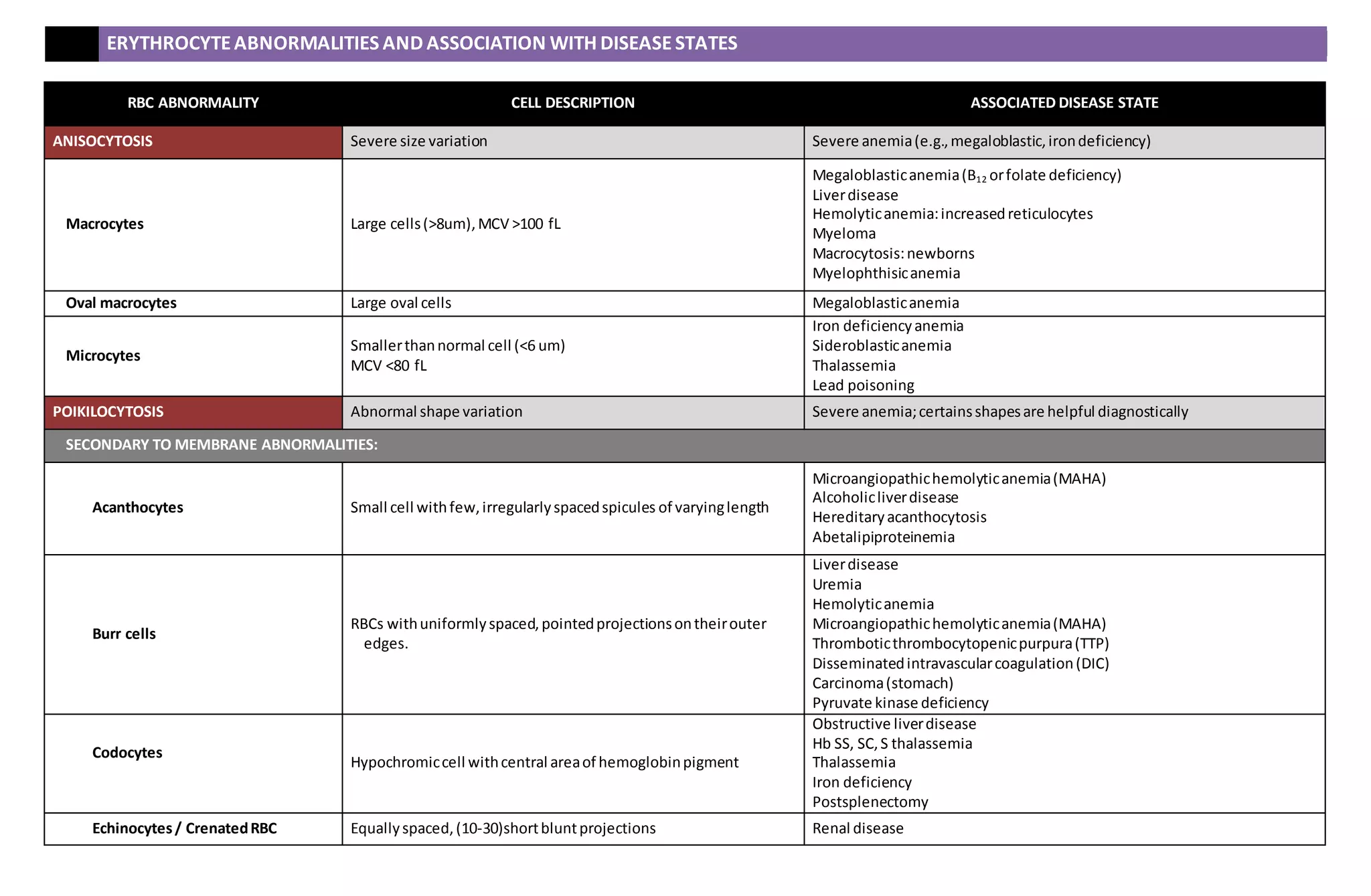
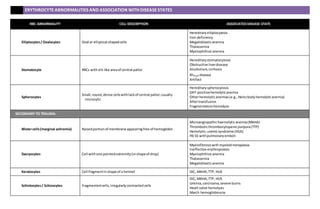
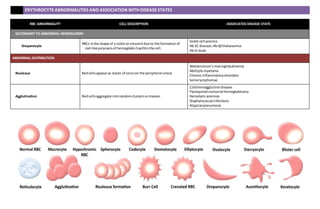
This document describes various red blood cell abnormalities and their associated disease states. It lists different types of abnormalities including anisocytosis, macrocytosis, microcytosis, poikilocytosis, spherocytosis, and drepanocytosis. Specific abnormalities are then defined such as burr cells, elliptocytes, and schistocytes. Each abnormality is paired with the disease states it is commonly associated with such as megaloblastic anemia for macrocytes and hereditary spherocytosis for spherocytes. Secondary abnormalities from membrane issues, trauma, abnormal hemoglobin, and distribution problems are also detailed.