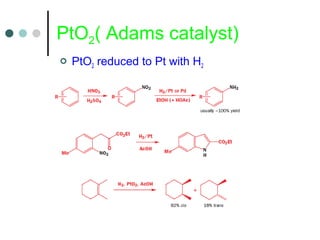
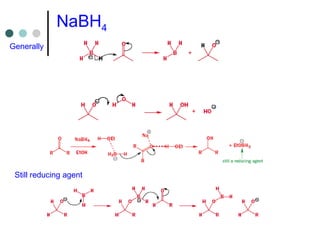
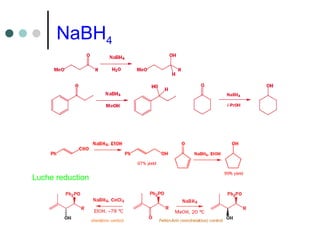
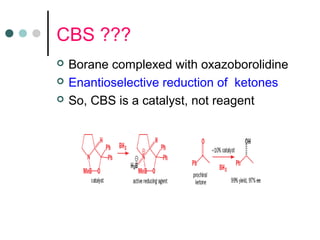
This document discusses various types of reduction reactions including:
1) Catalytic hydrogenation using metals like Pt, Pd, Ni, Ru, Rh to reduce double and triple bonds.
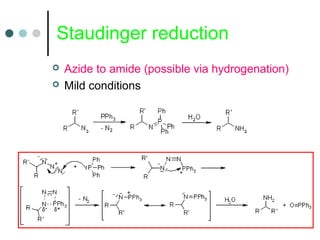
2) Hydride transfer reactions using sources like LiAlH4, NaBH4 to reduce carbonyl groups, nitro groups, and more.
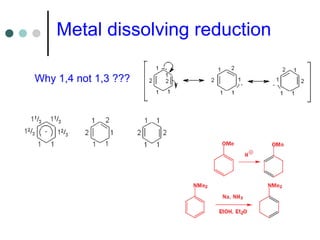
3) Dissolving metal reductions using reactive metals like Li, Na in ammonia solution (Birch reduction) to reduce aromatics.
4) Specific reducing agents and conditions are described for reducing different functional groups selectively like carbonyls, nitriles, alkynes and more.