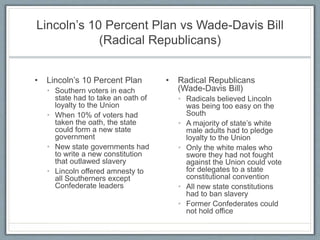
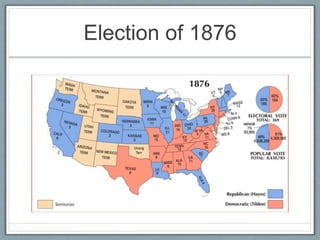
The document provides information about Reconstruction following the U.S. Civil War, including key events and policies. It discusses the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments and their effects. Lincoln's 10% Plan for Reconstruction is compared to the more radical Wade-Davis Bill. Andrew Johnson's more lenient reconstruction plans are outlined and his conflict with Radical Republicans discussed. The rise of groups like the Ku Klux Klan and policies like the Black Codes and Jim Crow laws are summarized.