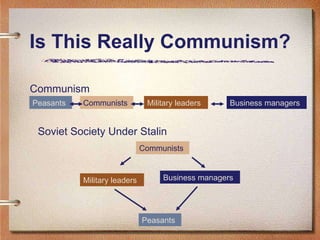
The document discusses life under Stalin's rule in the Soviet Union. It describes how Stalin imposed strict control over all aspects of society, including agriculture, the economy, culture, religion, and thought. Millions of Soviet citizens were arrested, executed, or sent to brutal labor camps for any perceived resistance or disobedience to the Communist regime. Stalin created a climate of fear and oppression through extensive propaganda, censorship, repression of religion, and purges of political opponents.