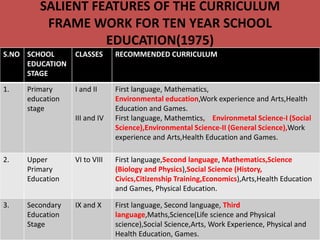
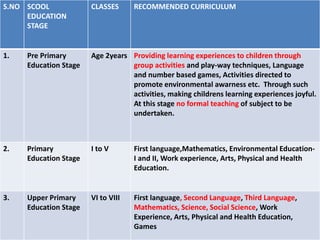
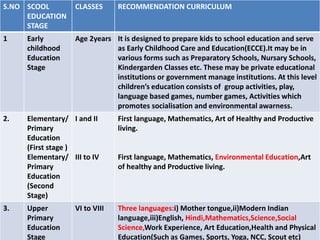
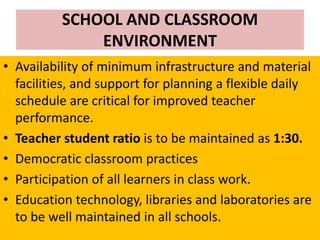
The document outlines the evolution of the school curriculum in India from 1975 to 2005, detailing key frameworks developed by the National Council for Educational Research and Training (NCERT). It describes various educational stages, including primary, upper primary, and secondary education, specifying the recommended curriculum components for each stage. Additionally, it highlights principles for curriculum design emphasizing learner engagement, interdisciplinary knowledge, and the importance of a supportive learning environment.