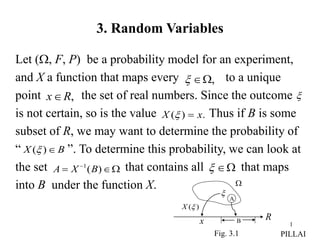
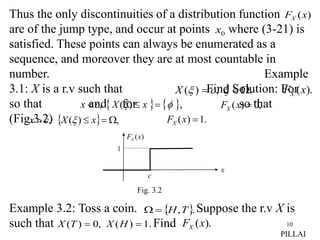
1. A random variable (X) is a function that maps outcomes of a probability experiment to real numbers. The probability distribution function (FX(x)) gives the probability that X takes on a value less than or equal to x.
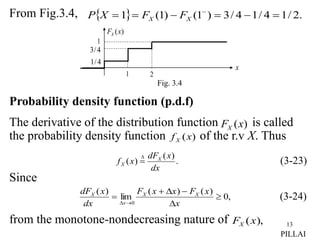
2. FX(x) satisfies properties of a distribution function - it is nondecreasing, right-continuous, and its limit as x approaches positive/negative infinity is 0/1.
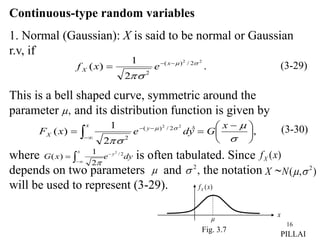
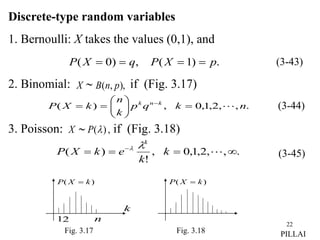
3. A random variable can be either continuous or discrete. FX(x) is continuous if it is continuous for all x, and discrete if it has jump discontinuities at countable points.