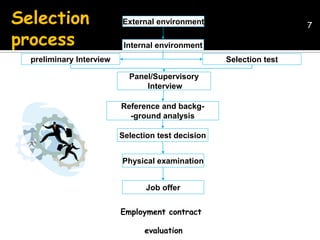
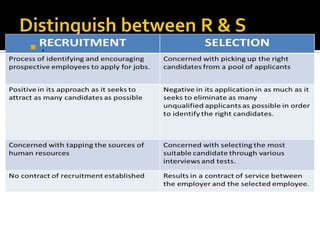
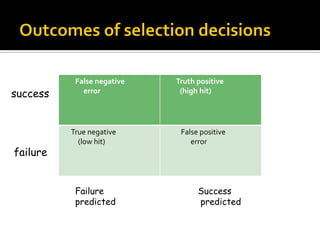
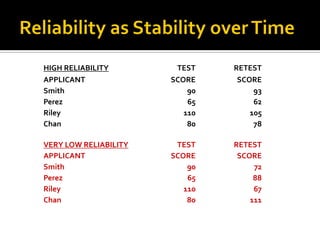
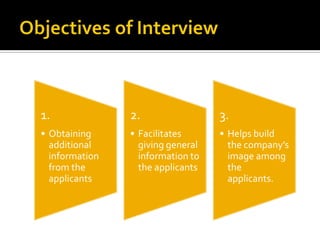
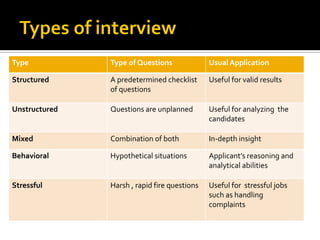
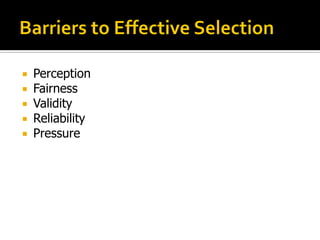
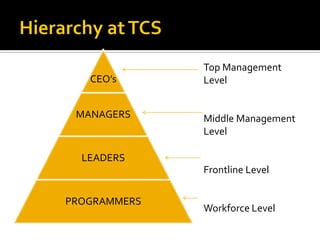
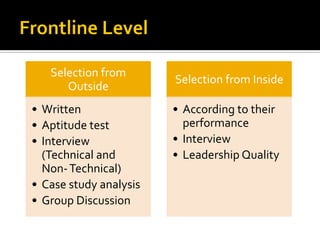
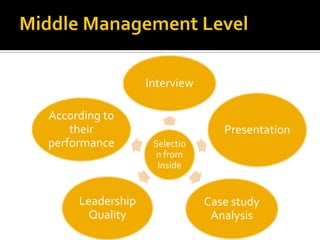
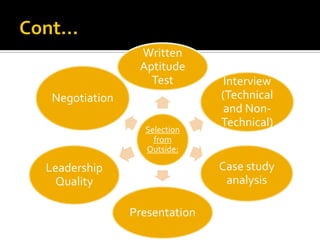
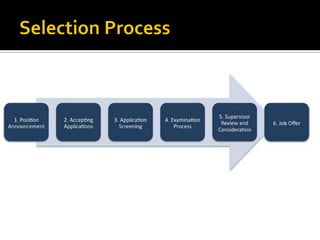
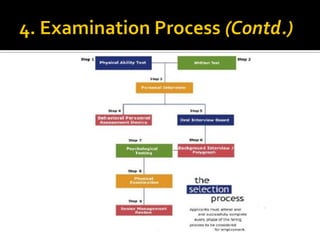
The document discusses the selection process at Google Inc. It begins by outlining the different levels in Google's organizational structure from top management to workforce. For selection from outside, the process involves an application, written and aptitude tests, technical and non-technical interviews, case study analysis, and group discussions. For selection from inside, the process focuses on performance, interviews, leadership quality, presentations, and case study analysis. The process concludes with offers and negotiations.