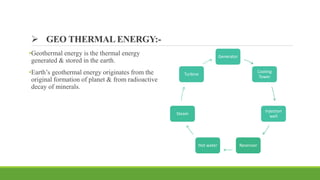
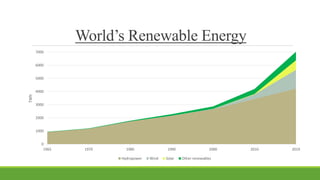
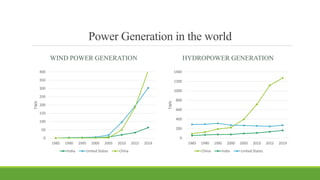
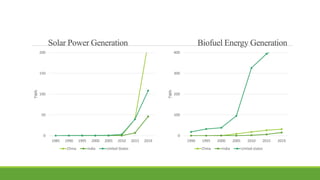
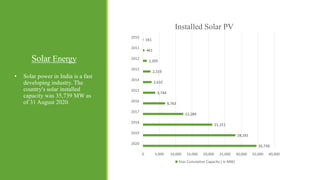
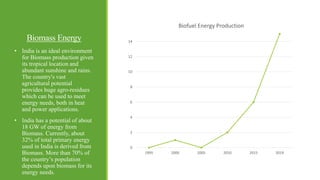
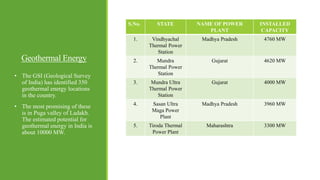
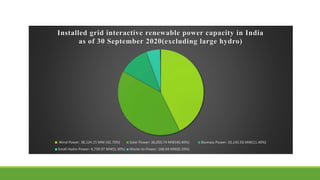
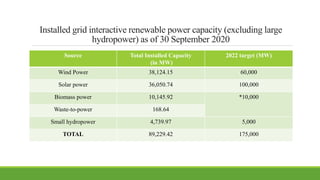
India has significant potential and prospects for renewable energy development. As of September 2020, India's installed renewable energy capacity excluding large hydro was over 89 GW, with wind and solar being the largest sources at over 38 GW and 36 GW respectively. India has set ambitious targets of achieving 450 GW of total installed renewable energy capacity by 2022, including 227 GW from sources like solar, wind, biomass, small hydro and other renewable sources. Key states leading wind and solar installations in India include Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Rajasthan. The government is also promoting renewable energy through initiatives like international solar alliances to make India a global renewable energy leader.