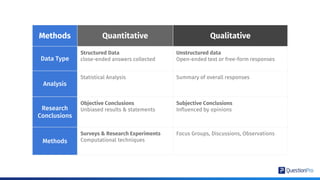
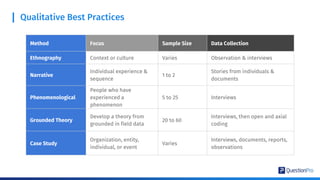
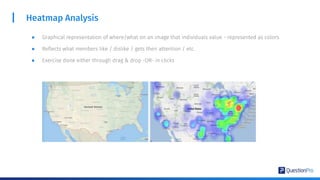
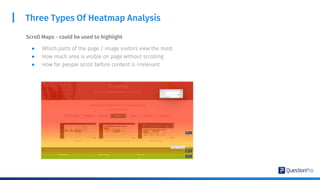
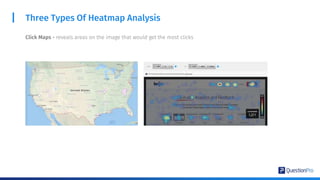
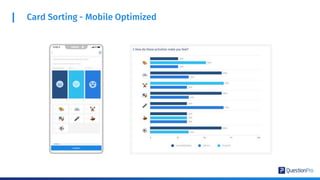
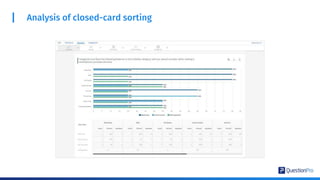
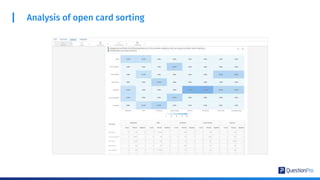
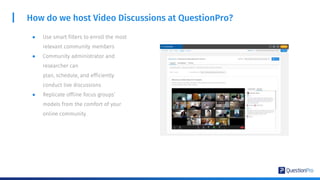
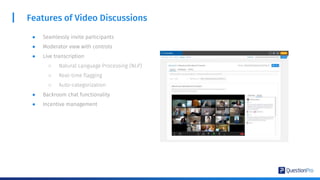
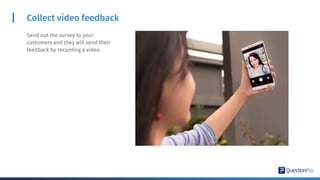
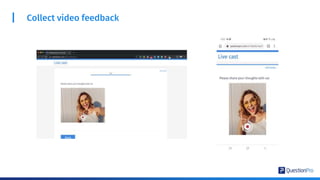
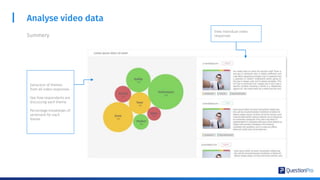
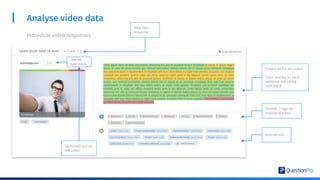
The document compares qualitative and quantitative research methodologies, highlighting their distinct characteristics, data types, and analysis approaches. It discusses best practices for each method, including various sampling techniques and data collection strategies such as card sorting and video discussions. The document also presents advanced tools like heatmap analysis and livecast technology for gathering and interpreting qualitative insights in research.