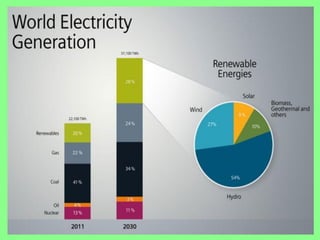
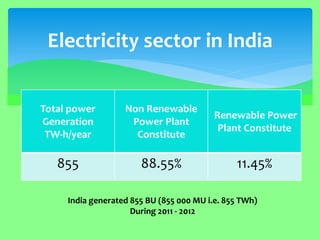
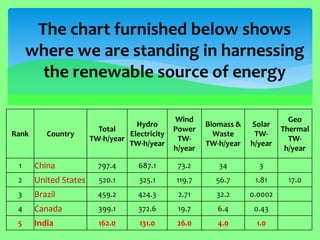
The document discusses the importance of renewable energy as an alternative to conventional energy sources, highlighting the environmental damage caused by exploitation of non-renewable resources. It presents India’s current standing and potential in harnessing renewable sources such as solar, wind, biomass, and geothermal energy, indicating a need for increased utilization. The content emphasizes the collaborative effort of government and public initiatives to boost renewable energy generation for sustainable development.