Embed presentation
Downloaded 26 times


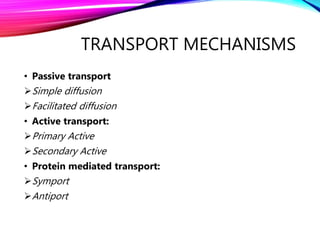
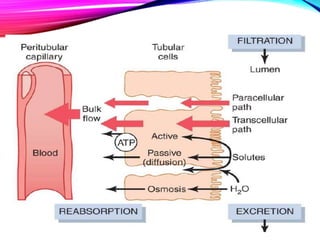
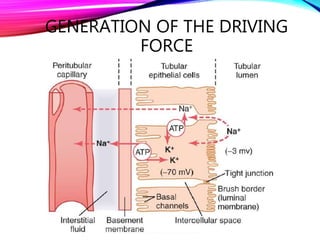
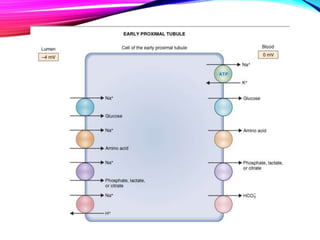
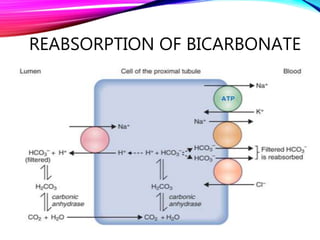
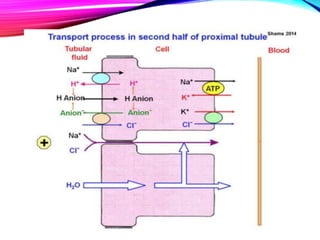
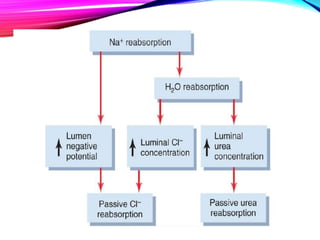
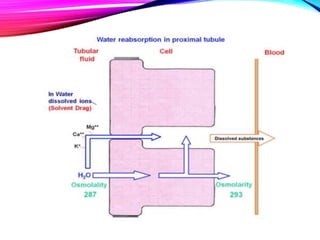

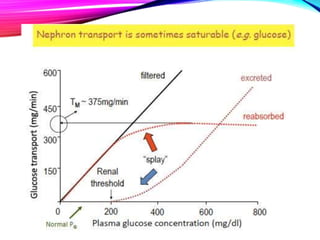
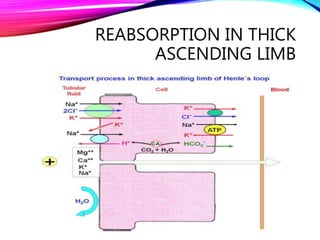
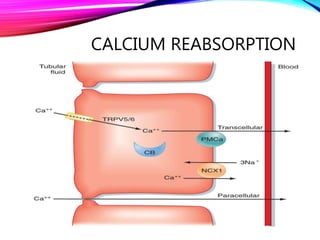
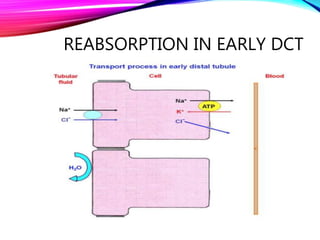



The document summarizes reabsorption processes in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), thick ascending limb (TAL), and early distal convoluted tubule (DCT). It outlines the objectives of reabsorption of electrolytes and water, the mechanisms involved including passive and active transport, and how medications can alter absorptive processes. Specific reabsorption topics discussed include bicarbonate, the concept of transport maximum, reabsorption in the TAL, calcium reabsorption, and reabsorption in the early DCT.
















