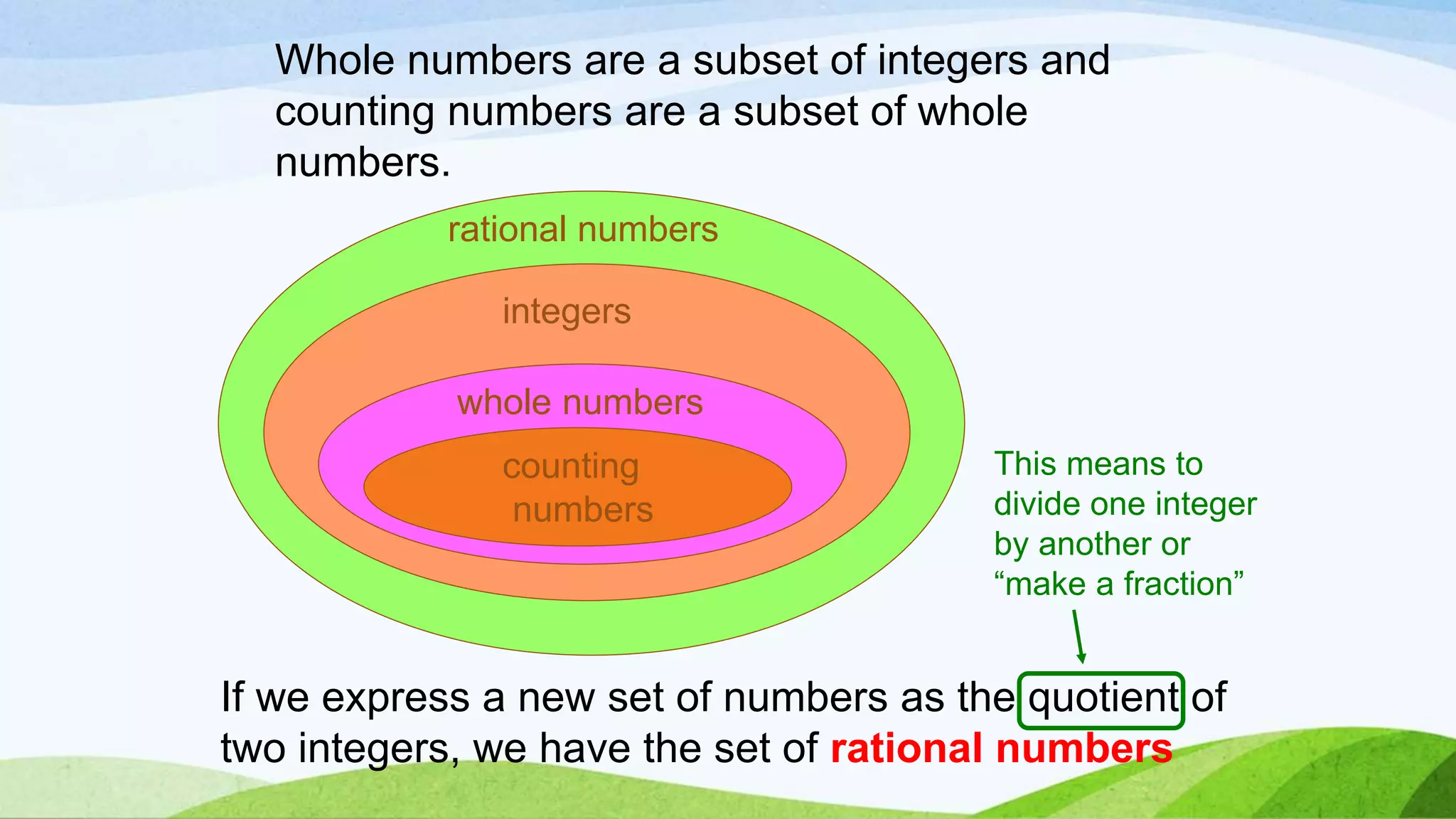
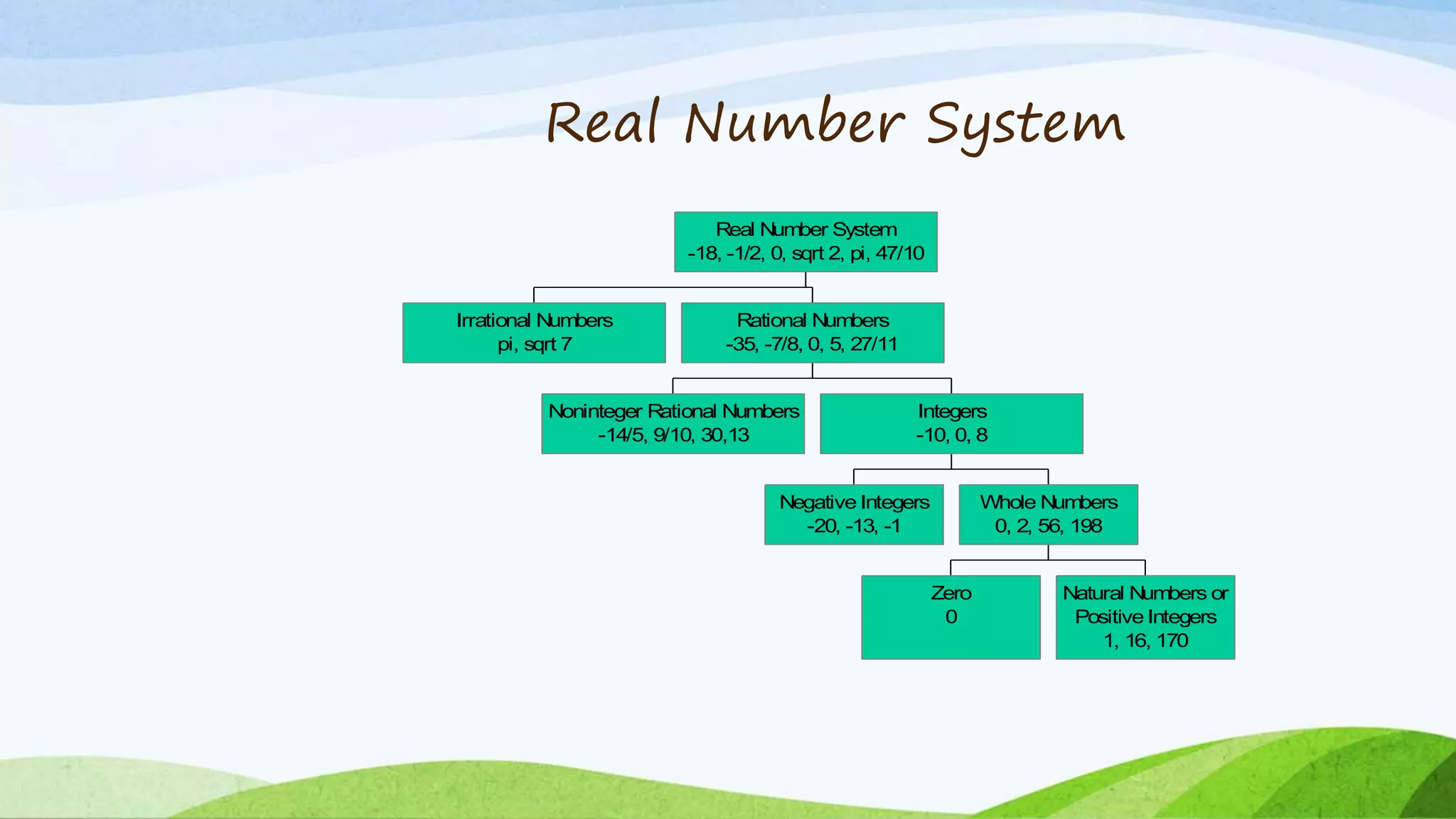
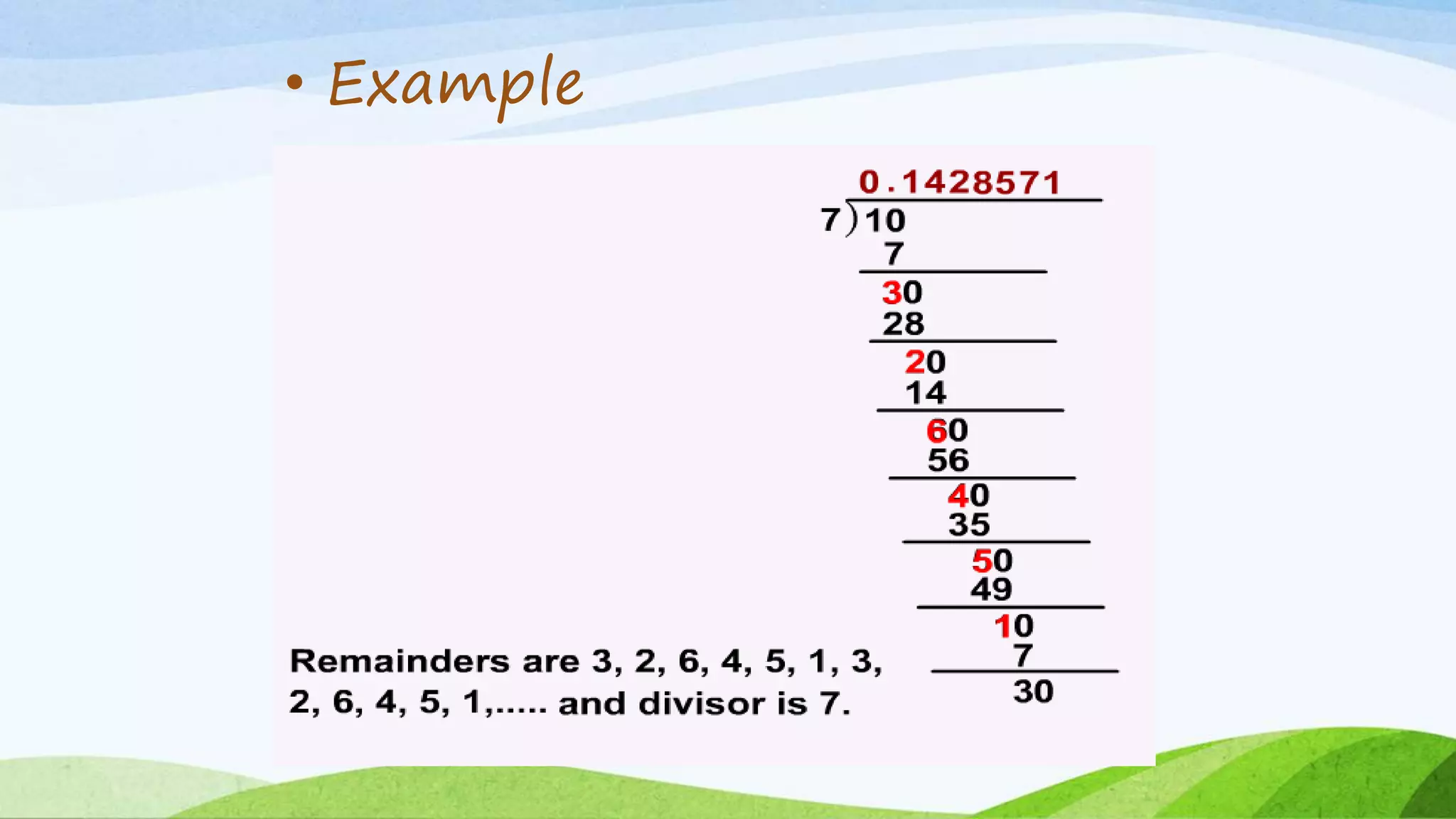
This document provides an introduction to rational numbers. It defines integers, whole numbers, counting numbers, and rational numbers. Rational numbers can be expressed as the quotient of two integers, such as fractions. Some numbers, like pi, cannot be expressed as quotients of integers and are called irrational numbers. The combination of rational and irrational numbers make up the set of real numbers. The document then provides examples and theorems regarding properties of rational numbers, such as Euclid's division algorithm for finding the highest common factor of two numbers and the fundamental theorem of arithmetic regarding unique prime factorizations.