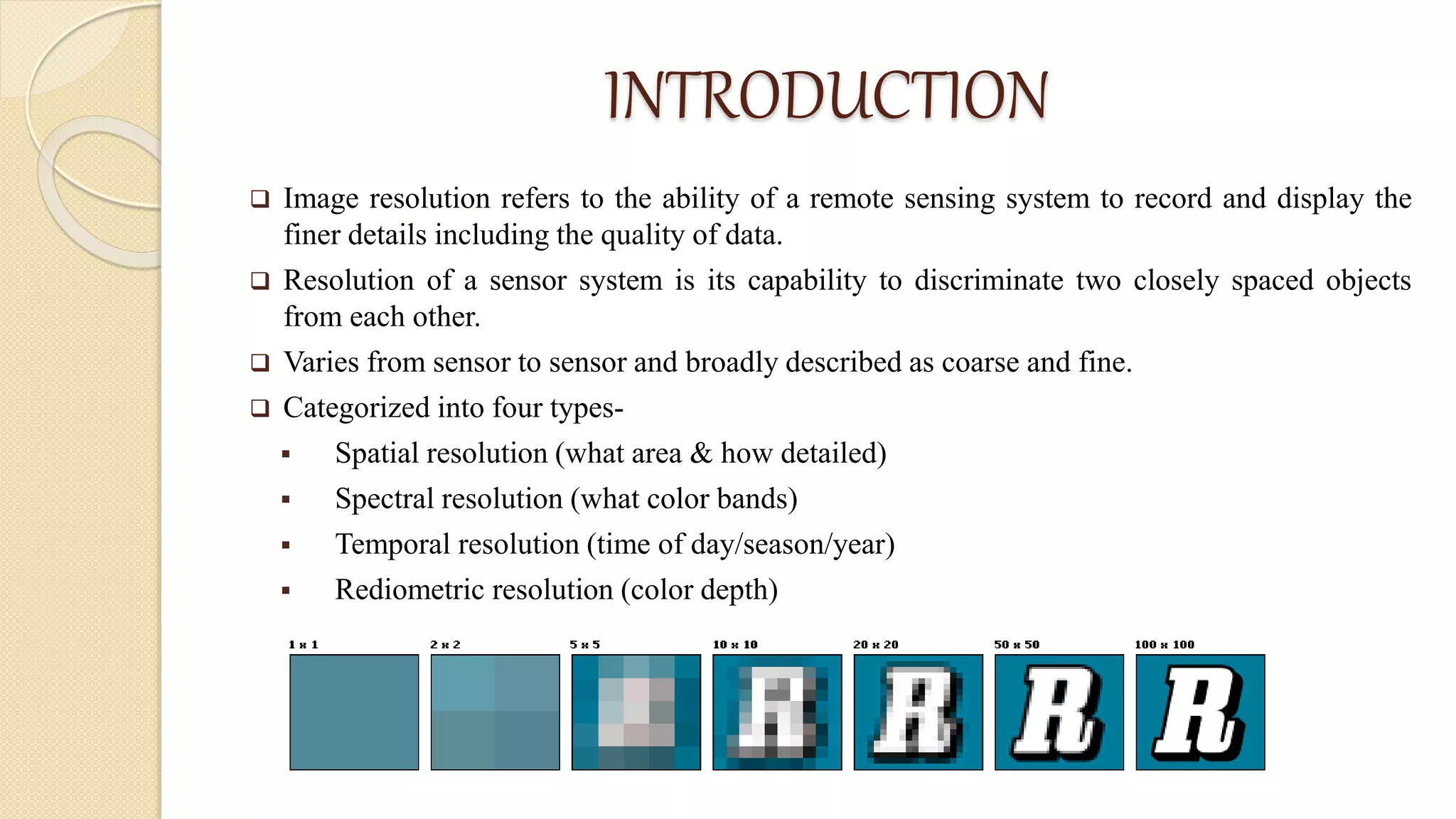
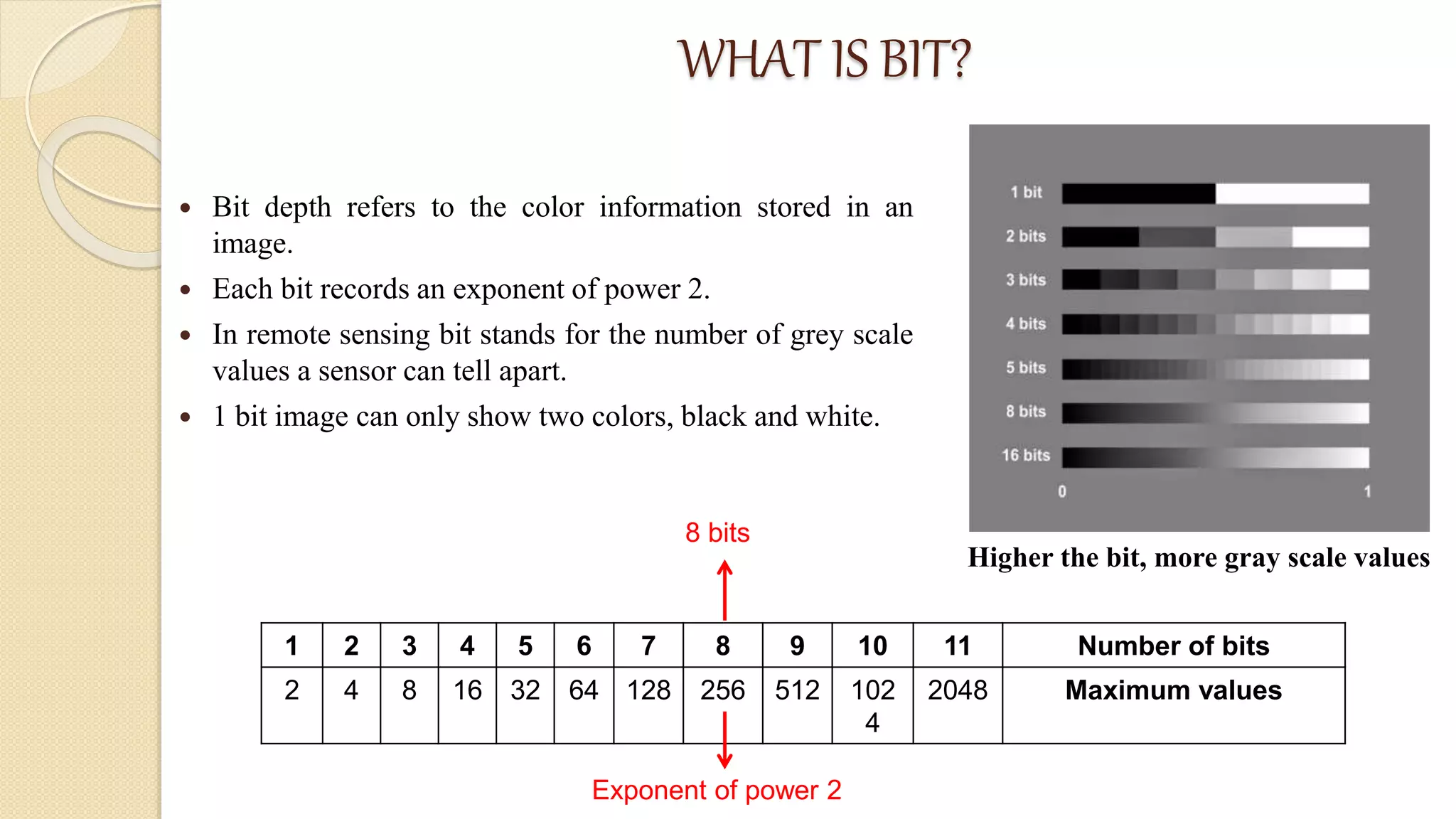
Radiometric resolution refers to a sensor's ability to distinguish slight differences in energy levels and is measured in bits. More bits allows an image to store more grayscale values, enabling better discrimination between classes. For example, Landsat-8 has 12-bit resolution, allowing it to distinguish over 4,000 grayscale levels and better characterize land cover compared to Landsat-7's 8-bit resolution of 256 levels. Higher radiometric resolution improves a sensor's sensitivity to capture subtle differences in surface reflectance.