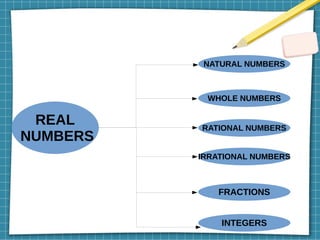
Real numbers comprise all natural numbers, whole numbers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, fractions, and decimal numbers. Real numbers can be rational, meaning they can be expressed as a ratio of two integers, or irrational, meaning they cannot. The document provides examples and proofs to demonstrate properties of real numbers, including that the square root of 2 is irrational and that any positive integer can be expressed in the forms 2q+1, 2q+3, or 2q+5. It also covers Euclid's division lemma, prime factorization, and operations on rational and irrational numbers.