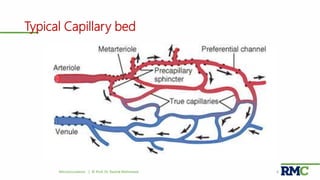
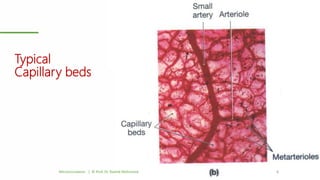
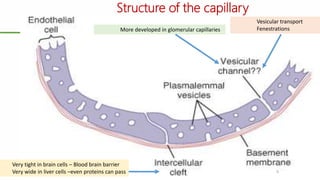
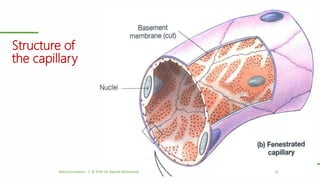
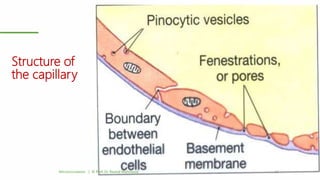
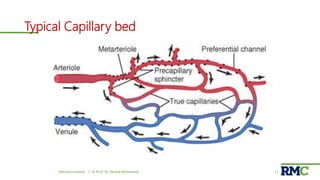
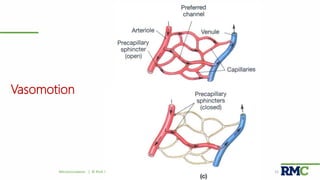
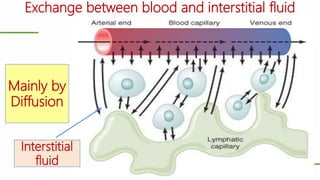
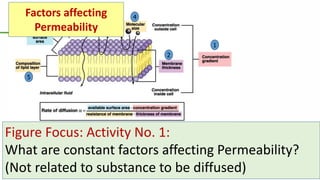
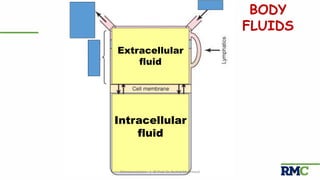
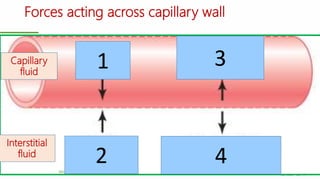
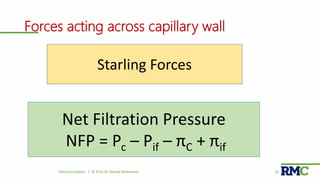
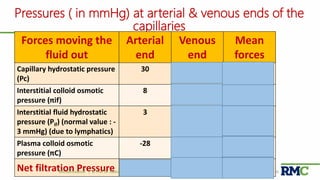
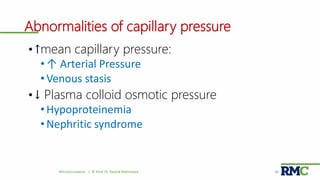
This document outlines a lecture on microcirculation. It begins by stating the objectives of understanding microcirculation functions and control. The content includes the structure of capillaries and microcirculation, factors that influence permeability, exchange of fluids between blood and tissues, Starling forces, and abnormalities in capillary pressure. Examples are given of typical capillary beds and how structures vary between tissues. The key concepts of vasomotion, Starling equilibrium, and net filtration pressure are also explained.