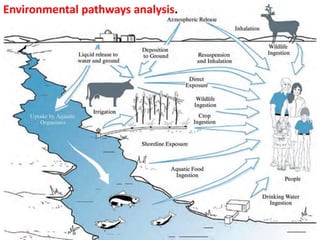
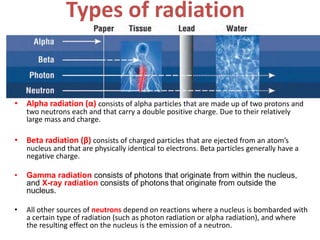
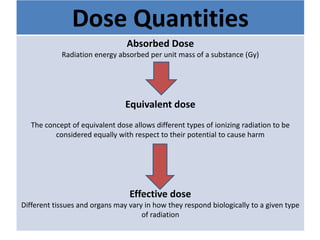
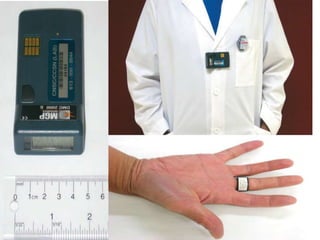
Dosimetry is the process of measuring radiation doses and assigning them to individuals. There are two types of exposure: external, where radiation comes from outside the body, and internal, where radiation is emitted from substances inside the body. Radiation can be measured using personal dosimeters, environmental monitoring, or biological sampling. The main types of radiation are alpha, beta, gamma, and neutrons. Radiation dose is quantified using absorbed dose, equivalent dose, and effective dose. Dosimeters come in passive and active varieties to measure external radiation doses, while internal doses require estimating intake and calculating dose to organs over time. Measurement uncertainty arises from factors like dosimeter calibration and environmental variability.