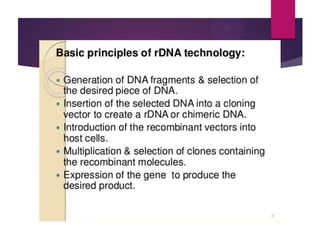
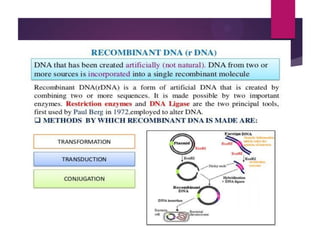
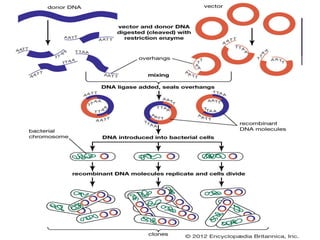
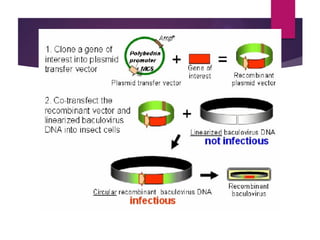
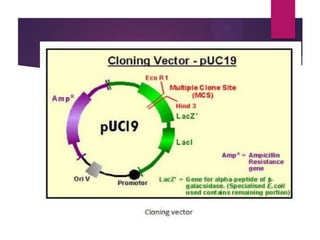
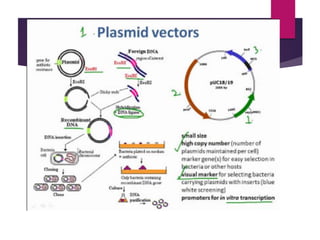
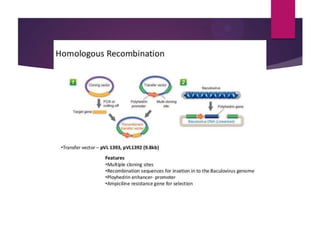
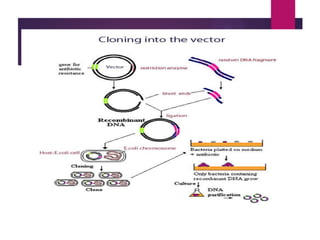
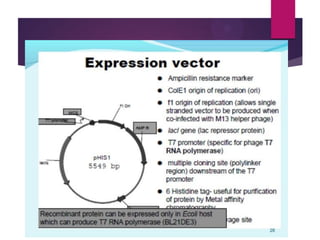
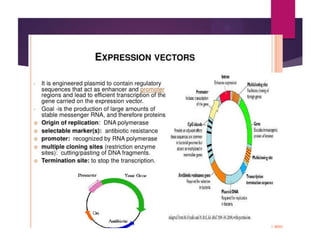
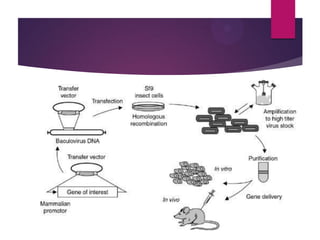
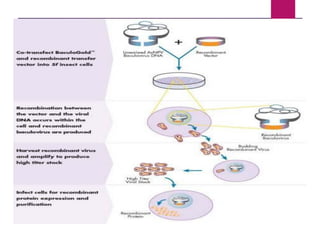
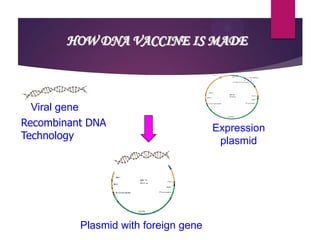
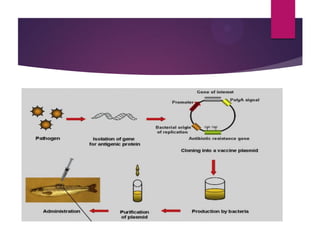
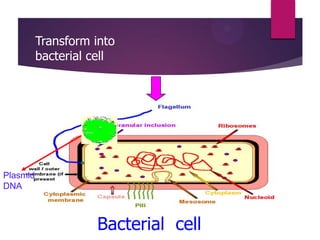
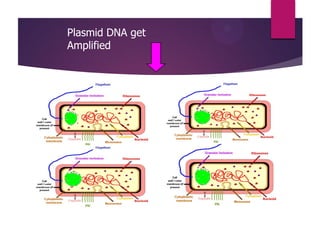
This document discusses the properties and production of recombinant vaccines. It notes that recombinant vaccines are produced using recombinant DNA technology by inserting DNA encoding an antigen into cells to express and purify the antigen. The first approved recombinant vaccine was for hepatitis B. The document outlines the types of recombinant vaccines and the process of recombinant DNA technology, including isolating genetic material, amplifying genes of interest, and inserting recombinant DNA into host cells to produce the foreign gene product. It lists some advantages as being able to more quickly produce recombinant vaccines in larger quantities without infectious particles, making them safer for immunosuppressed individuals.