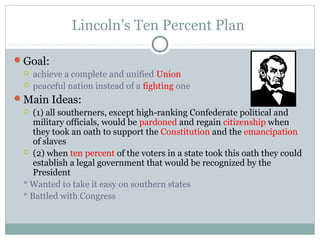
The Reconstruction Era followed the Civil War from 1867 to 1877. There were three main plans for rebuilding the southern states: Lincoln's Ten Percent Plan, Johnson's stricter plan, and the Radical Republican's Congressional Reconstruction Act of 1867, which divided the South into military districts requiring new state constitutions guaranteeing African American suffrage. However, the withdrawal of federal troops led to the imposition of Jim Crow laws segregating blacks and whites.