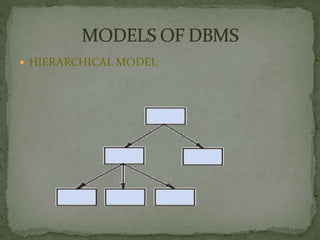
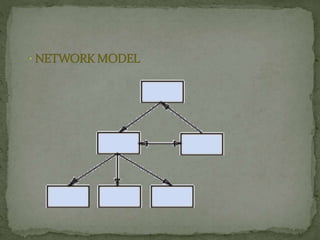
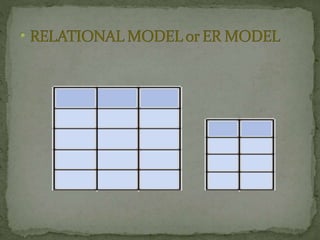
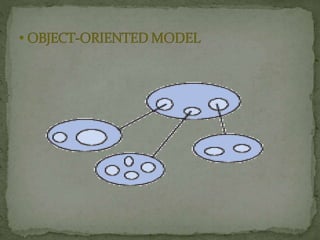
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a set of programs that controls the creation and use of databases for an organization. A DBMS represents complex relationships between data, controls data redundancy, and ensures data sharing and security through user-defined rules. It provides benefits like flexibility, fast response to queries, lower training costs, and reduced storage needs. However, implementing a DBMS also involves costs like hardware, software, training, and potential database damage. Common DBMS models include hierarchical and relational models.