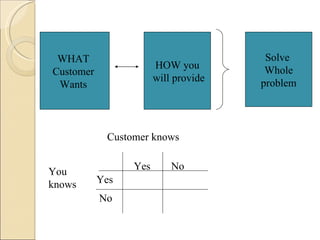
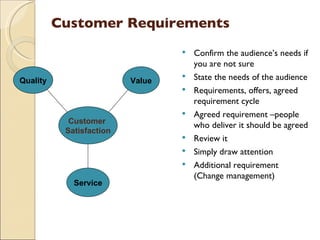
ISO 9001 provides standards for quality management systems that can be applied to service organizations. It aims to achieve customer satisfaction by meeting requirements and continually improving processes. Key aspects of a quality management system include management responsibility, resource management, developing and delivering services, and monitoring and improving processes. Implementing such a system helps organizations improve quality, consistency and customer satisfaction.