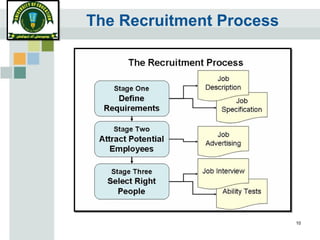
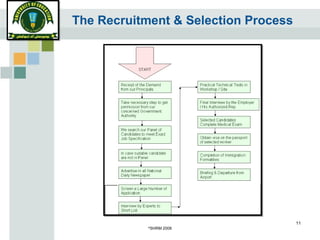
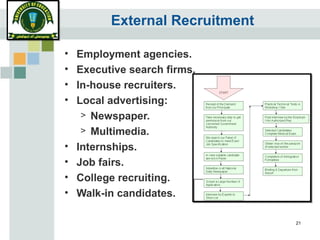
The document discusses the recruitment and selection process. It begins by outlining the stages of recruitment, including job announcements, applicant screening, testing, interviews, and final selection. It then discusses factors that can affect recruitment and selection, such as external authorities, market conditions, and legislation. Finally, it provides guidance on effective recruitment through developing strategy, ensuring equal opportunity, keeping applicants informed, and maintaining confidentiality.