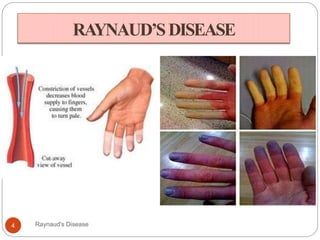
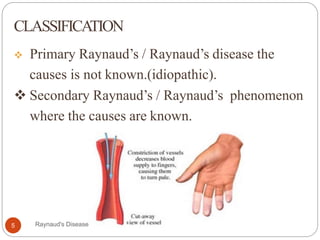
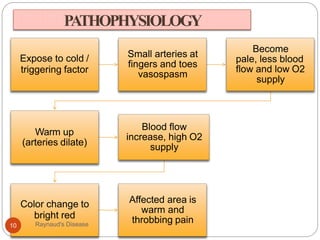
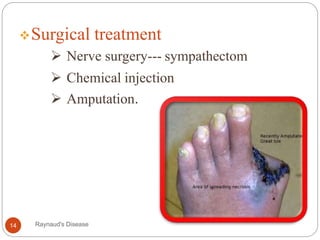
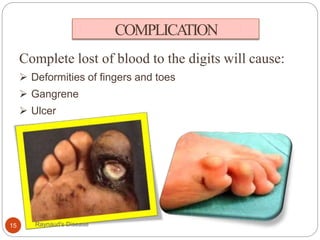
Raynaud's disease is a rare disorder characterized by decreased blood flow to the fingers and toes in response to cold temperatures or stress. It causes color changes in the affected areas, typically starting as they turn pale or white (vasoconstriction), then blue, and finally red as they warm up again (vasodilation). There are two types - primary Raynaud's, where the cause is unknown, and secondary Raynaud's, which has an underlying cause like connective tissue diseases. Symptoms include numbness, pain, and sometimes skin ulcers or gangrene in severe cases. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes and medications to dilate blood vessels like calcium channel blockers.