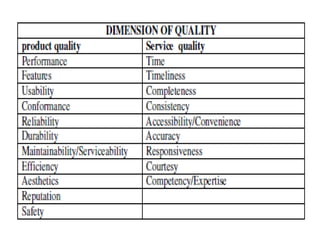
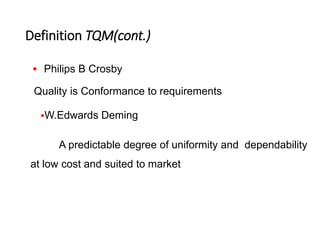
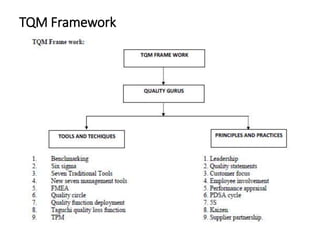
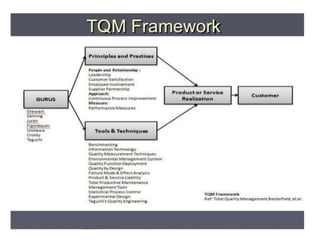
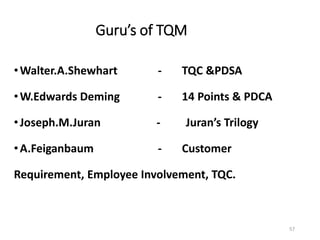
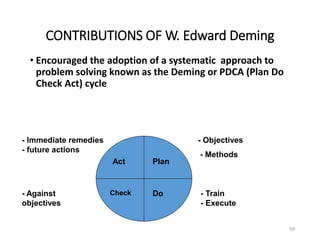
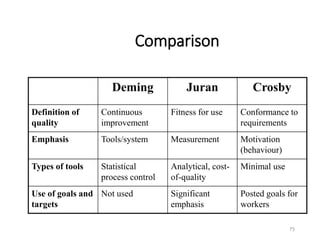
This document provides an overview of the objectives and syllabus for the course GE6757-TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT. The syllabus is divided into 5 units which cover topics such as the introduction and definitions of quality management, TQM principles like leadership and process improvement, TQM tools and techniques including control charts and quality function deployment, quality systems like ISO standards and implementing TQM. It also lists the textbook and references used for the course.

















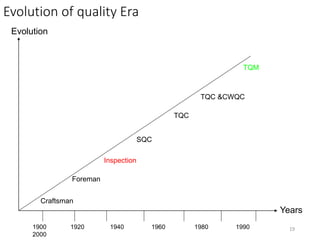

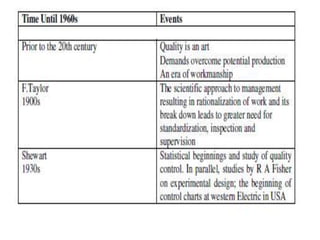
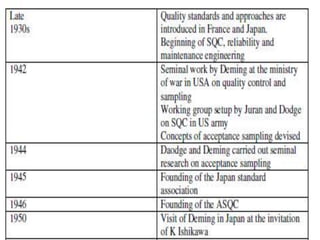
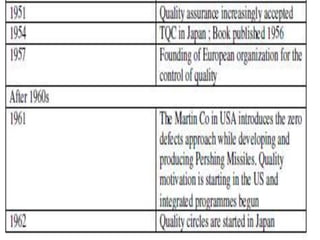
















































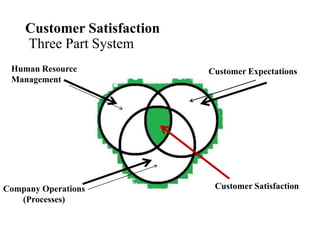

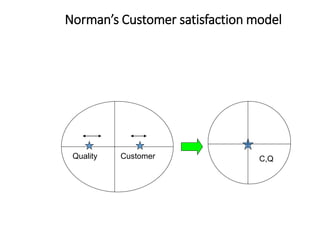
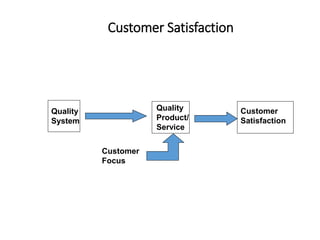
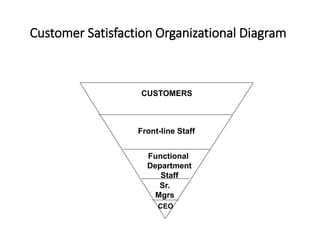

![Customer types
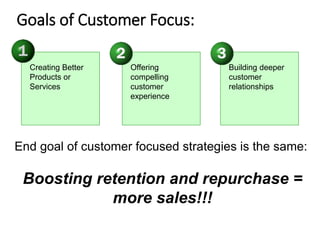
•External and Internal customers
•External – current, prospective and lost customers
•Internal – Every person in a process is a customer of
the previous operation.( applies to design,
manufacturing, sales, supplies etc.) [Each worker
should see that the quality meets expectations of
the next person in the supplier-to-customer chain ]
•TQM is commitment to customer-focus - internal
and external customers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ge6757unit-1-230418081129-7f45775d/85/GE6757-UNIT-1-ppt-88-320.jpg)