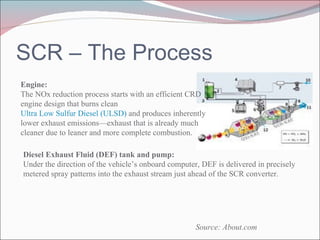
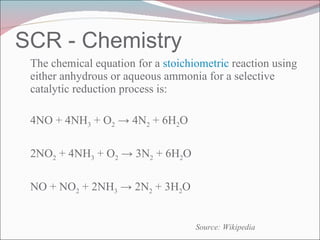
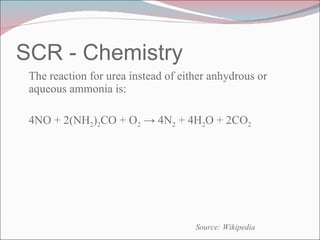
Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are produced during combustion processes and can harm human health and the environment. Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) is a process that uses a catalyst to convert NOx in exhaust gases into less harmful nitrogen and water. SCR systems inject ammonia or urea into exhaust to facilitate the reaction on the catalyst. Proper operation of SCR systems and monitoring of emissions helps control NOx and improve air quality.






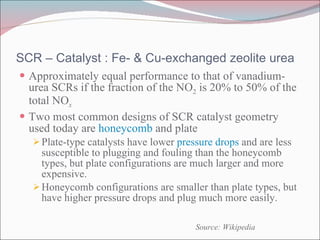
![Selective Catalytic Reduction Means of converting nitrogen oxides , also referred to as NO x with the aid of a catalyst into diatomic nitrogen , N 2 , and water , H2O. known to reduce the NOx emissions by nearly 70-95%. SCR provides emissions after-treatment well into the exhaust stack. Commercial selective catalytic reduction systems are typically found on large utility boilers , industrial boilers , and municipal solid waste boilers and have been shown to reduce NOx by 70-95%. [1] More recent applications include diesel engines , such as those found on large ships, diesel locomotives , gas turbines , and even automobiles . Source: Wikipedia.com About.com & Ezinearticles.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-100318010842-phpapp02/85/Selective-Catalytic-Reduction-of-NOx-9-320.jpg)