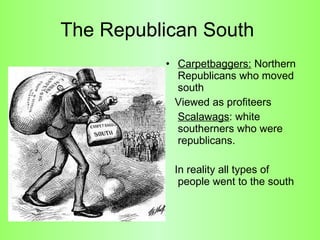
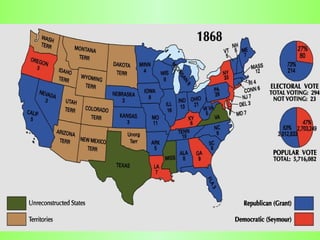
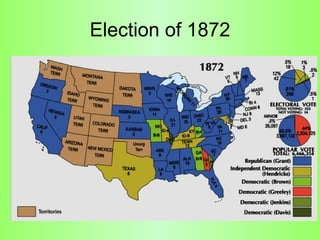
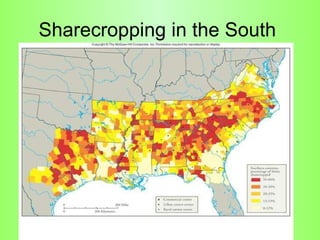
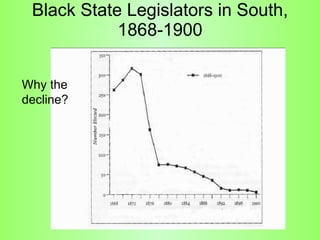
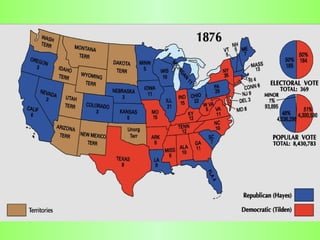
Reconstruction (1865-1877) aimed to rebuild the South after the Civil War and restore Southern states to the Union. It involved several plans and acts by Lincoln, Johnson, and Congress to repair infrastructure, establish the Freedmen's Bureau to aid former slaves, and define citizenship and voting rights through amendments to the Constitution. However, the withdrawal of federal troops from the South in 1877 after the Compromise effectively ended Congressional Reconstruction and left black southerners vulnerable to violence and intimidation through organizations like the Ku Klux Klan and oppressive policies like black codes and sharecropping.