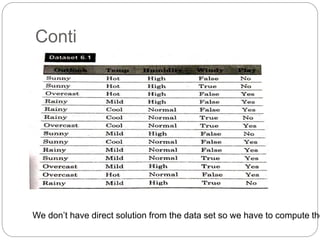
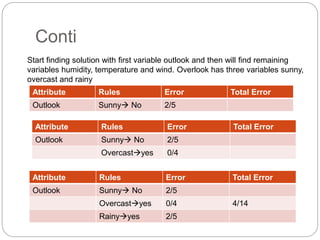
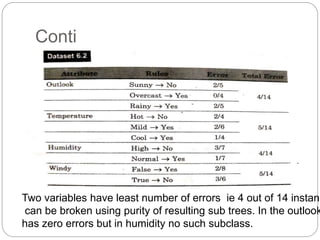
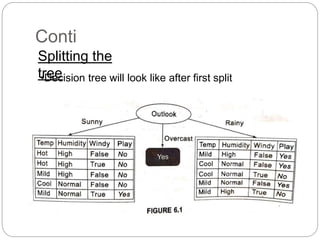
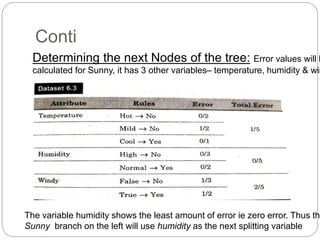
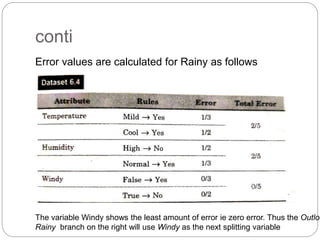
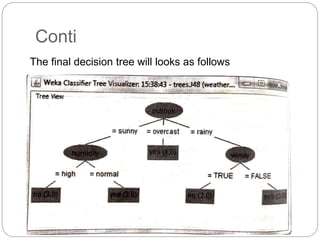
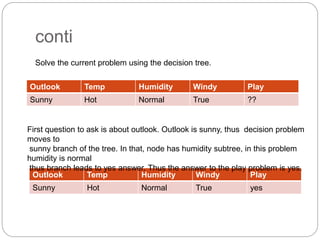
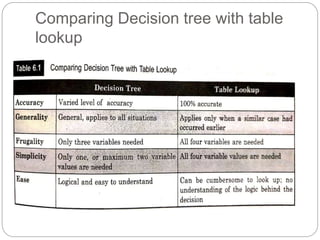
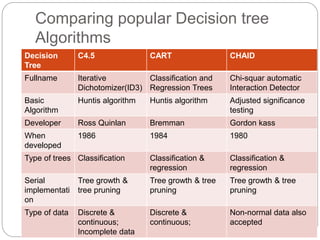
The document focuses on decision trees, emphasizing their structure, efficiency, and application in decision-making processes using past data points. It details steps for constructing a decision tree, including selecting variables, splitting criteria, and pruning methods to enhance predictive accuracy. The document also compares popular decision tree algorithms such as C4.5, CART, and CHAID, highlighting their characteristics and use cases.