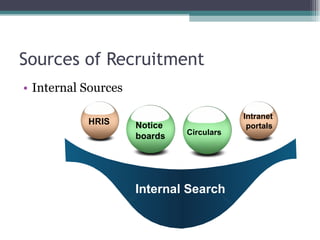
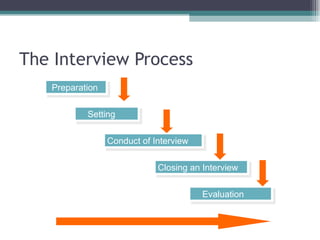
The document discusses recruitment and selection processes. It covers factors affecting recruitment like organizational, environmental, political, economic, social and technological factors. It also discusses different sources of recruitment like internal sources, external sources and their merits and demerits. Different methods of recruitment like internal promotions, campus recruitment, advertisements, employment agencies are explained. Key aspects of a good recruitment policy and evaluating a recruitment program are highlighted. The selection process involves shortlisting applications, conducting tests, interviews, reference checks and making a job offer. Different types of selection tests and interviews are explained.