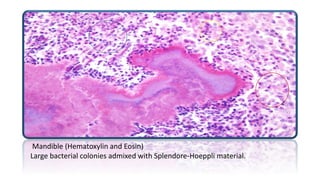
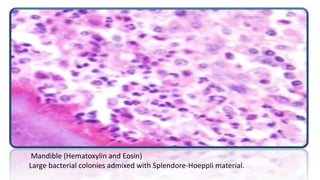
Actinomycosis lumpy jaw disease is a chronic infection of cattle affecting the mandible and maxilla bones, characterized by abscess formation and bone necrosis. It is caused by the Actinomyces bovis bacteria. Macroscopically, there is enlargement of the jaw bones with a honeycomb appearance. Microscopically, bacterial colonies are seen surrounded by Splendore-Hoeppli material and zones of neutrophils, macrophages, lymphocytes and connective tissue. A case study describes a cow with a 7-8 month history of a proliferative jaw growth, which upon removal and microscopic examination revealed granulomas containing bacterial colonies consistent with actinomycosis.