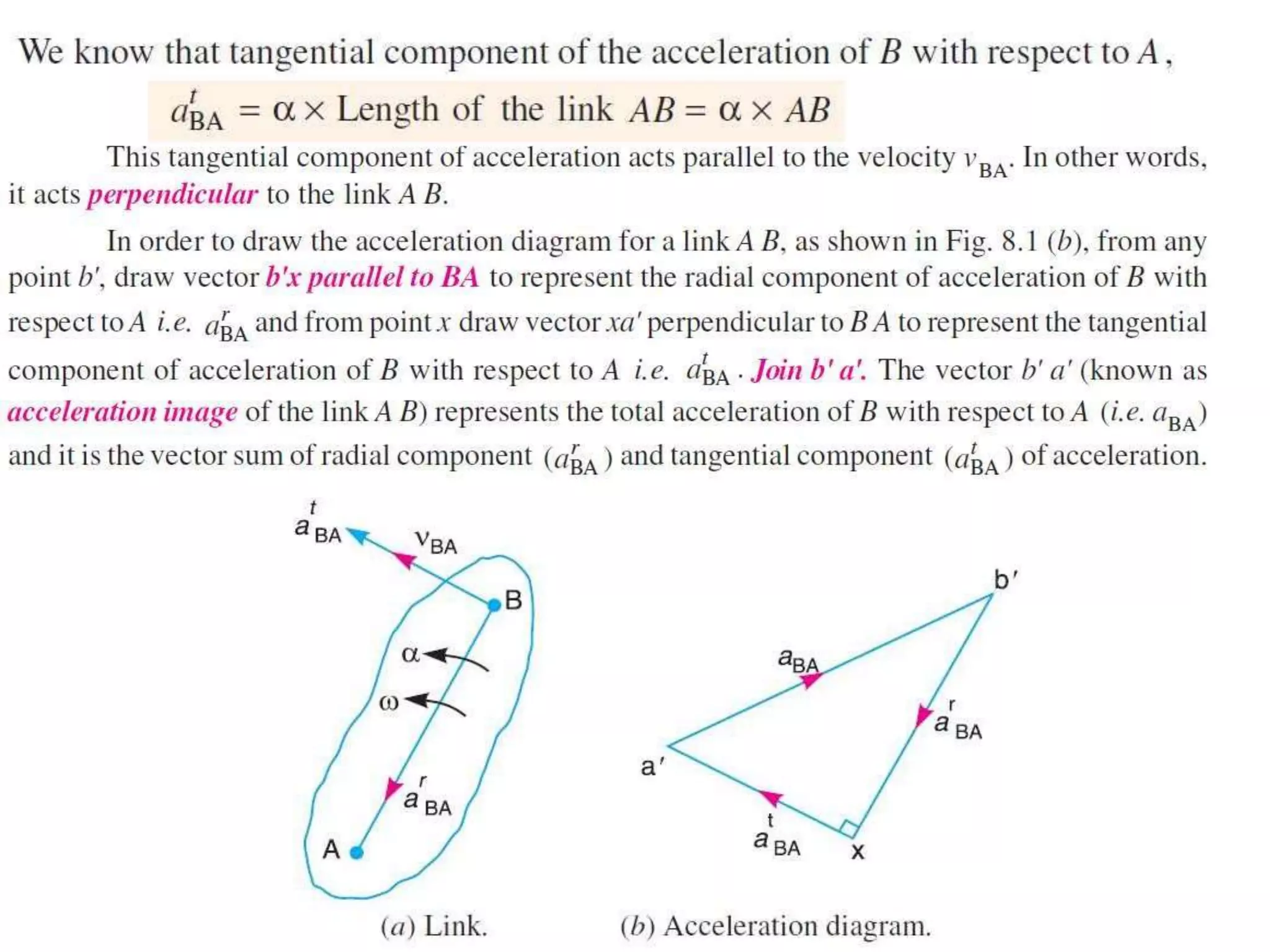
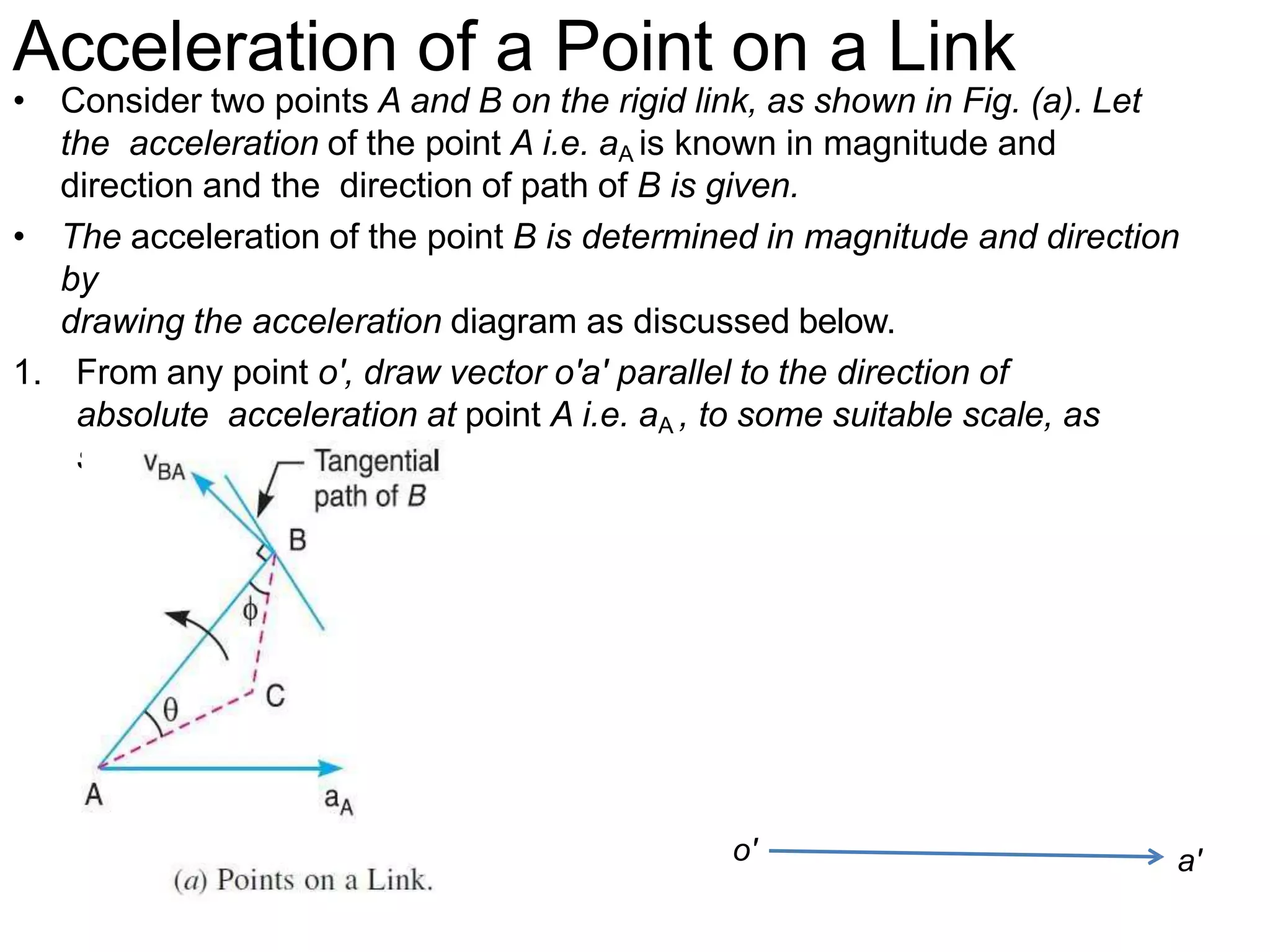
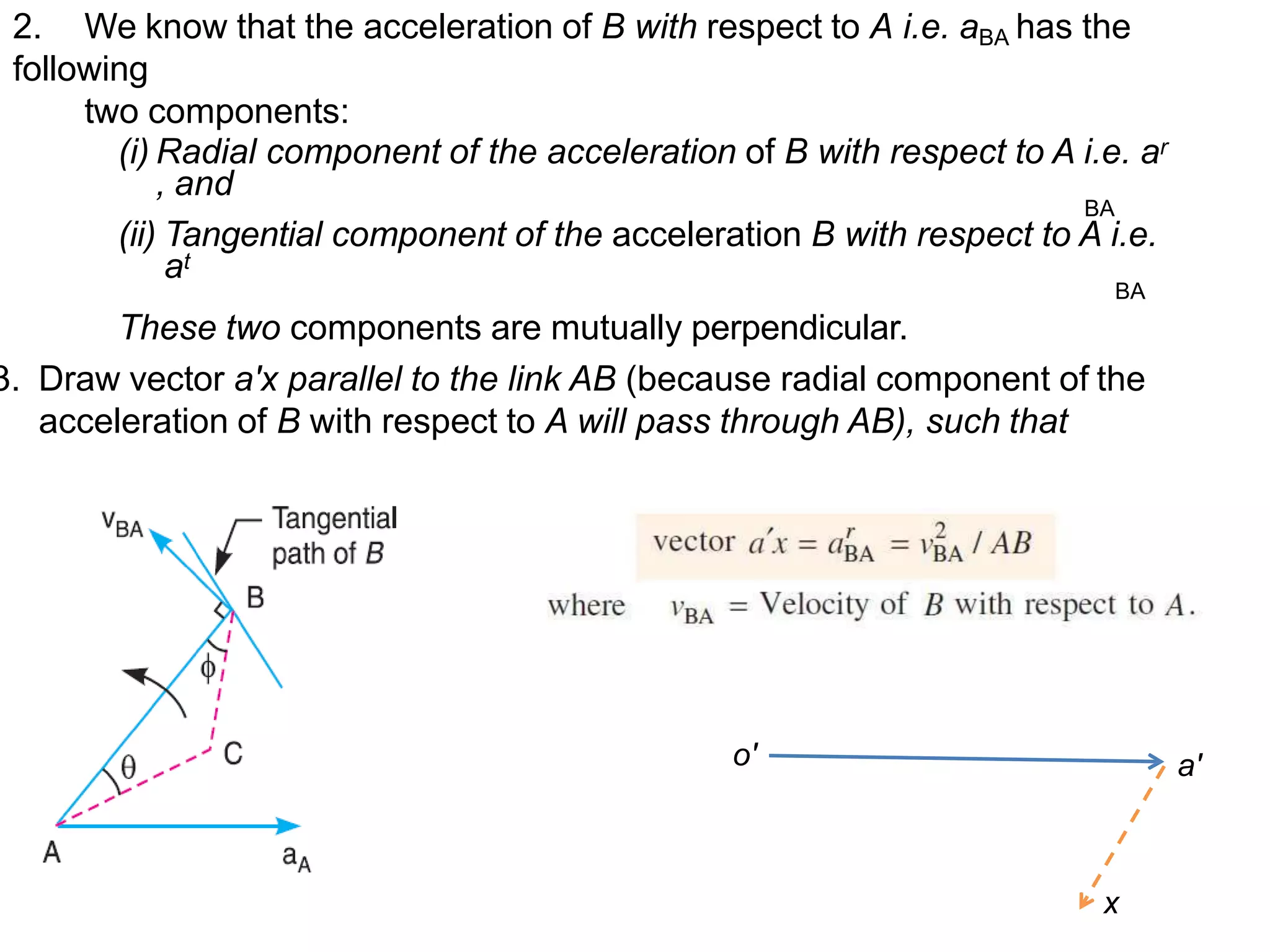
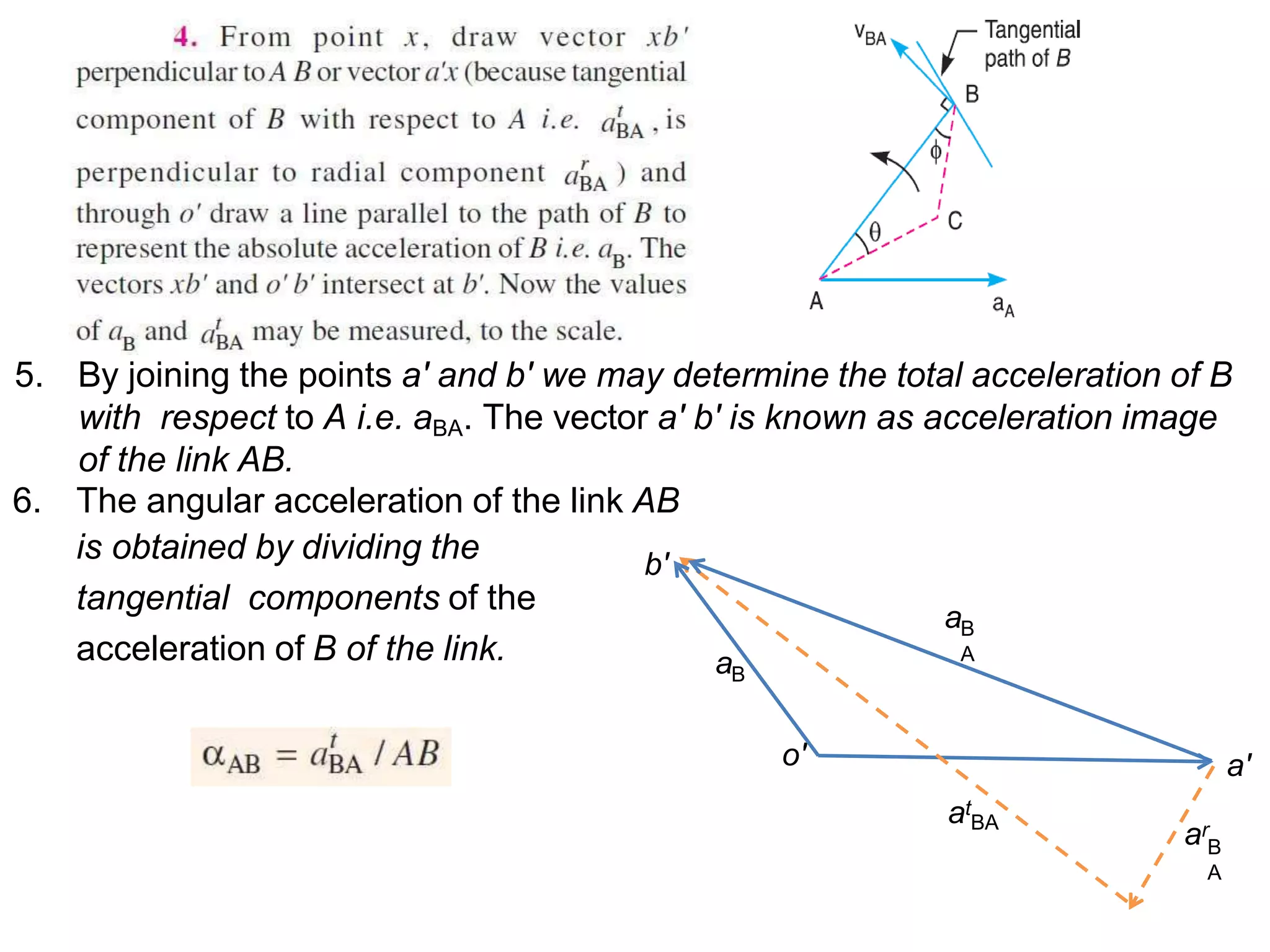
The document describes how to determine the acceleration of a point on a rigid link. It explains that the acceleration has two components - a radial component perpendicular to the velocity and a tangential component parallel to the velocity. It provides steps to draw an acceleration diagram: 1) Draw a vector for the acceleration of point A, 2) Draw a vector parallel to the link AB for the radial component, 3) Draw a vector for the tangential component perpendicular to the radial component, and 4) Join the vectors to determine the total acceleration of point B with respect to point A.