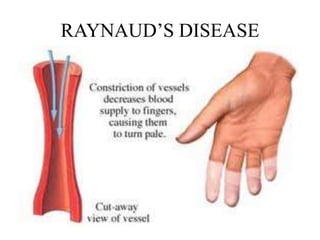
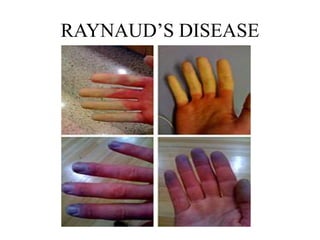
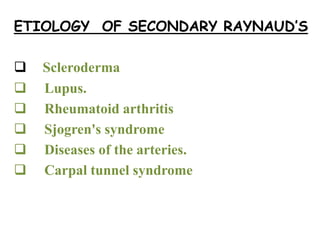
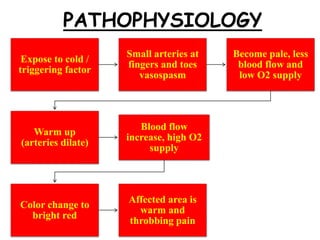
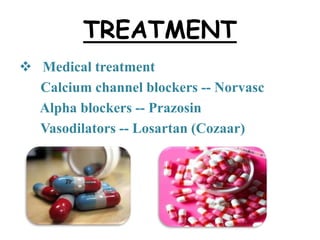
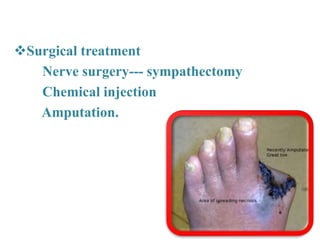
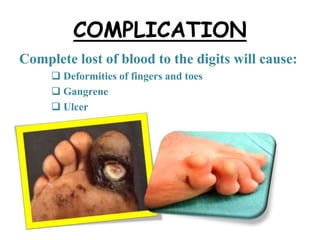
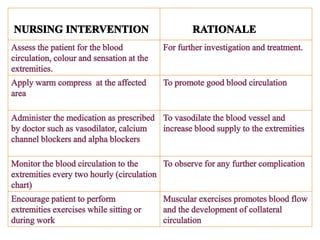
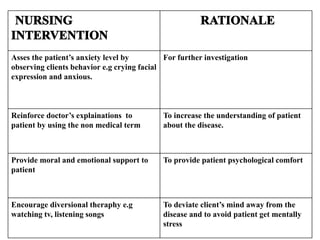
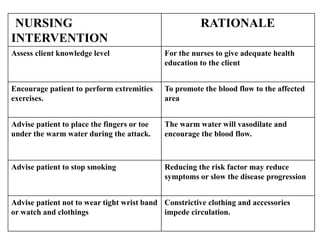
This document provides information about Raynaud's disease. It begins with an introduction that defines Raynaud's as a rare disorder affecting the arteries that causes vasospasm and reduced blood flow to the fingers and toes. It then covers the classification of Raynaud's disease into primary and secondary types. The causes, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluations, treatment options including medications and surgery, complications, health education, and nursing care plans are all discussed in detail.