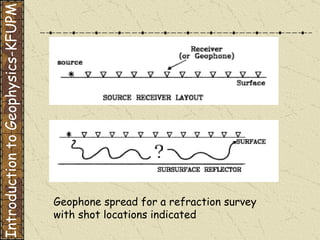
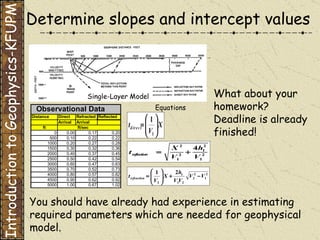
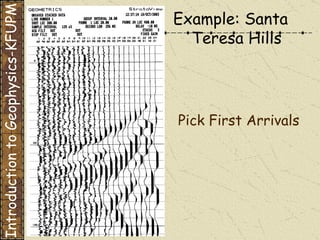
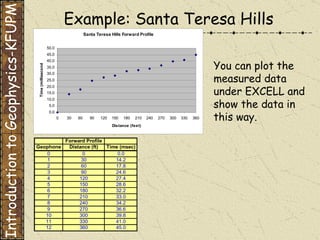
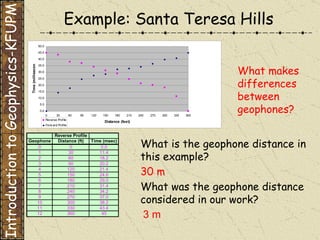
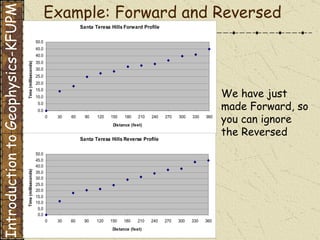
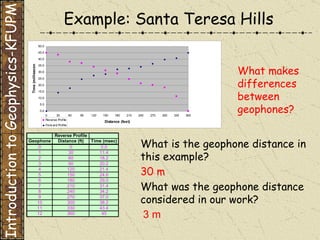
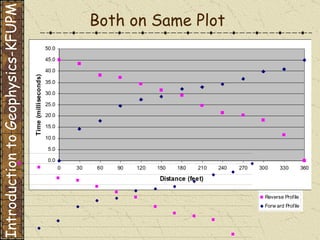
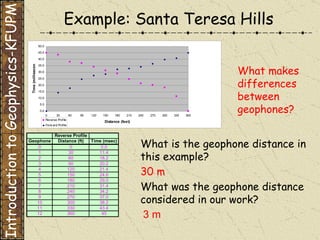
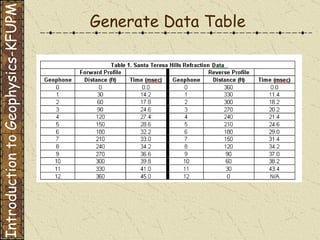
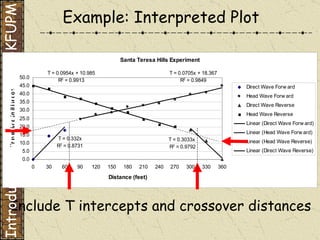
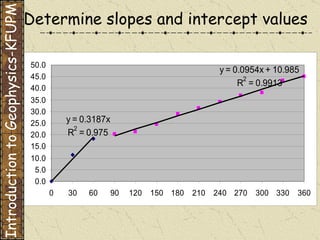
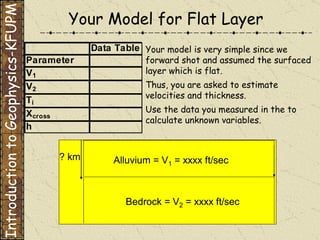
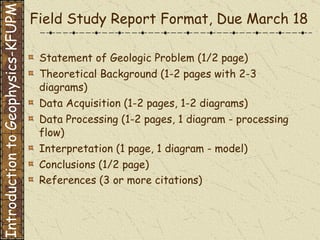
The document discusses refraction seismology field work. It covers types of seismometers used, how a refraction survey is set up with geophone spreads and shot locations, and controlled seismic sources like impact and vibrating sources. An example refraction profile from Santa Teresa Hills is shown and discussed, including determining intercept times and velocities to develop a geophysical model of subsurface layers. Students are assigned a field study report on their refraction data due next month.
![Introduction to Geophysics Ali Oncel [email_address] Department of Earth Sciences KFUPM Refraction Seismology: Field Work Introduction to Geophysics-KFUPM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-1-091220221922-phpapp01/85/ONCEL-AKADEMI-INTRODUCTION-TO-GEOPHYSICS-1-320.jpg)