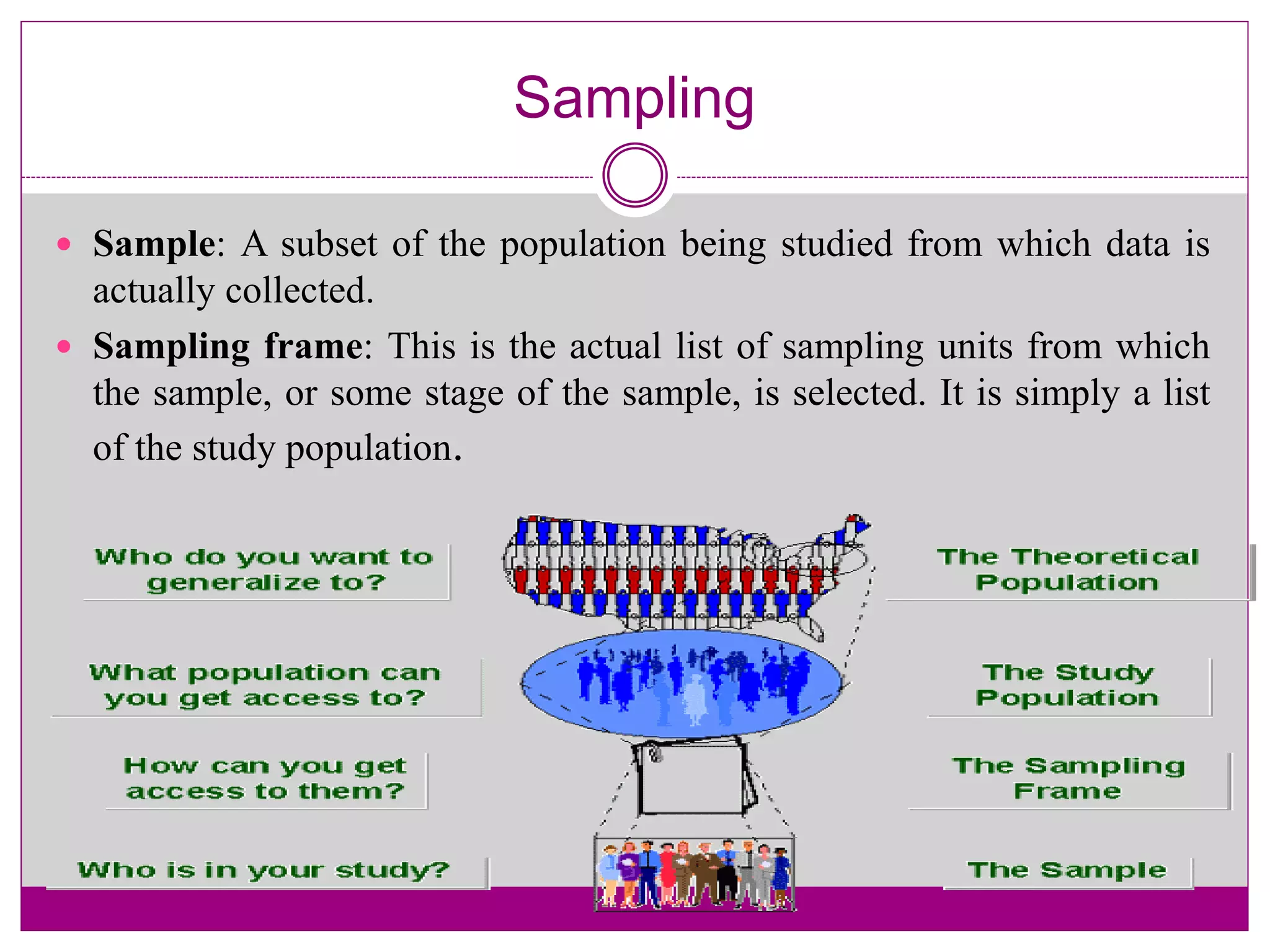
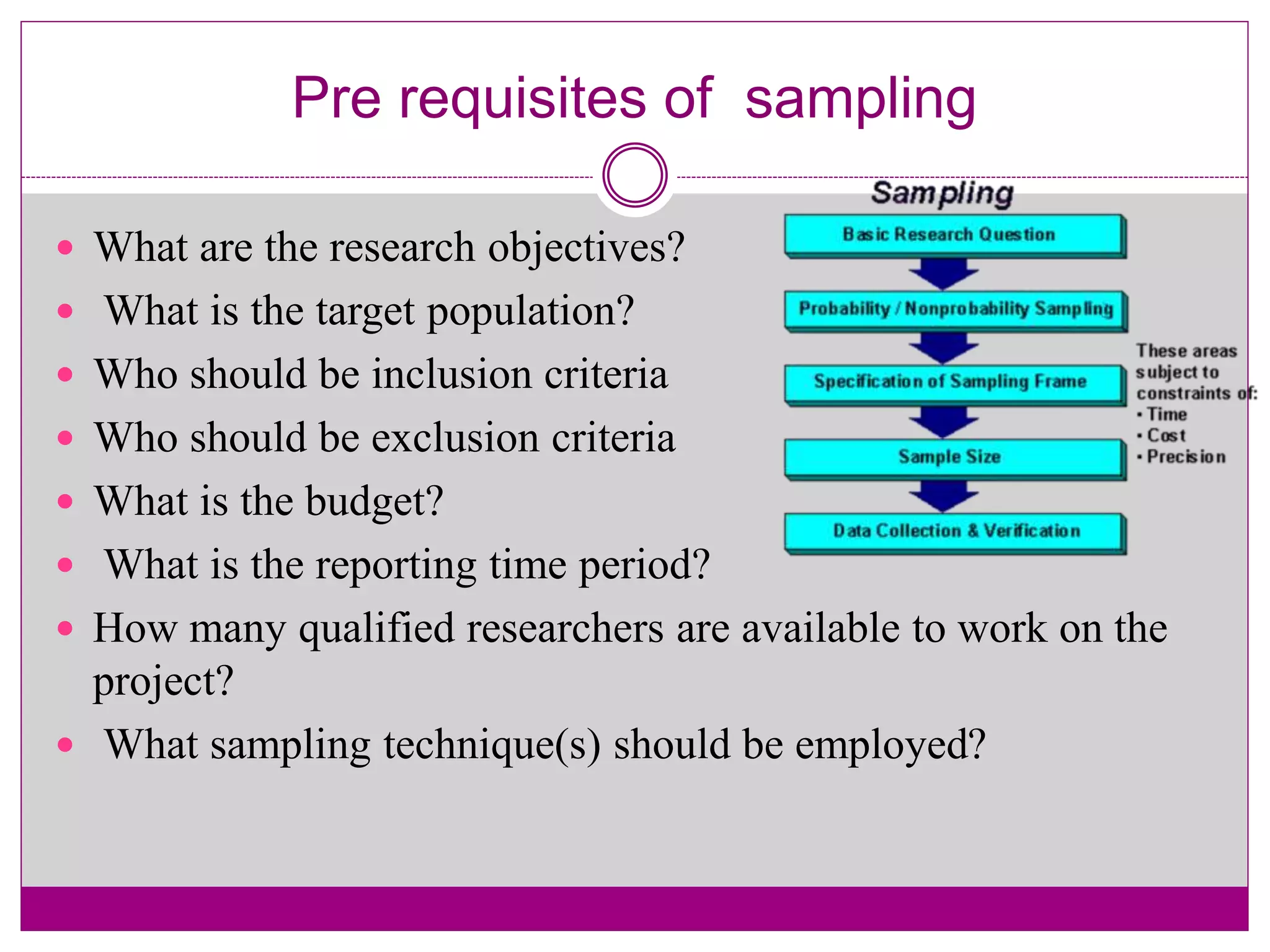
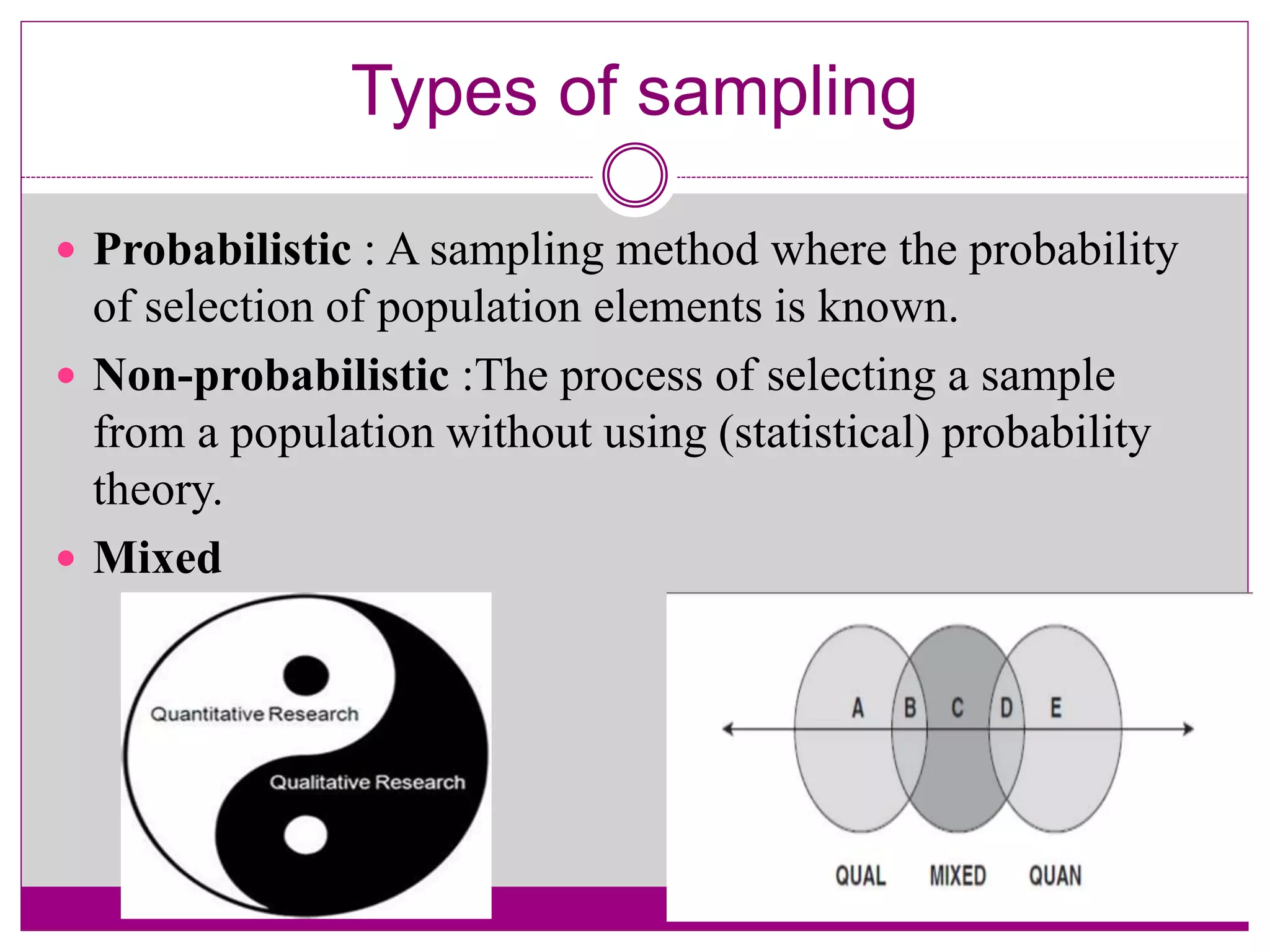
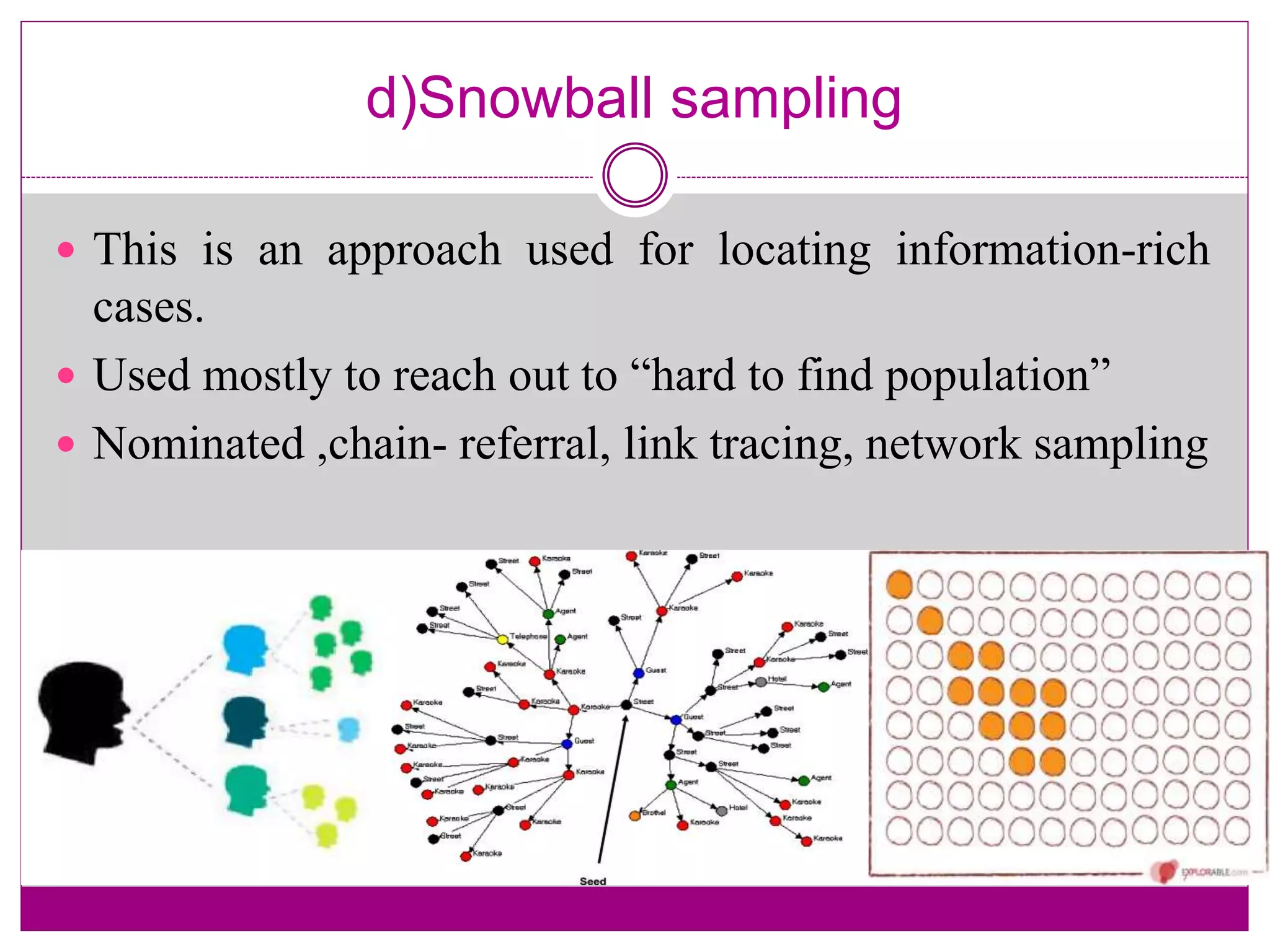
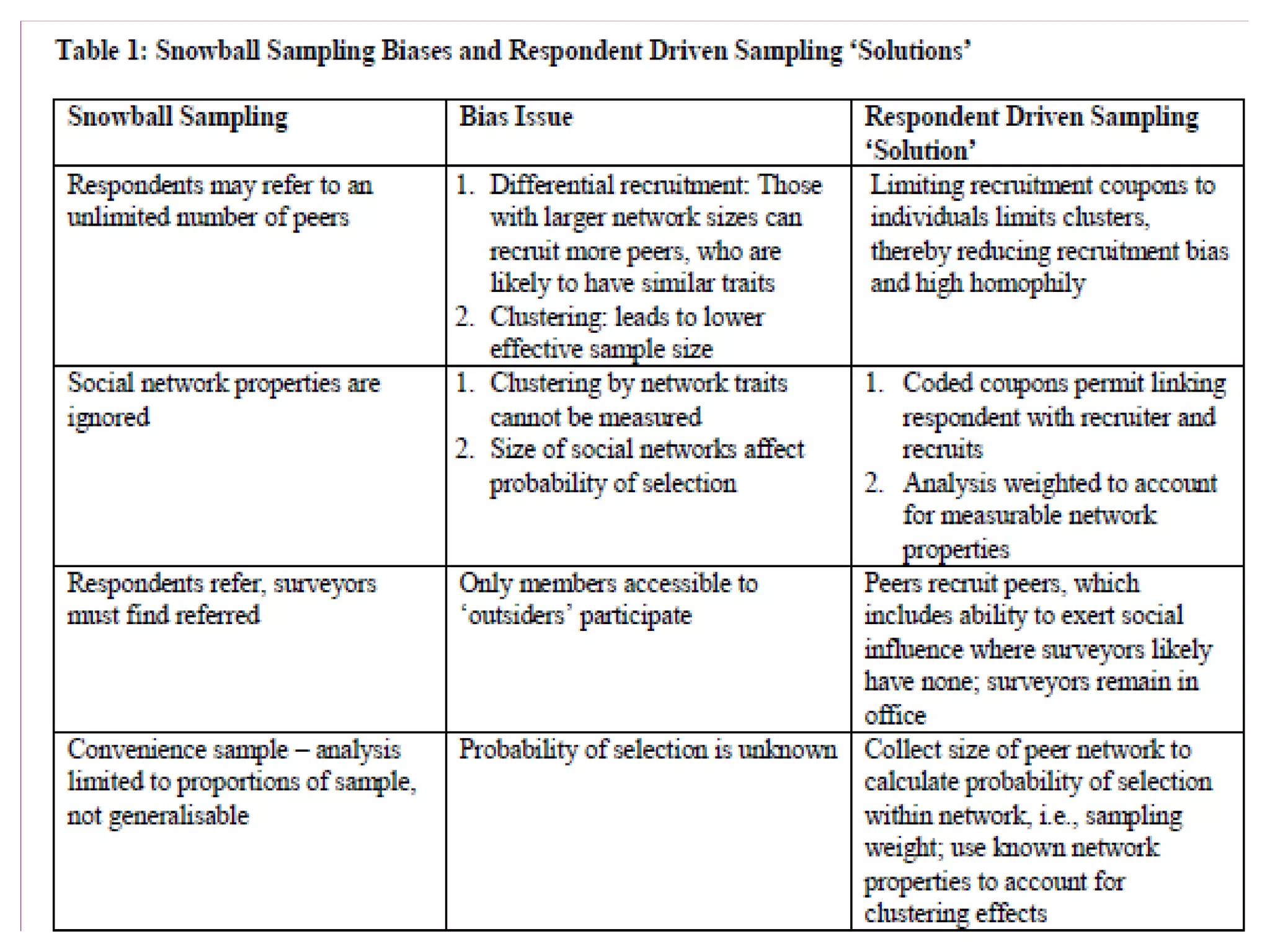
The document discusses various sampling techniques used in qualitative research. It begins by defining key sampling concepts like sampling frame, sample design, and sample size. It then outlines prerequisites to consider for sampling like research objectives, target population, and budget. The main types of sampling covered are probabilistic, non-probabilistic, and mixed. Specific non-probabilistic strategies discussed include purposive sampling, convenience sampling, and quota sampling. The document concludes by noting biases that can occur in sampling and emphasizing that non-probabilistic techniques are commonly used in qualitative research.