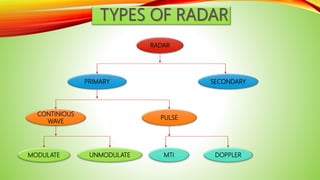
This presentation is about radar and is presented by 6 students to their lecturer. It includes an introduction, history of radar including its development from experiments in the late 19th century to use in World War II. It also outlines the different types of radar, how radar works, and its various applications such as in weather forecasting, air traffic control, police speed detection, and military uses. The presentation concludes by discussing advances in radar technology and its increasing role in the future.