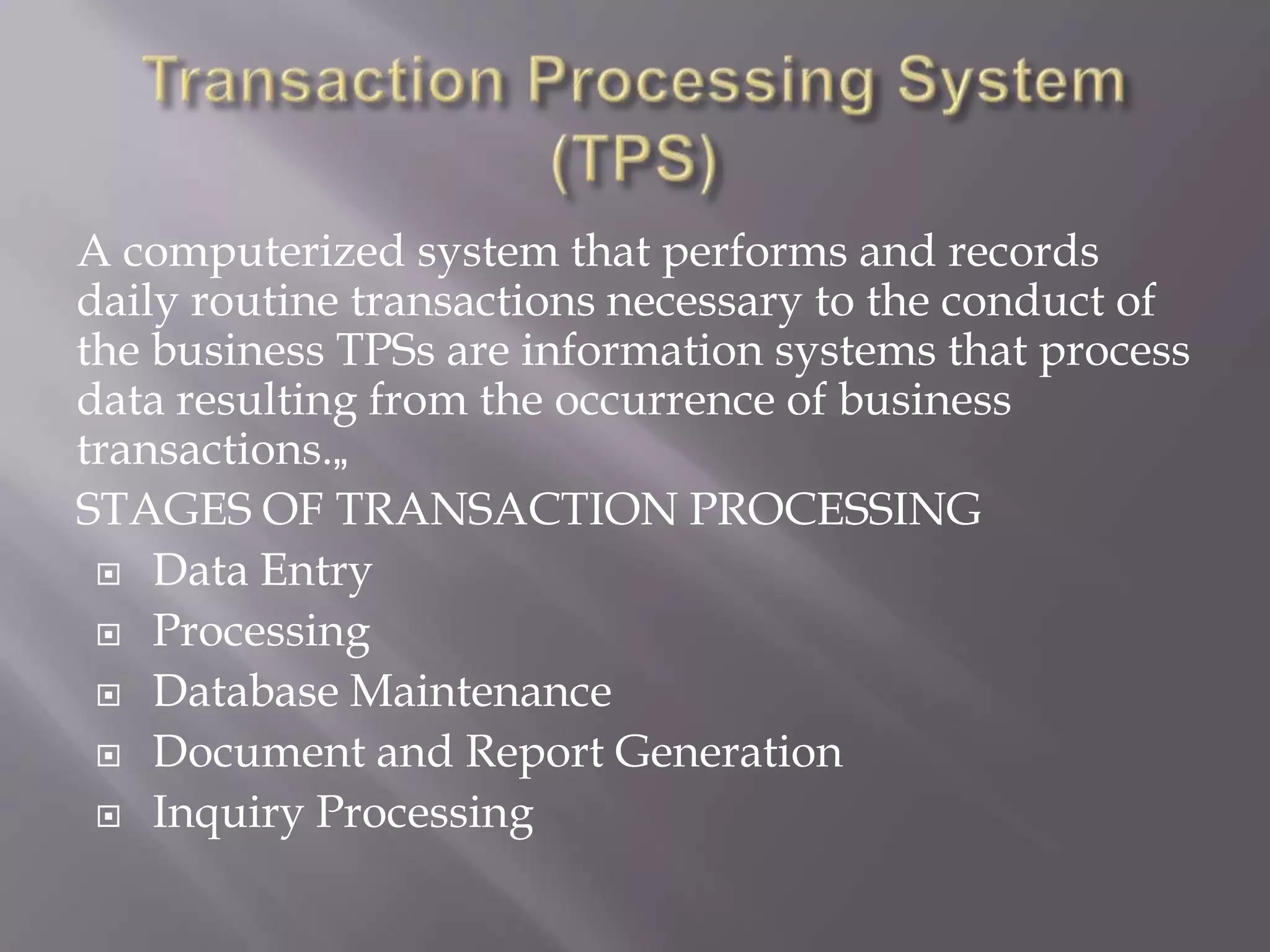
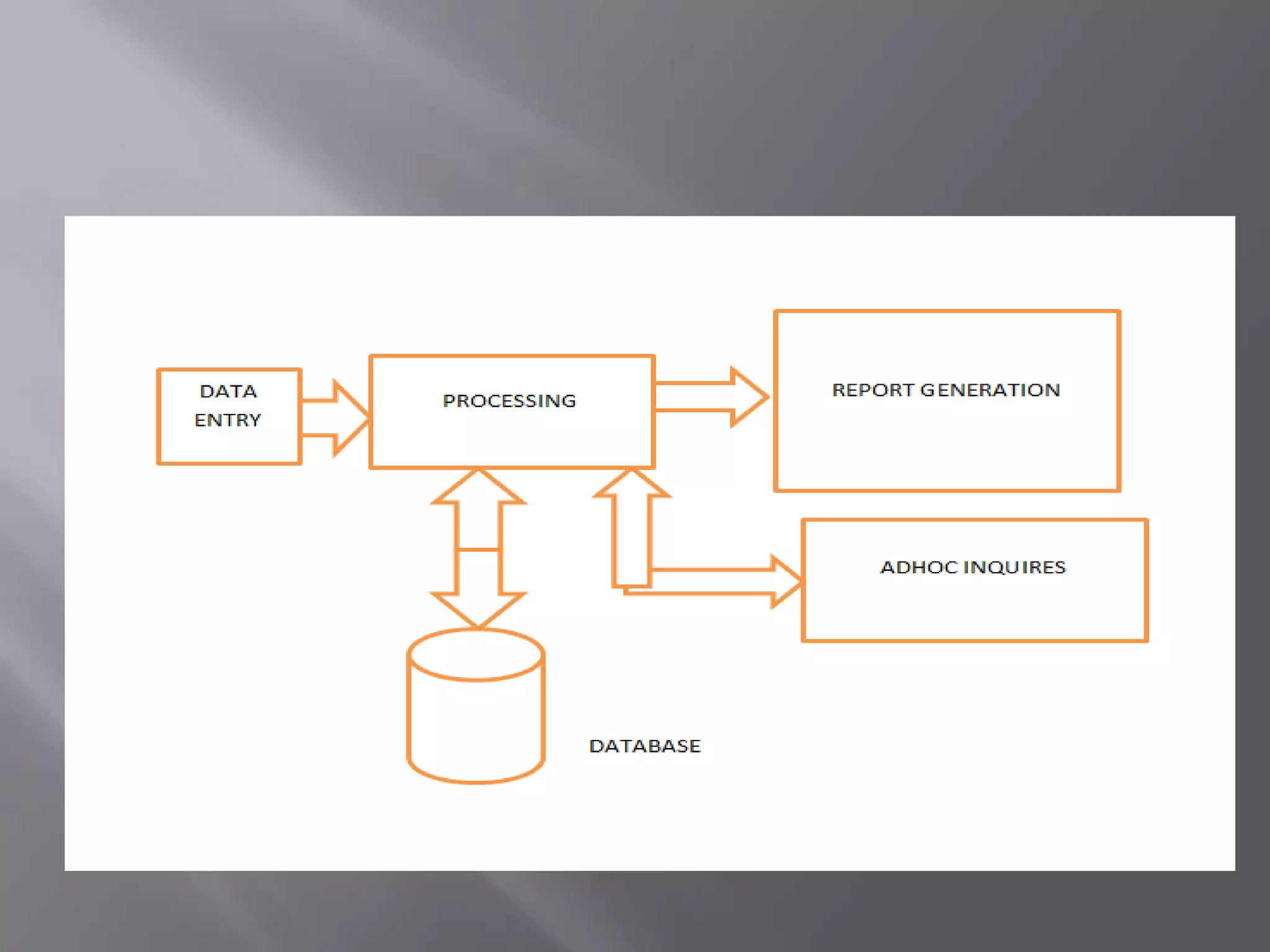
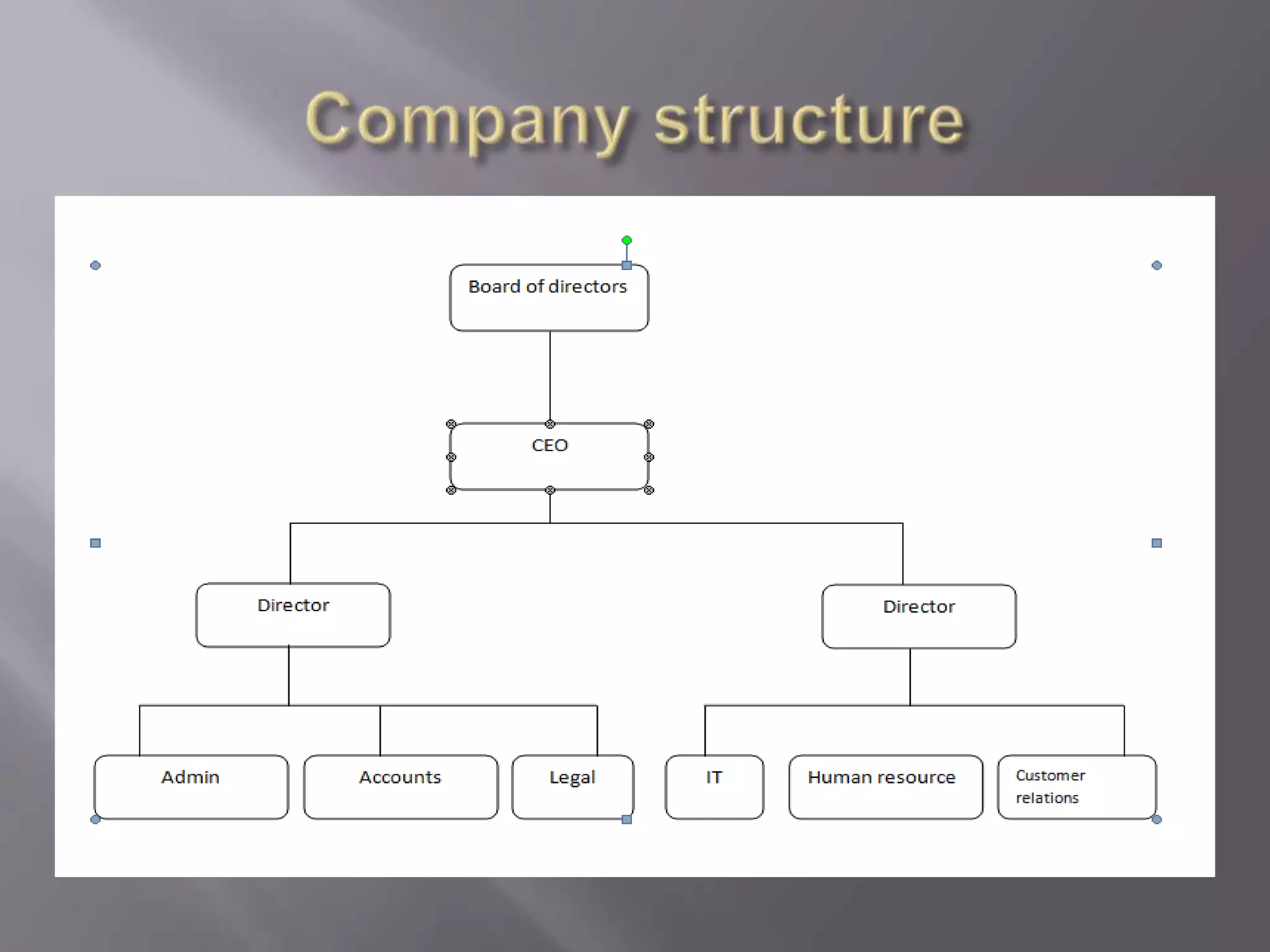
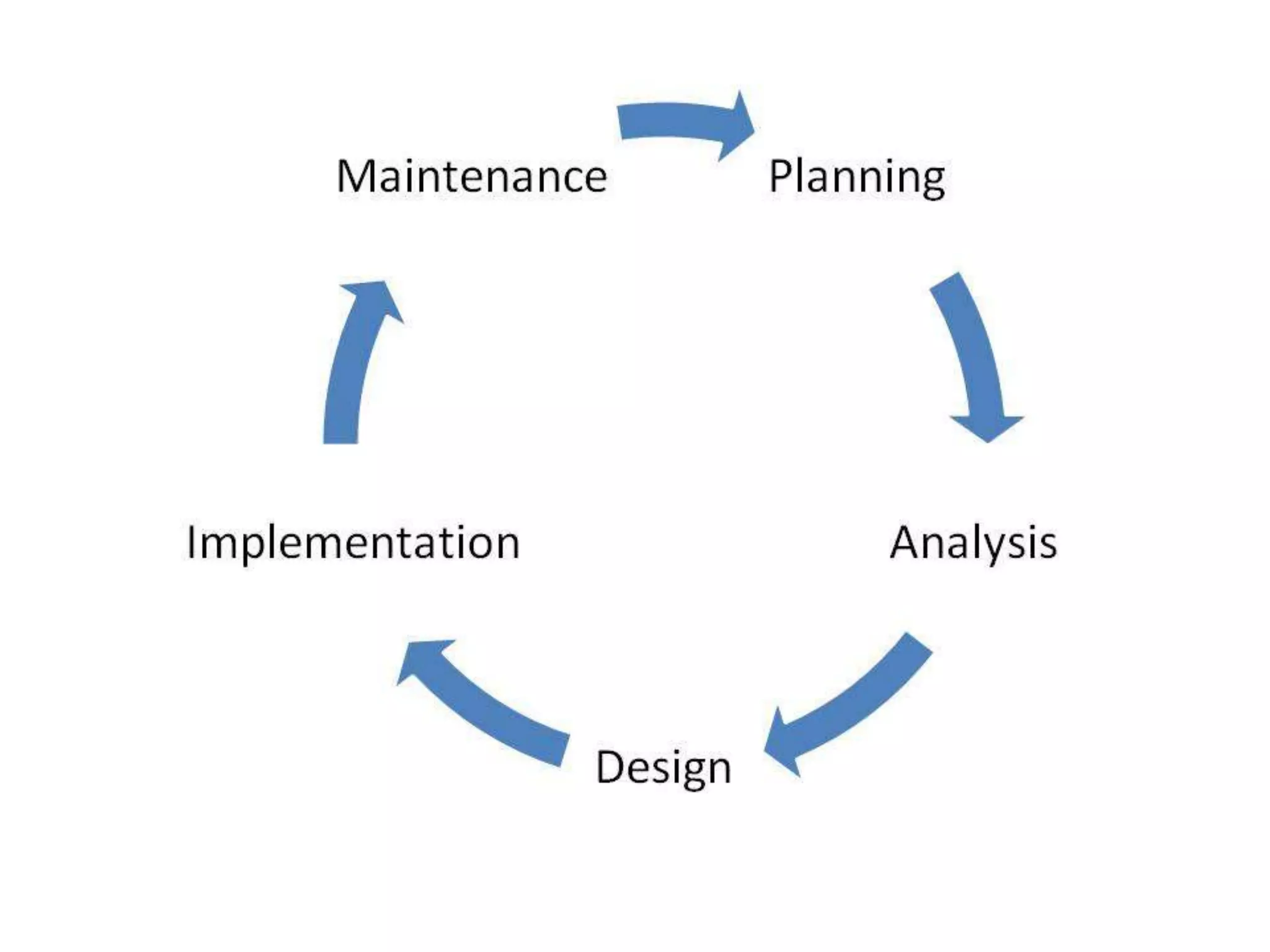
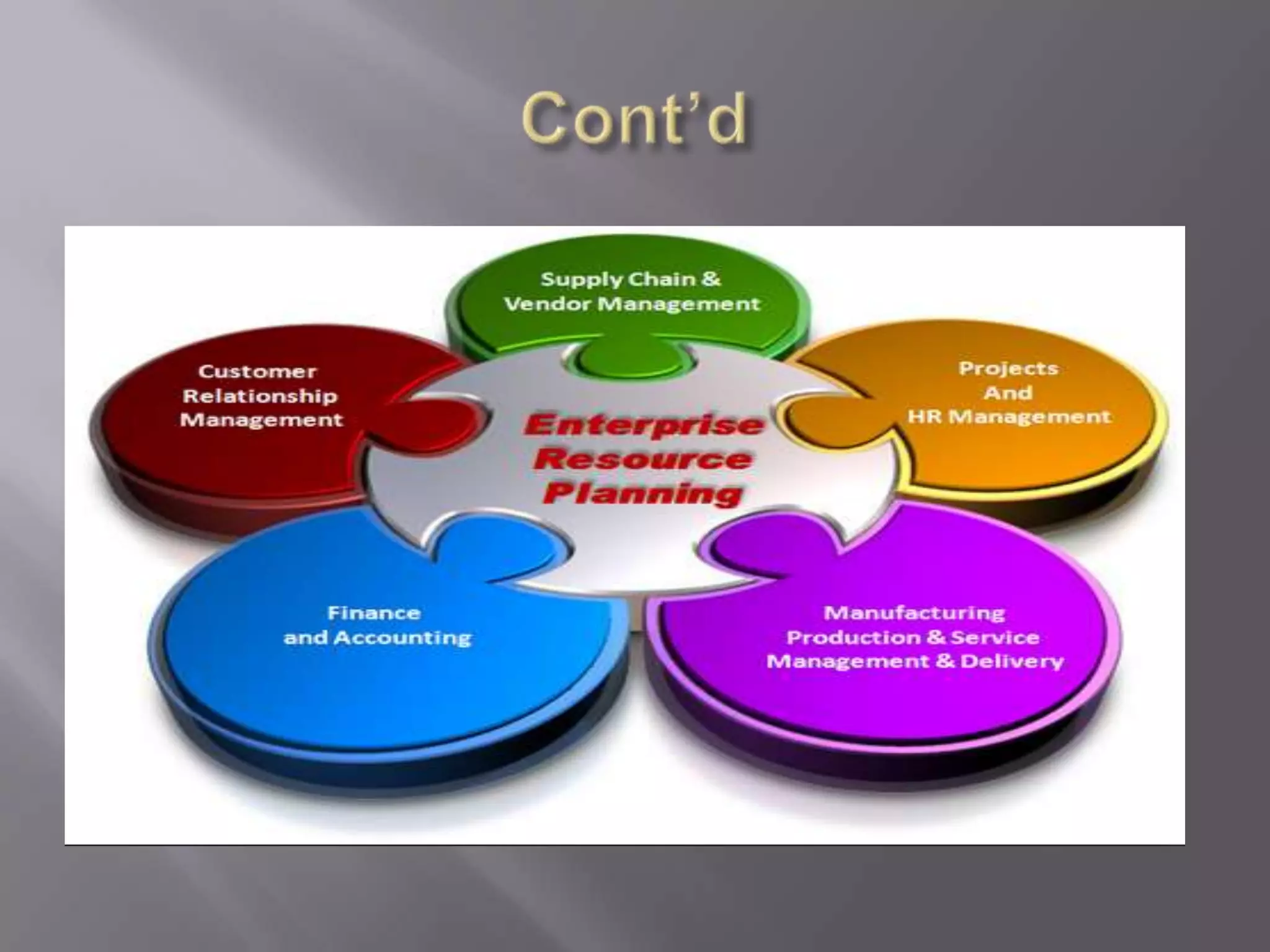
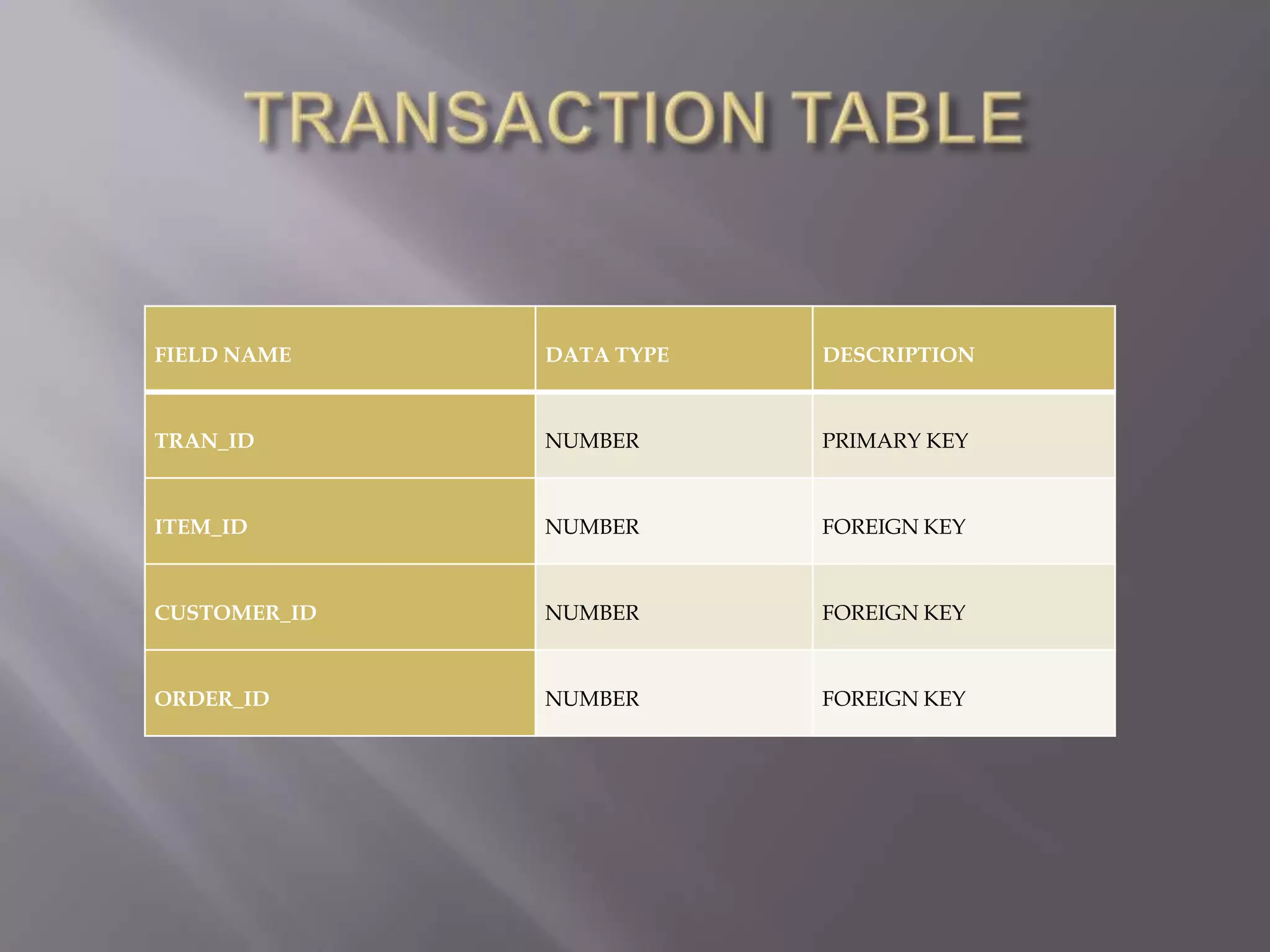
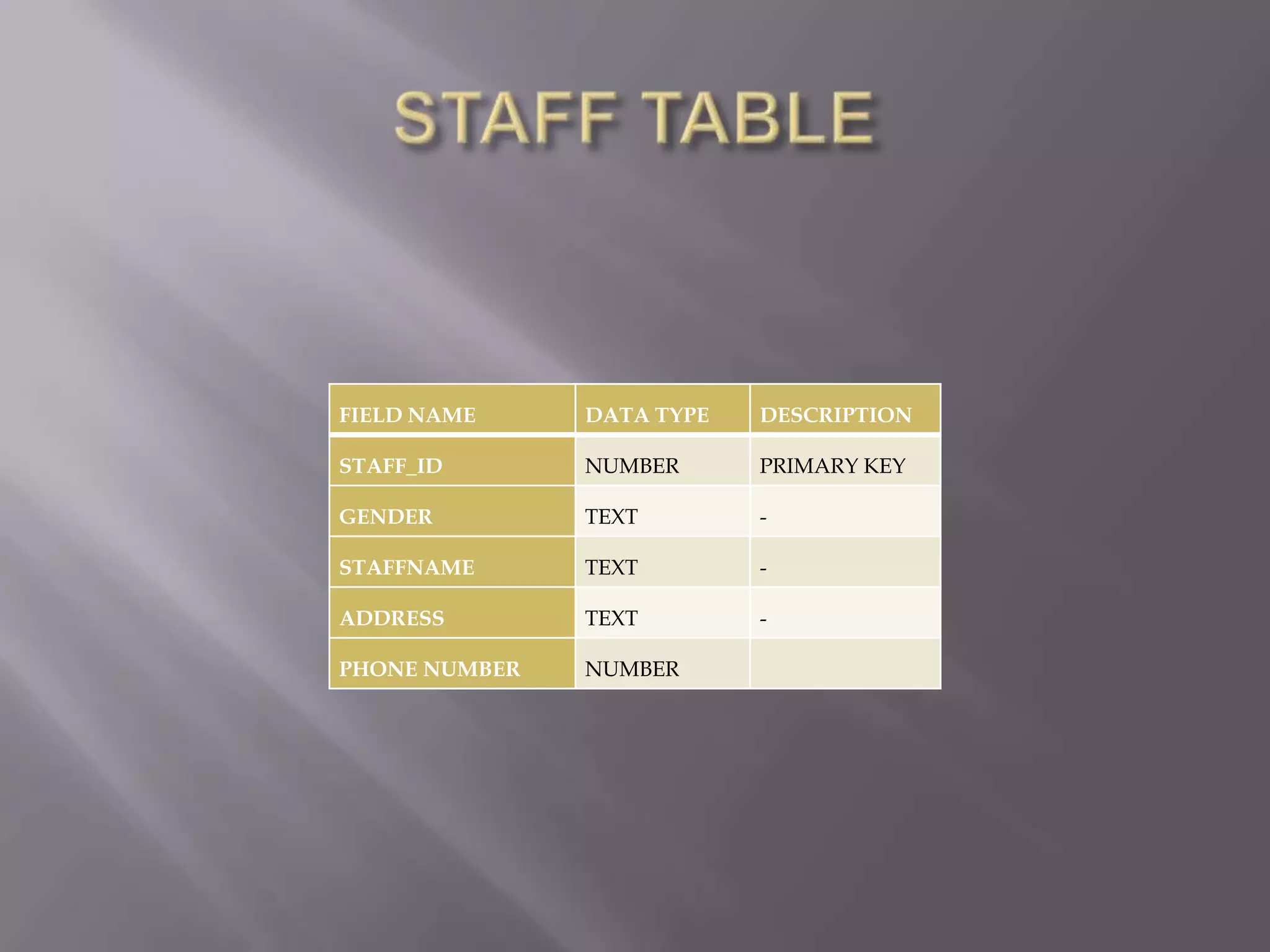
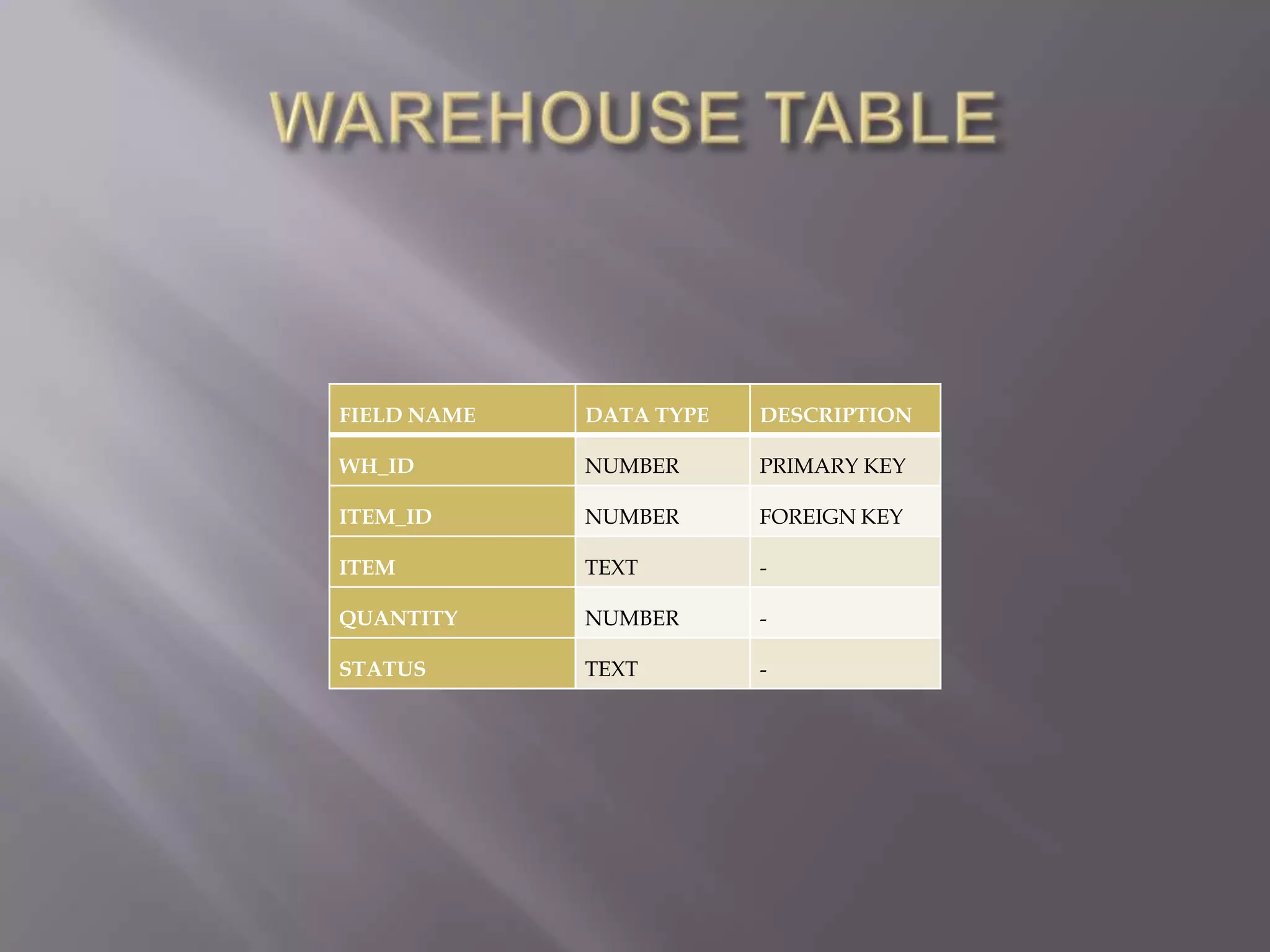
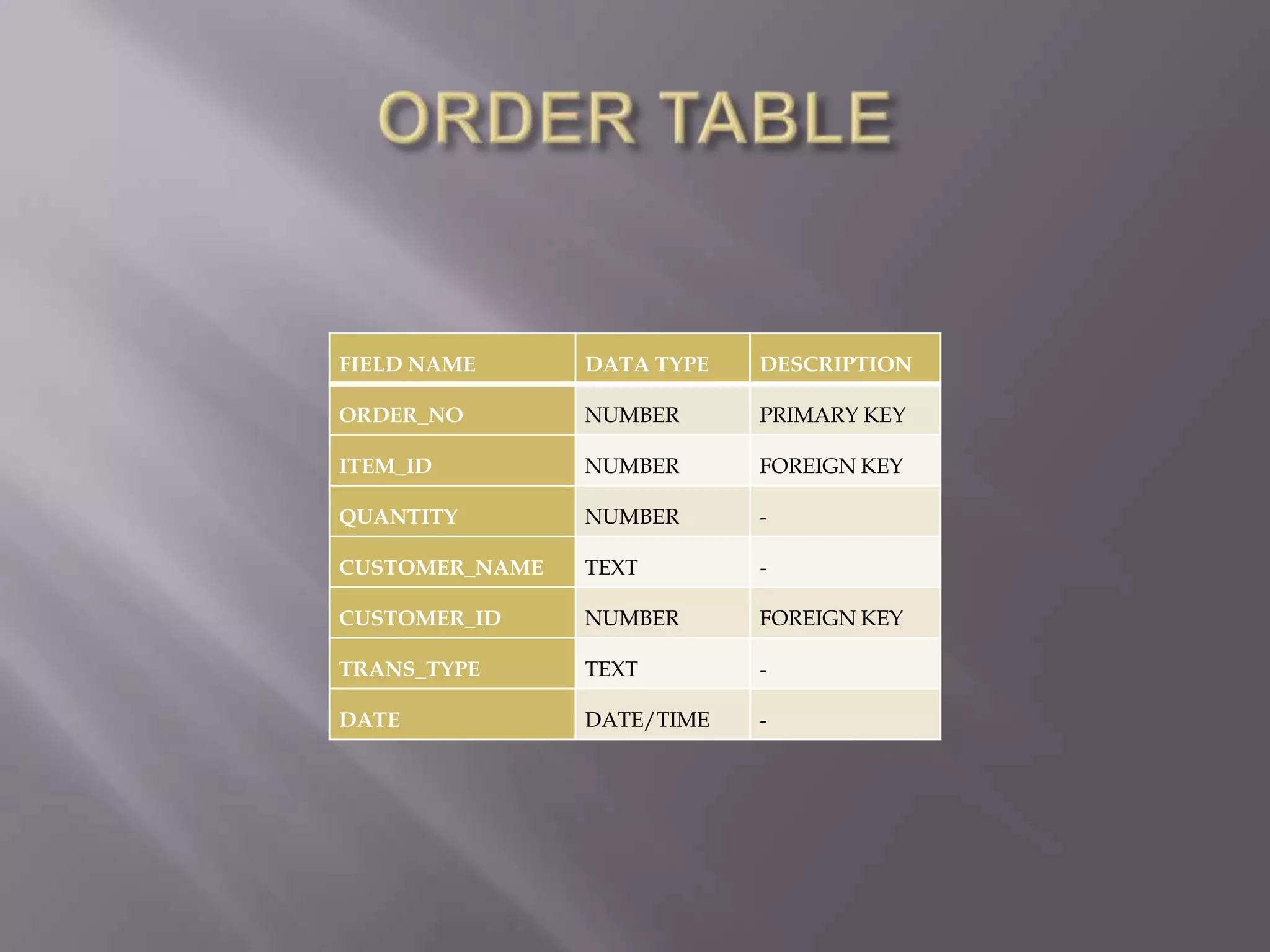
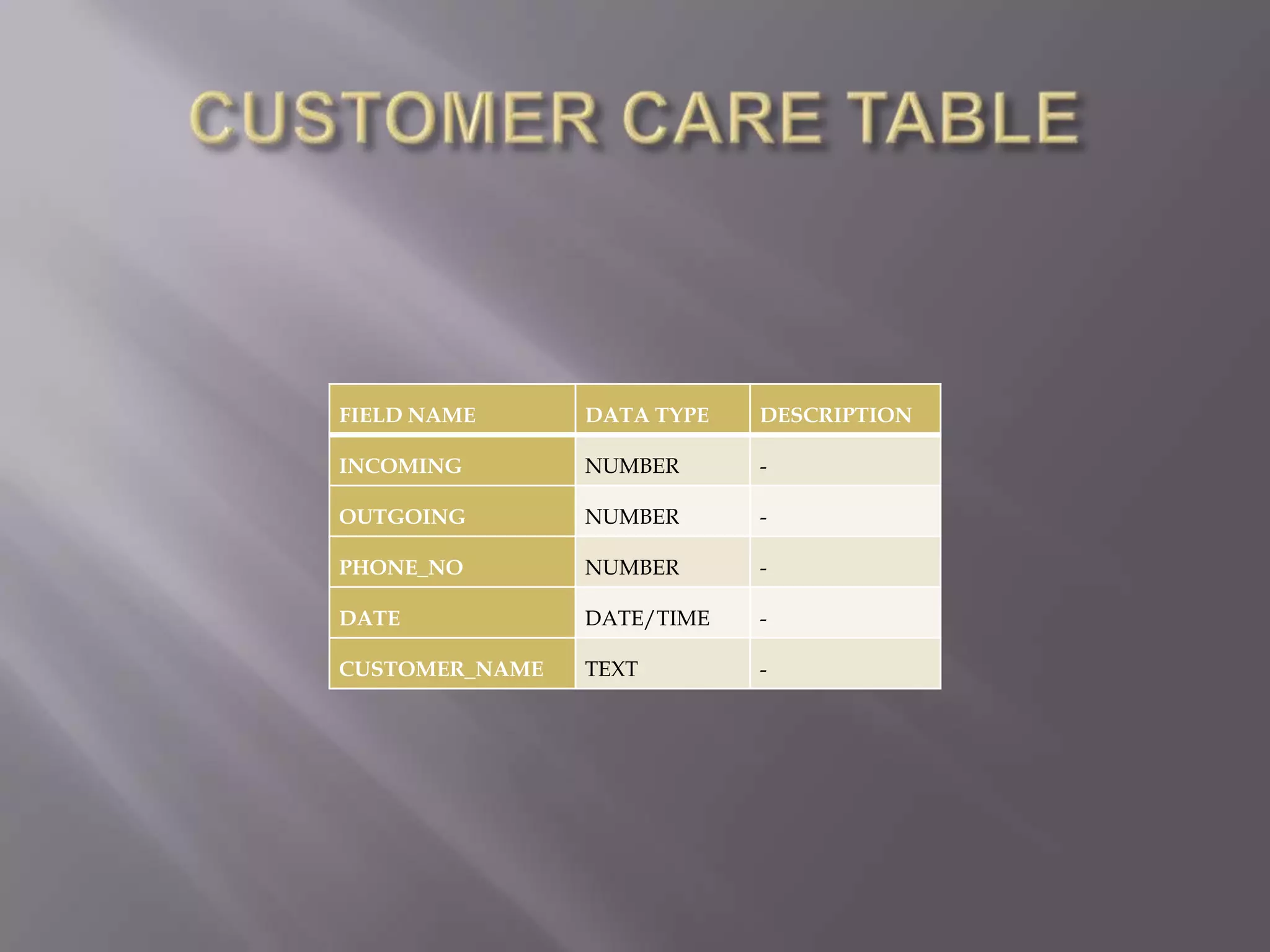
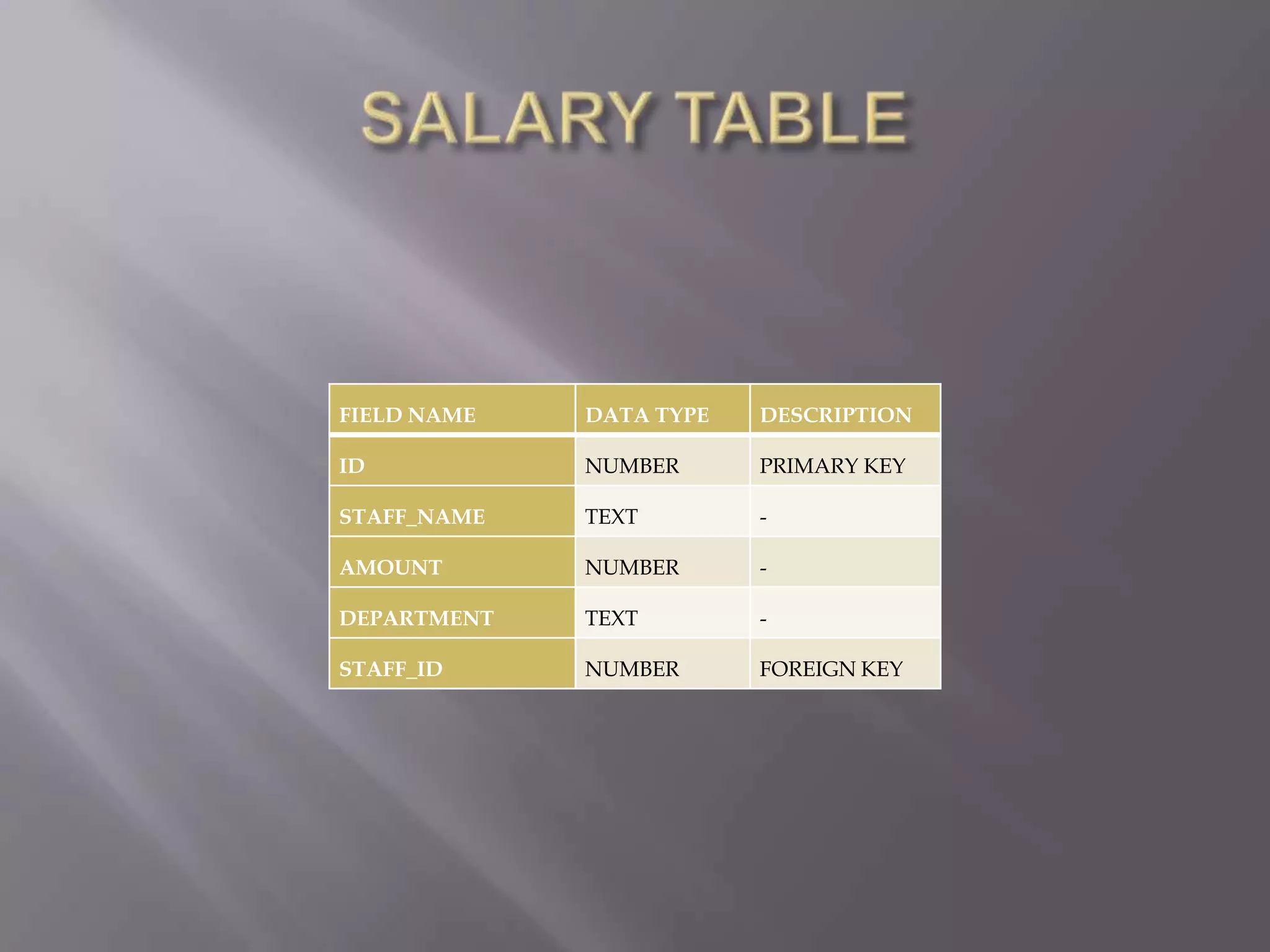
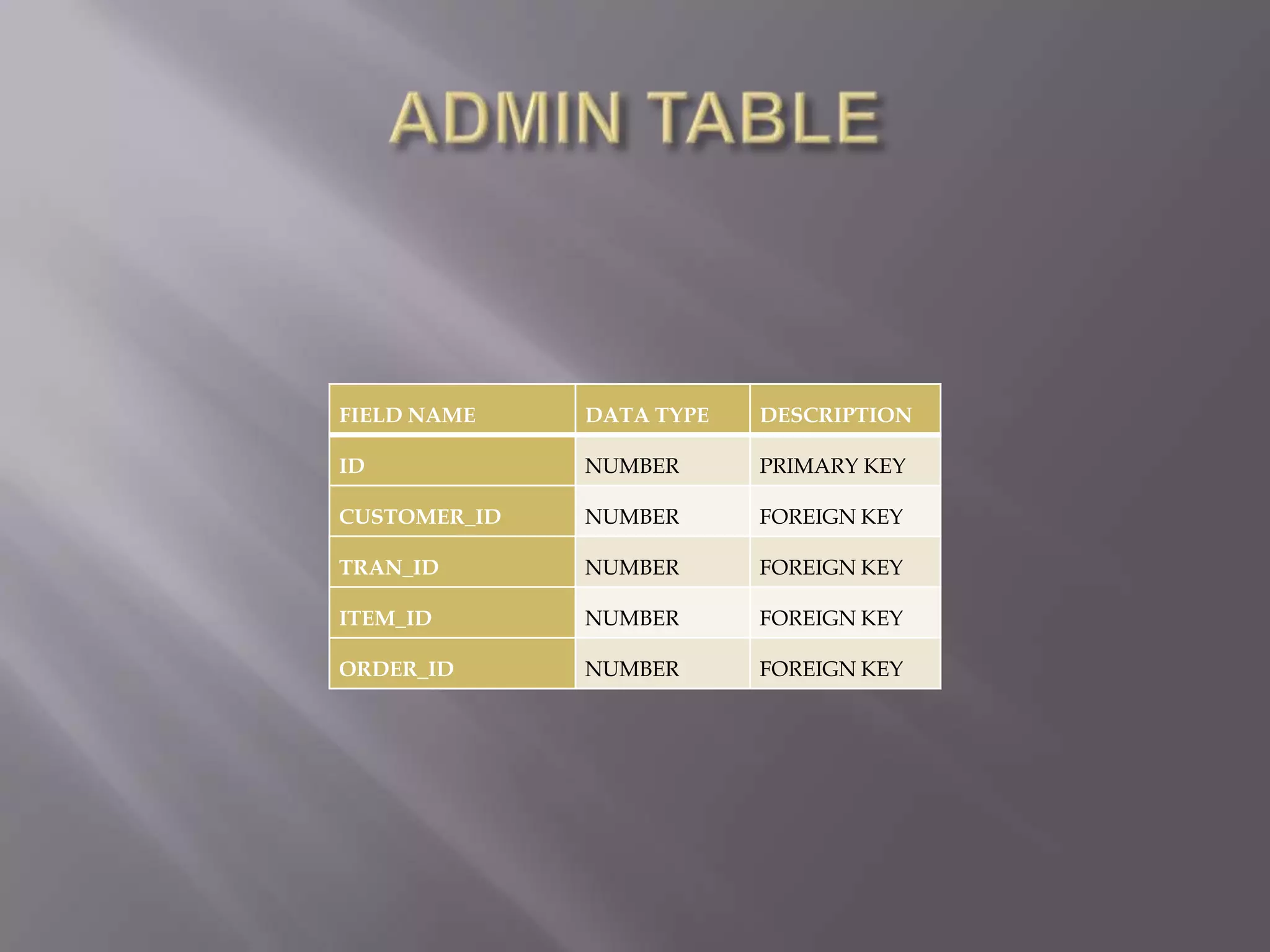
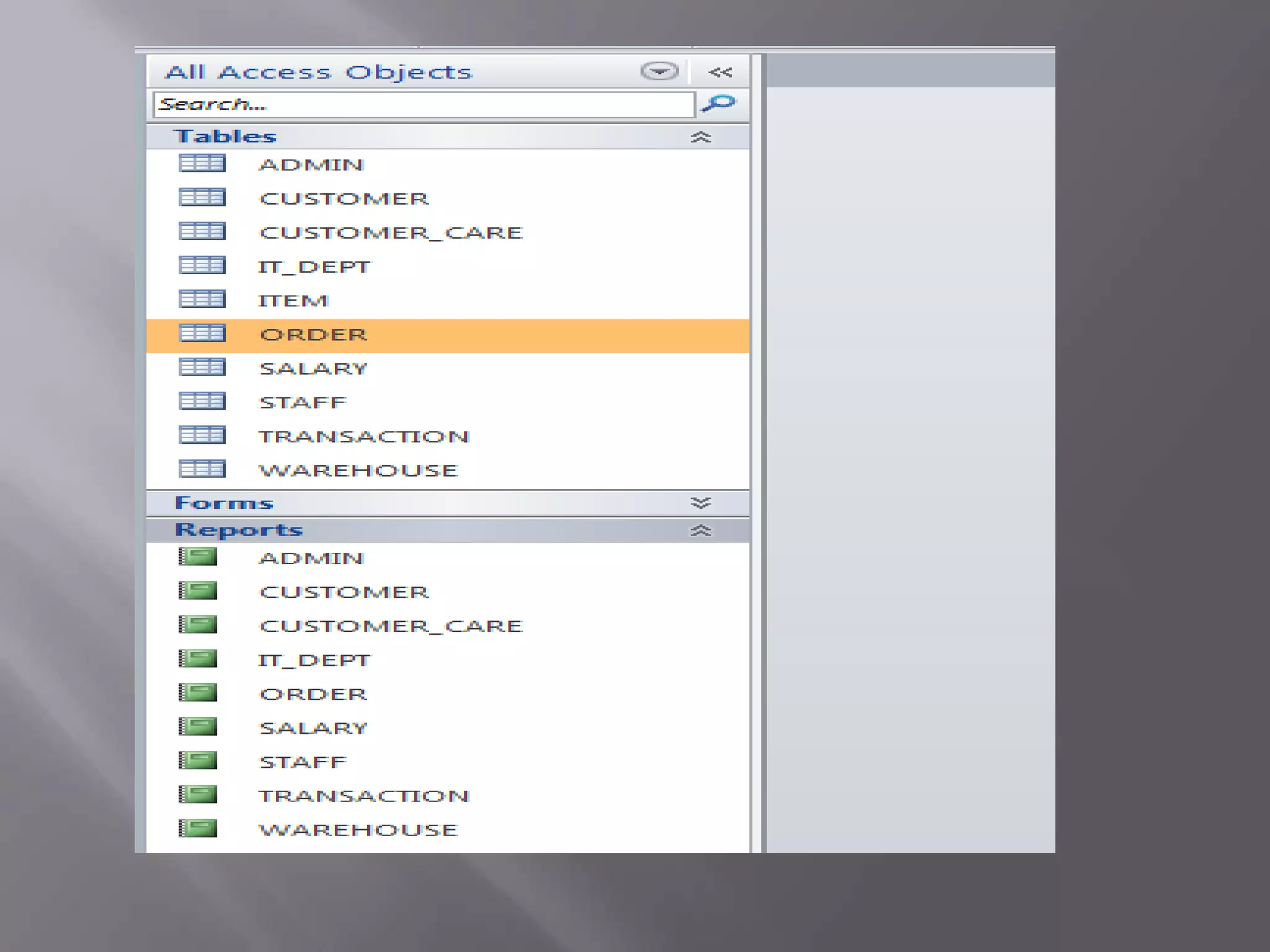
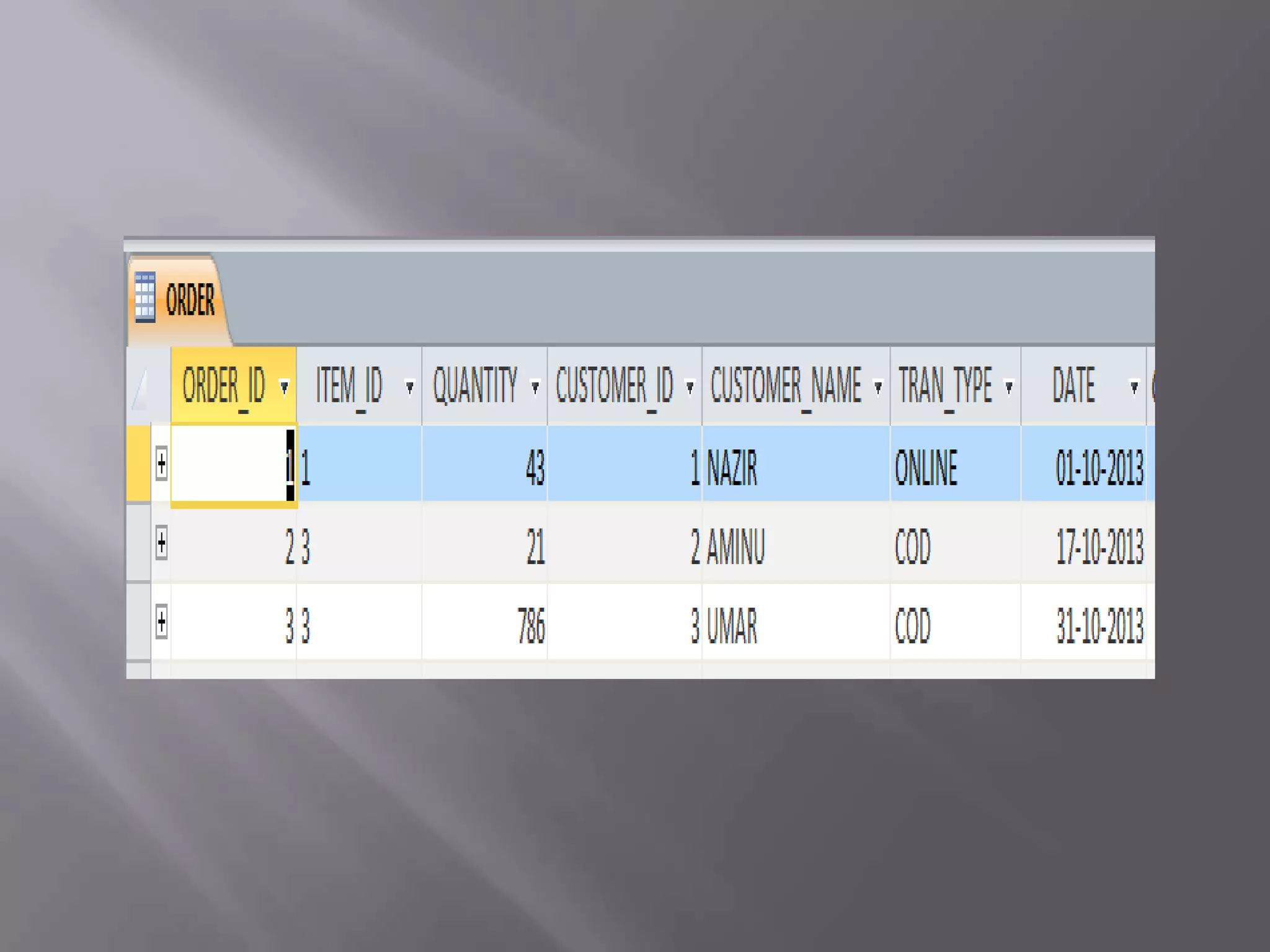
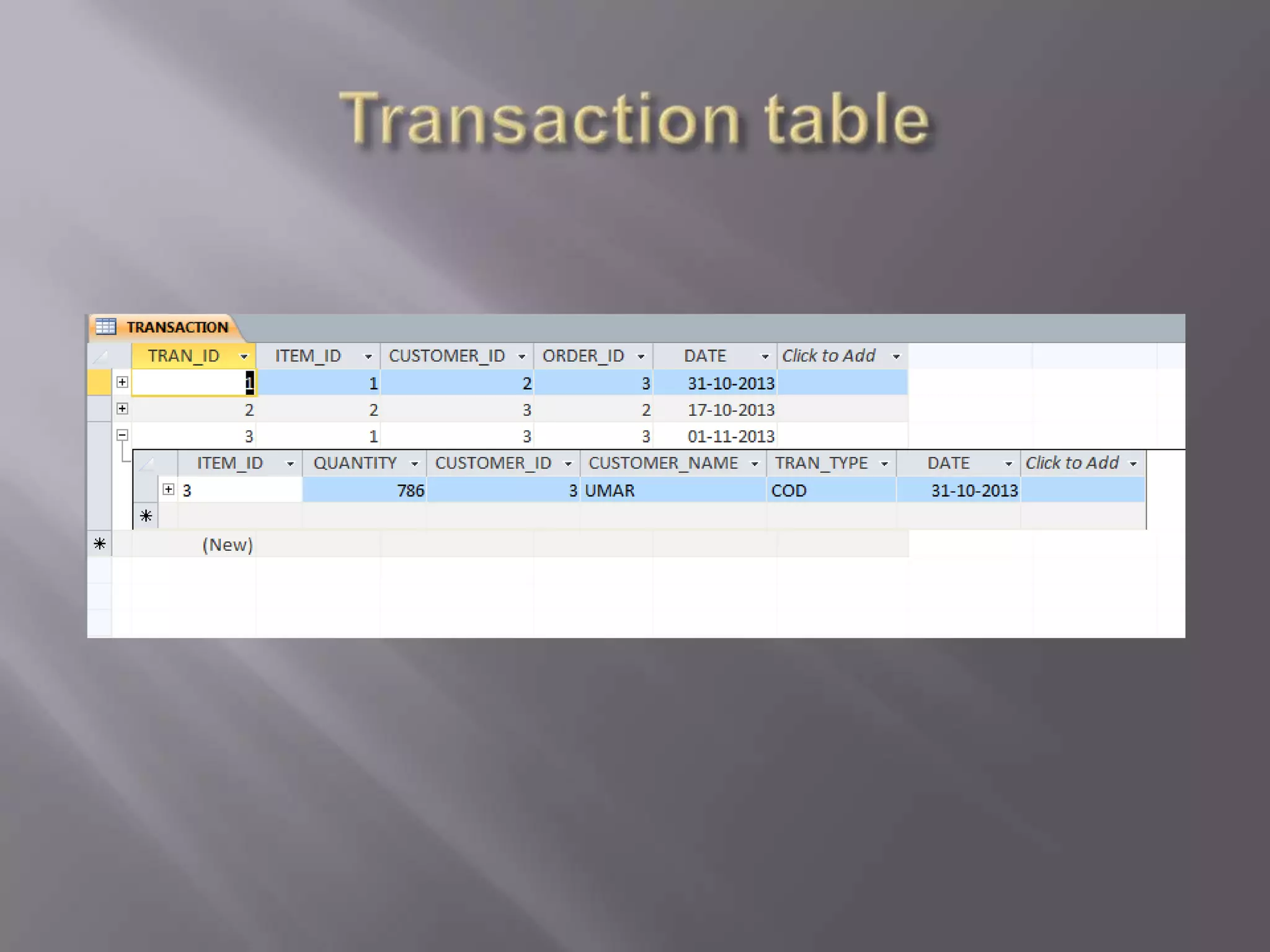
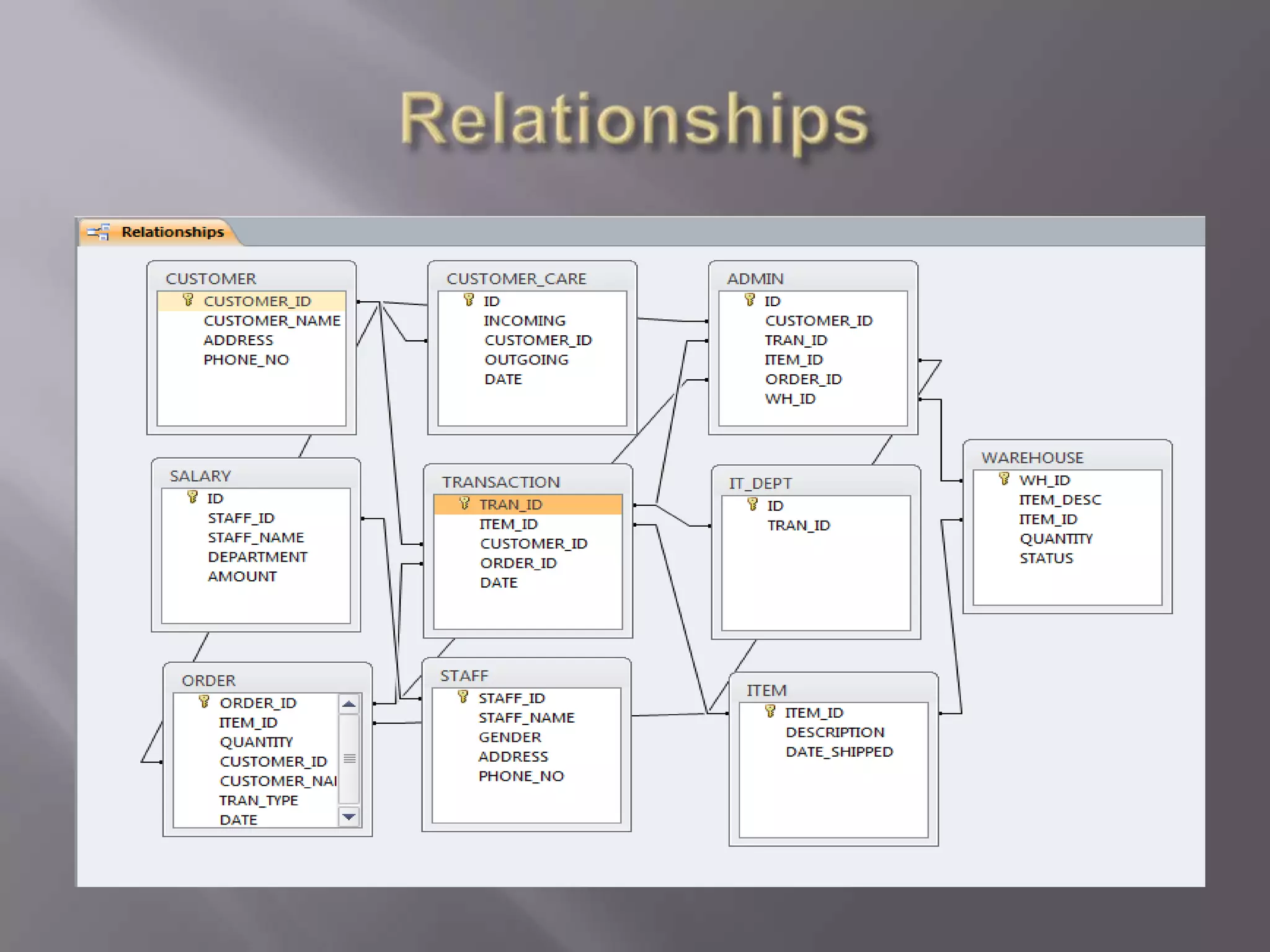
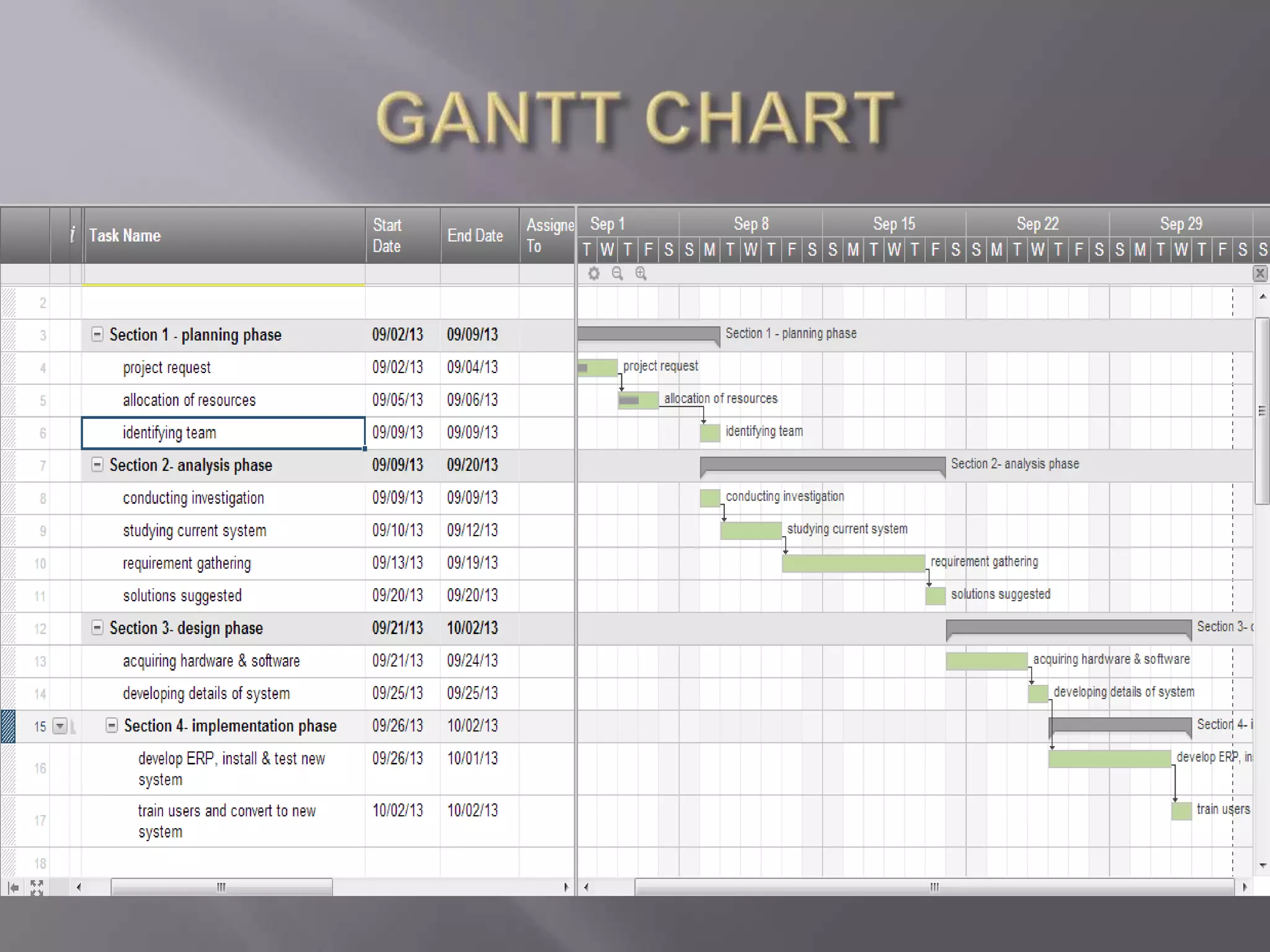
This document discusses the key aspects of developing a management information system (MIS) for a company. It defines what an MIS is and its purposes. It then outlines the stages of transaction processing, types of management decisions supported, and types of decision support systems. The document proceeds to discuss the systems development life cycle (SDLC) process and specific issues identified in the company's current systems. Potential solutions are proposed, such as implementing a customer ID database, RFID attendance tracking, and a CRM system. Finally, database tables to support the new system are defined.