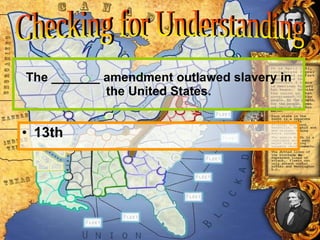
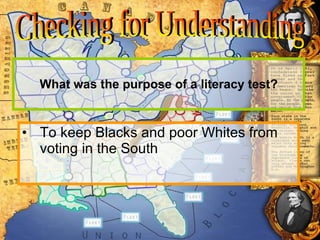
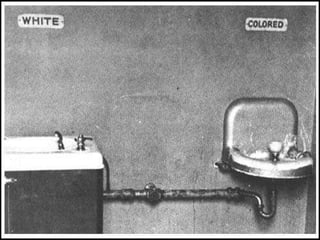
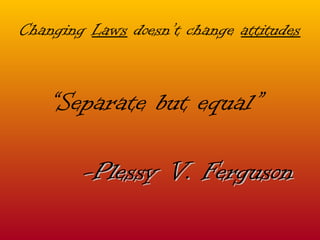The document discusses Abraham Lincoln's views on slavery and saving the Union, the establishment of the Freedmen's Bureau after the Civil War to aid refugees, and the passage of amendments and laws aimed at protecting the rights of former slaves. However, southern states later imposed Jim Crow laws and policies like literacy tests and poll taxes to deny African Americans the right to vote and maintain racial segregation.