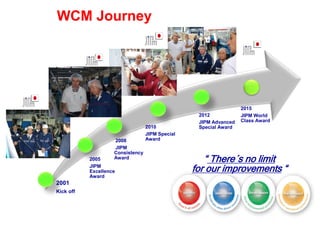
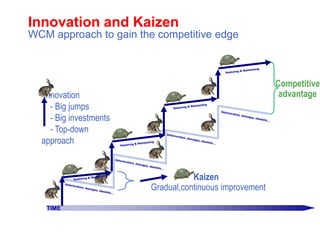
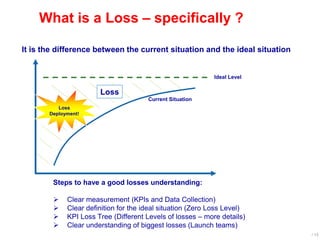
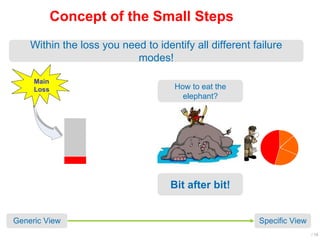
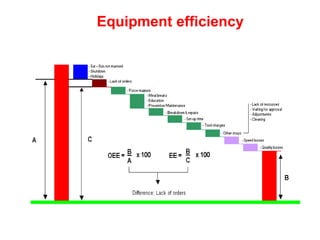
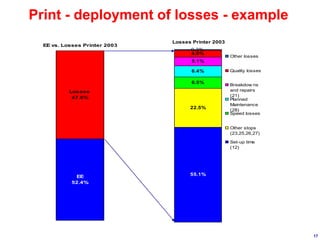
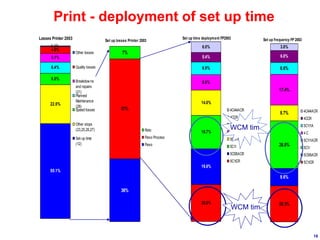
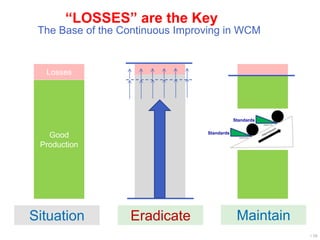
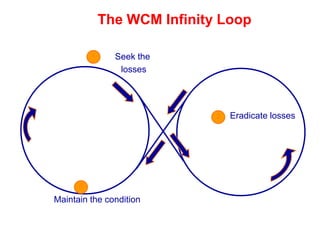
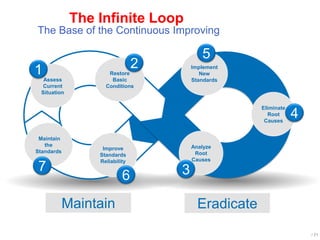
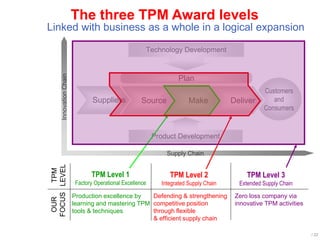
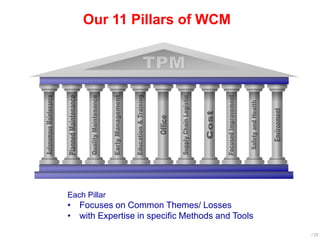
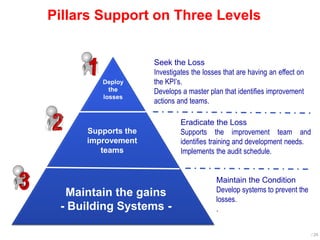
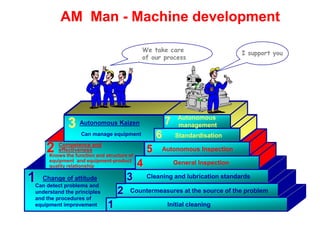
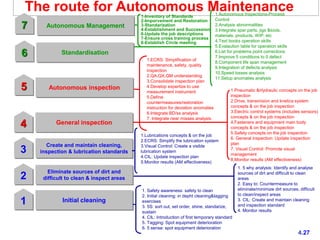
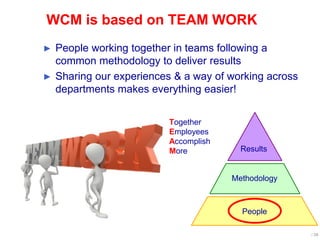
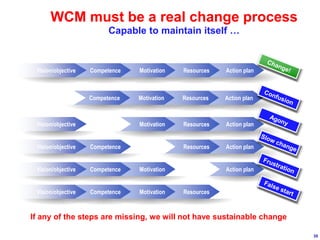
World Class Manufacturing (WCM) is a continuous improvement system rooted in Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), emphasizing reliability, productivity, and waste reduction. WCM aims for zero accidents, breakdowns, and defects through employee engagement, standardized processes, and a structured approach to problem-solving. The system incorporates teams and methodologies to enhance efficiency and quality, ultimately striving for a zero-loss organization.