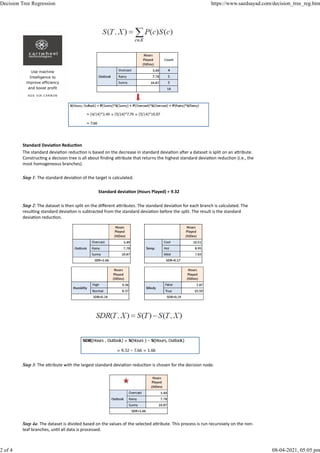
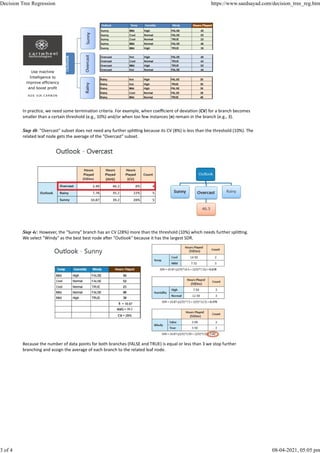
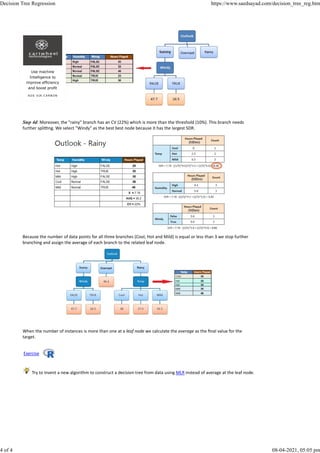
Decision trees are a type of predictive model that breaks down a dataset into smaller subsets based on the values of predictor variables. They can be used for regression by measuring the reduction in standard deviation when splitting on variables. The algorithm works top-down, recursively splitting the data on the variable that produces the greatest standard deviation reduction until reaching a minimum number of observations or coefficient of variation. Leaf nodes then contain the average target value for that subset of the data.