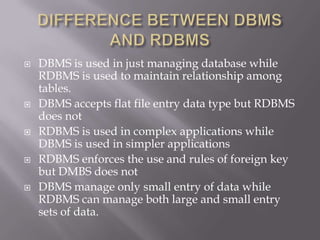
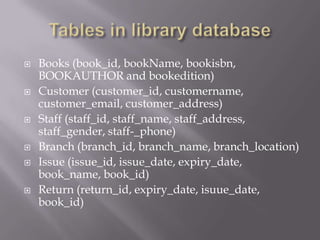
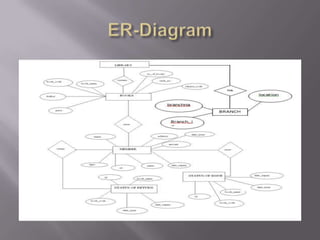
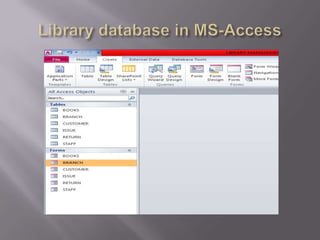
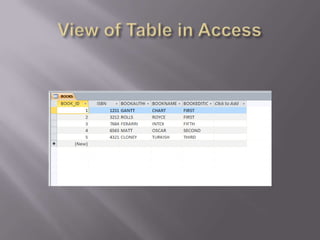
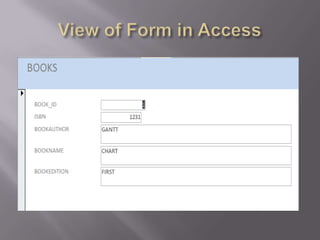
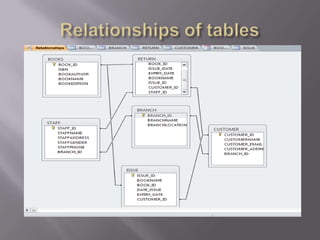
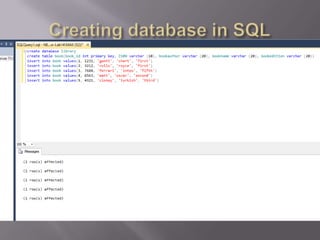
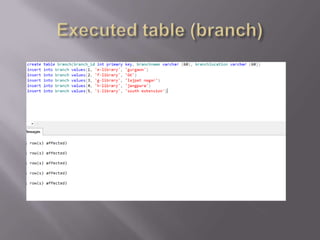
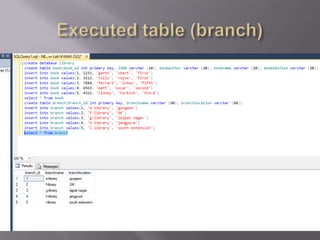
This document discusses SQL and relational database management systems. It provides definitions of SQL, DML, DDL, and DCL. SQL is used to manipulate data stored in relational databases. Relational database management systems (RDBMS) use relational models to store information and maintain relationships between tables. Examples of RDBMS software include Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, and Oracle. The document also discusses using SQL and RDBMS for a library management system, with examples of database tables to store book, customer, staff, branch, issue, and return information. It recommends using a computerized customer service system, digital IDs, RFID chips in books, and restricting database access for security.