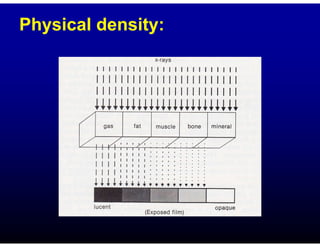
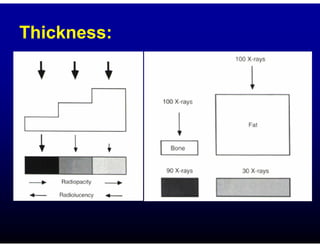
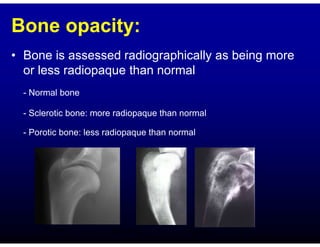
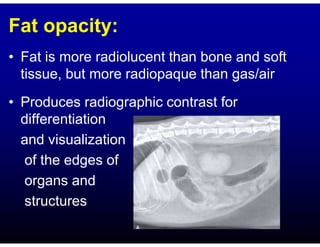
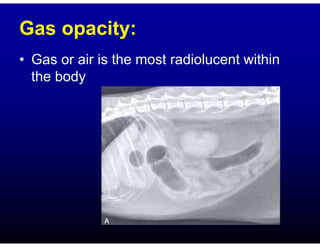
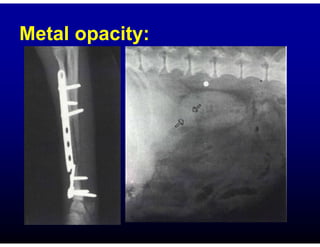
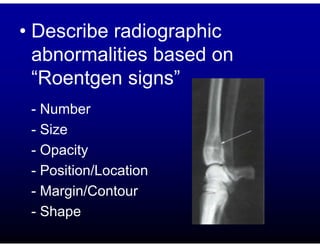
This document discusses the basics of radiographic interpretation. It explains that radiographs create images based on the differential absorption of x-rays as they pass through various tissues, with metal and bone appearing white and gas appearing black. The document outlines the typical radiographic appearance of different tissues like bone, soft tissue, fat, and gas. It emphasizes that interpretation involves correlating radiographic findings with clinical history and evaluating images for abnormalities defined by characteristics like number, size, and location. The goal is to integrate radiographic and clinical information to make an accurate diagnosis.