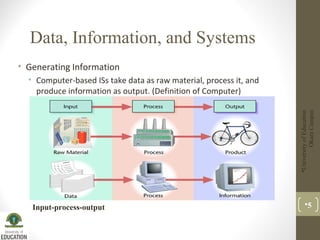
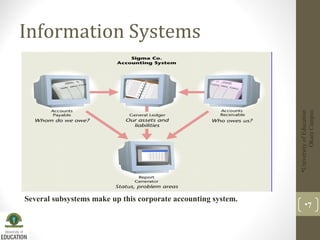
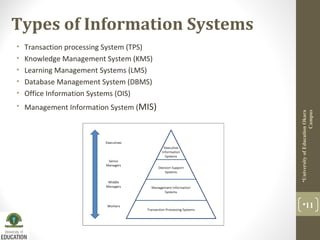
This document discusses information systems and their components. It defines an information system as a study of complementary networks of hardware and software that people and organizations use to collect, process, filter, create, and distribute data. An information system takes data as raw material, processes it, and produces useful information as output. The basic components of an information system include hardware, software, databases, networks, and procedures.