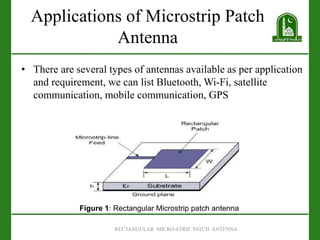
This document discusses the rectangular micro-strip patch antenna. It introduces microstrip patch antennas and their applications. It describes the different shapes of microstrip patch antennas including rectangular, circular, ring, triangular and hexagonal. It also discusses the bandwidth, feeding techniques, S-parameters, VSWR, gain, and calculations for the width and length of rectangular microstrip patch antennas. Finally, it outlines the advantages of low cost and profile and limitations of narrow bandwidth for microstrip patch antennas.