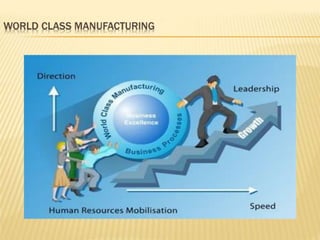
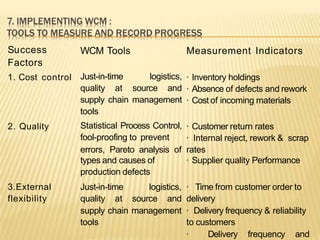
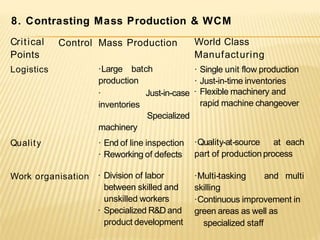
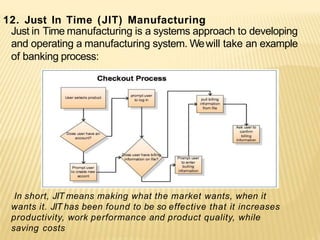
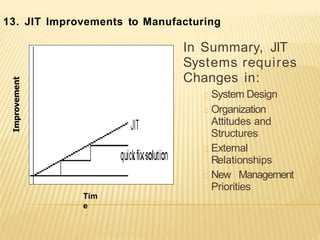
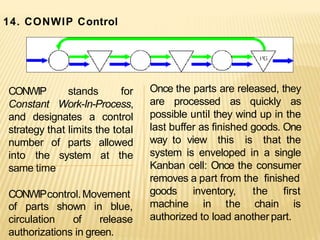
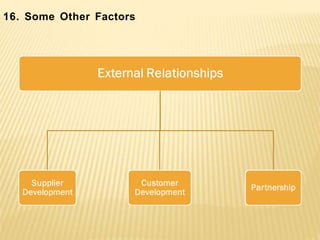
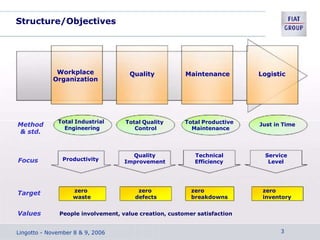
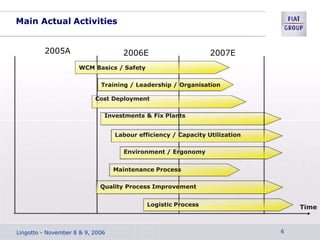
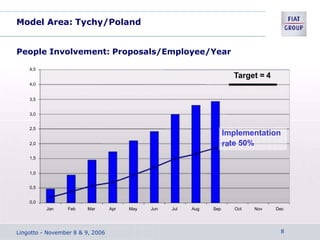
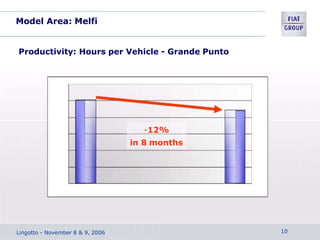
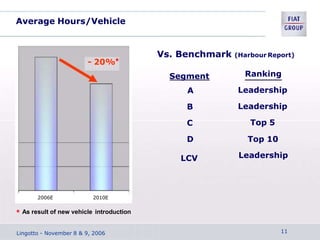
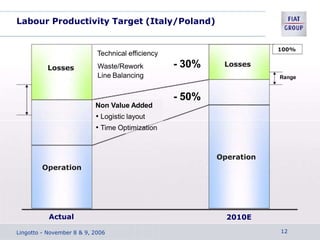
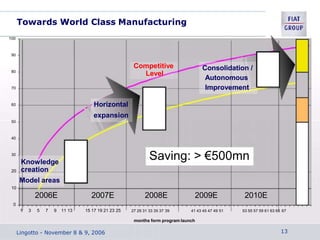
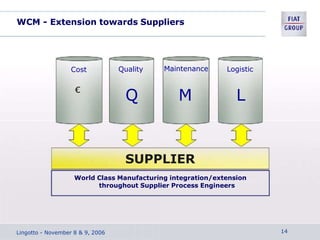
The document discusses the key aspects of achieving world-class manufacturing status. It outlines 16 factors for becoming world-class and describes tools like just-in-time manufacturing, Kanban control, and CONWIP control. It provides a checklist for assessing world-class criteria in areas like customer service, quality, flexibility, and innovation. The conclusion discusses starting a program to achieve world-class manufacturing standards through continuous improvement and employee contributions at all levels of the organization.