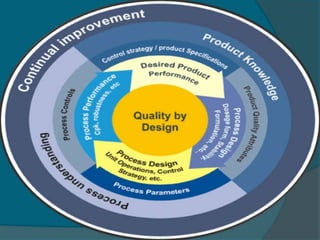
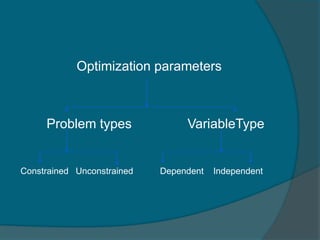
The document discusses Quality by Design (QbD), which is defined as a systematic approach to pharmaceutical development and manufacturing that begins with predefined objectives and emphasizes product and process understanding based on sound science and quality risk management. QbD aims to eliminate batch failures, minimize deviations and investigations, avoid regulatory issues, and allow for continuous improvement. It promotes building scientific knowledge, ensuring consistent high quality products, and incorporating risk management into the design and manufacturing process.