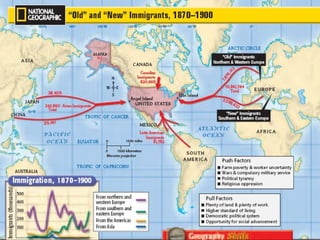
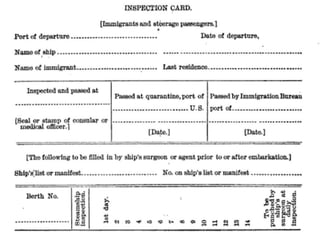
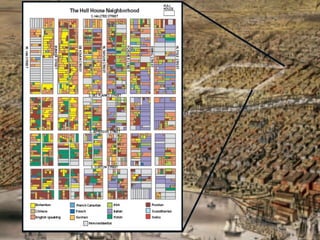
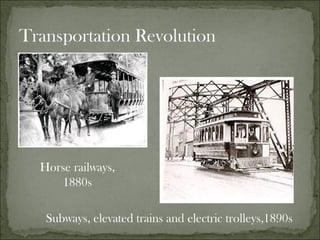
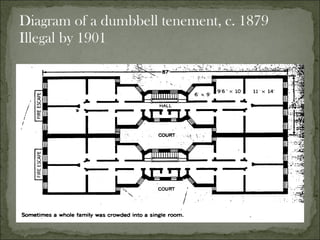
The document discusses the mass immigration to U.S. cities in the late 19th century following the Civil War. Millions of European and Asian immigrants arrived seeking opportunity but faced challenges assimilating. They lived in overcrowded tenement neighborhoods and faced discrimination, while their cheap labor fueled industrialization and urbanization. Political machines exploited new immigrants by providing services in exchange for votes.