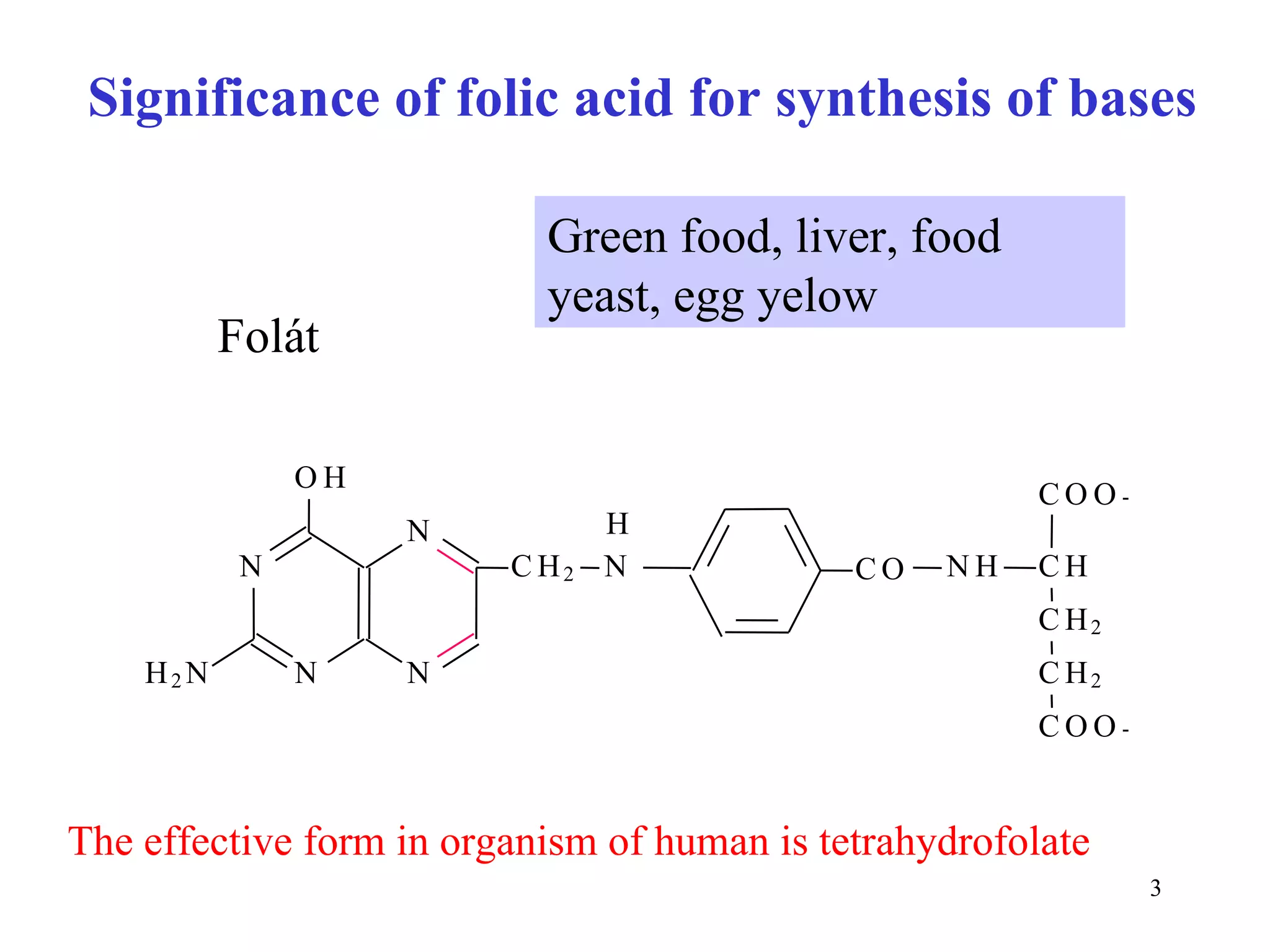
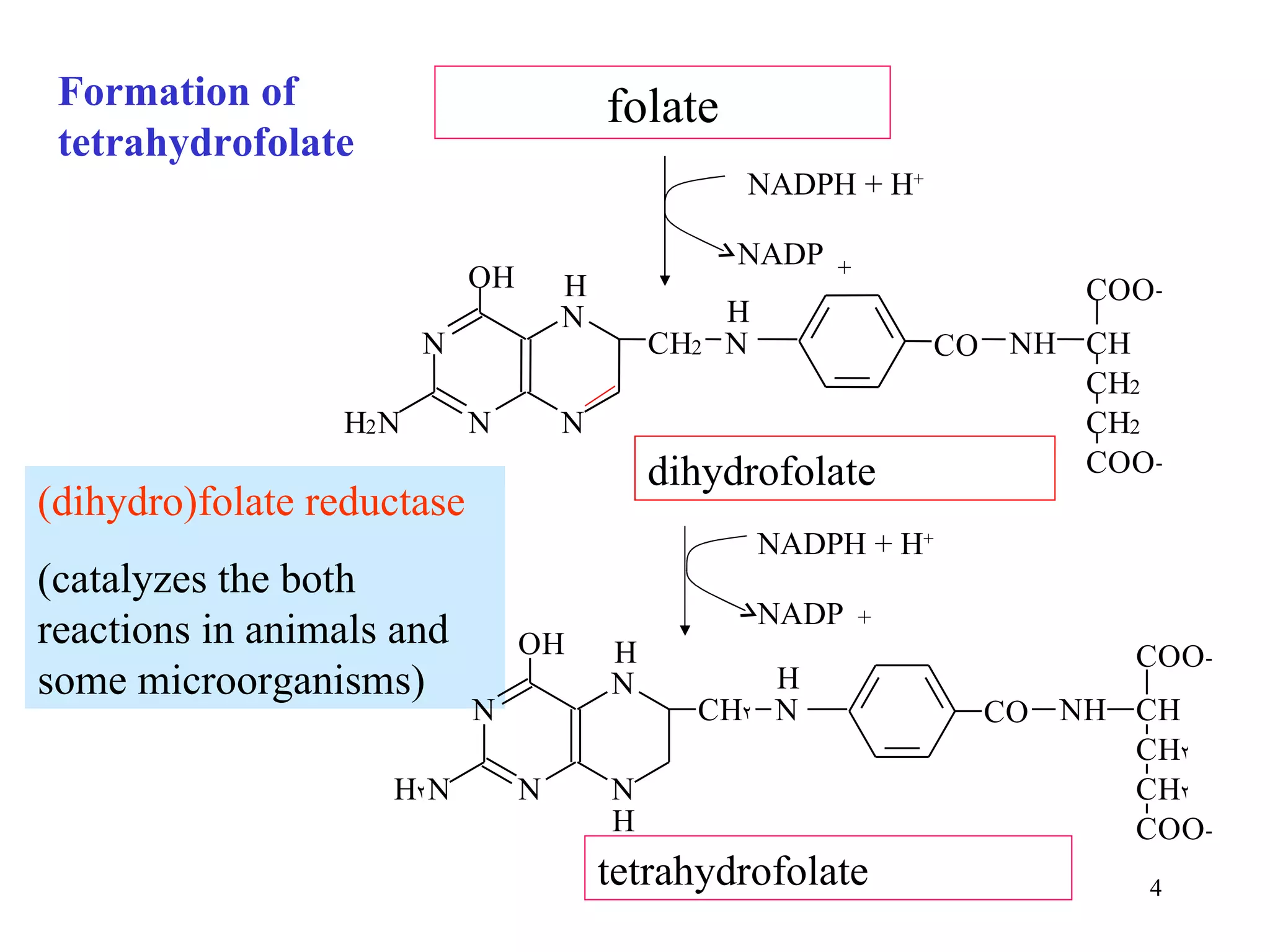
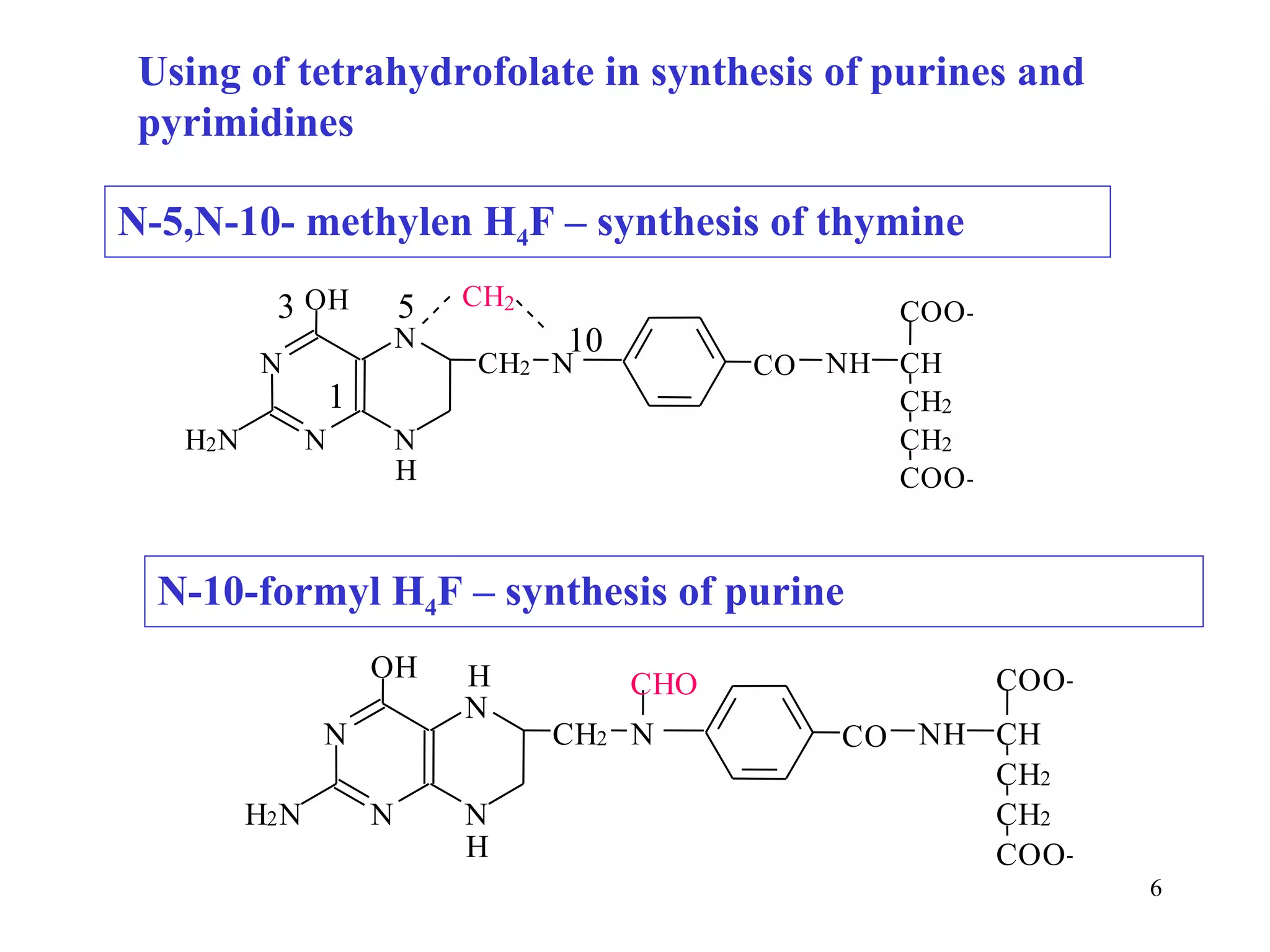
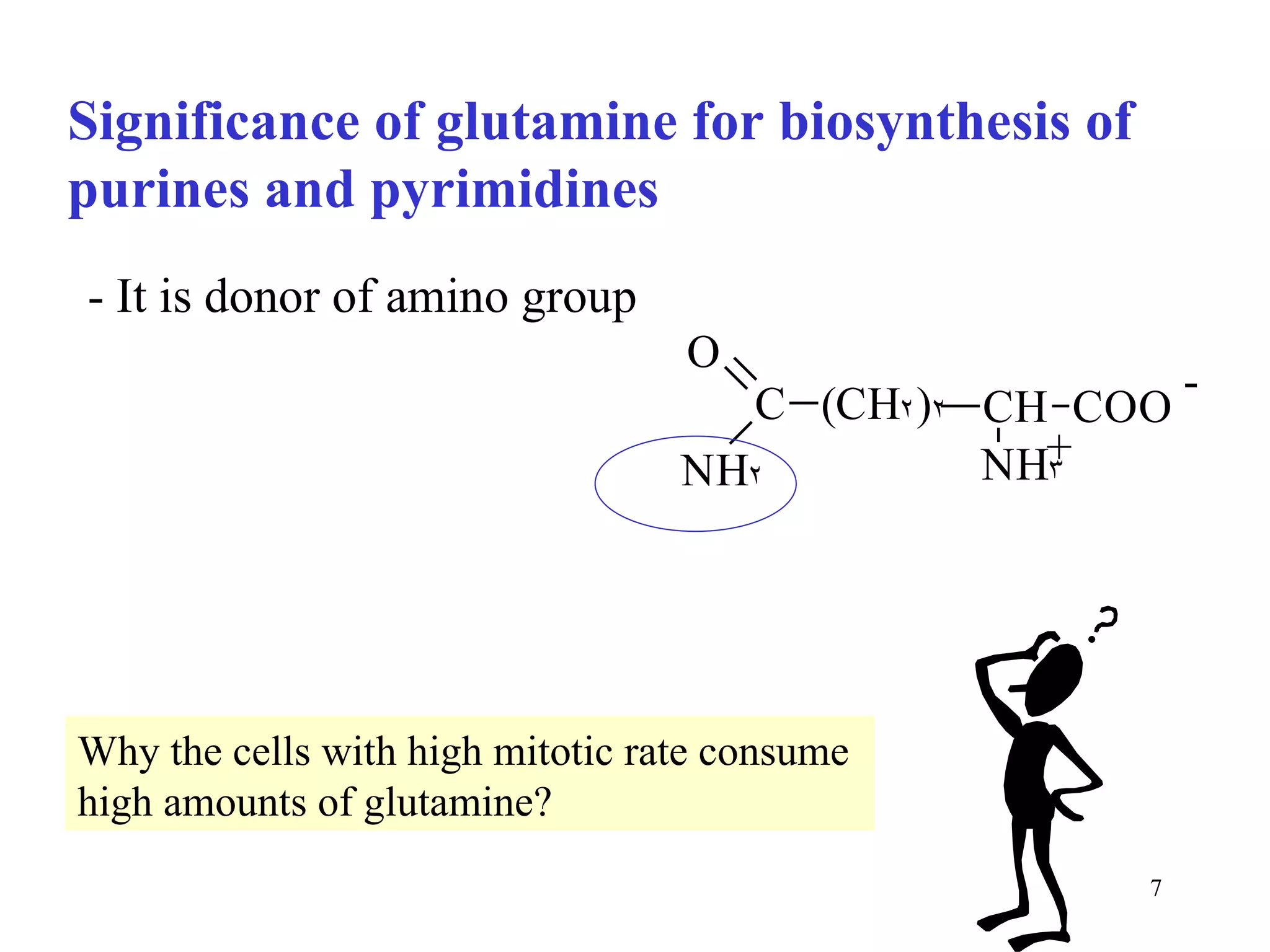
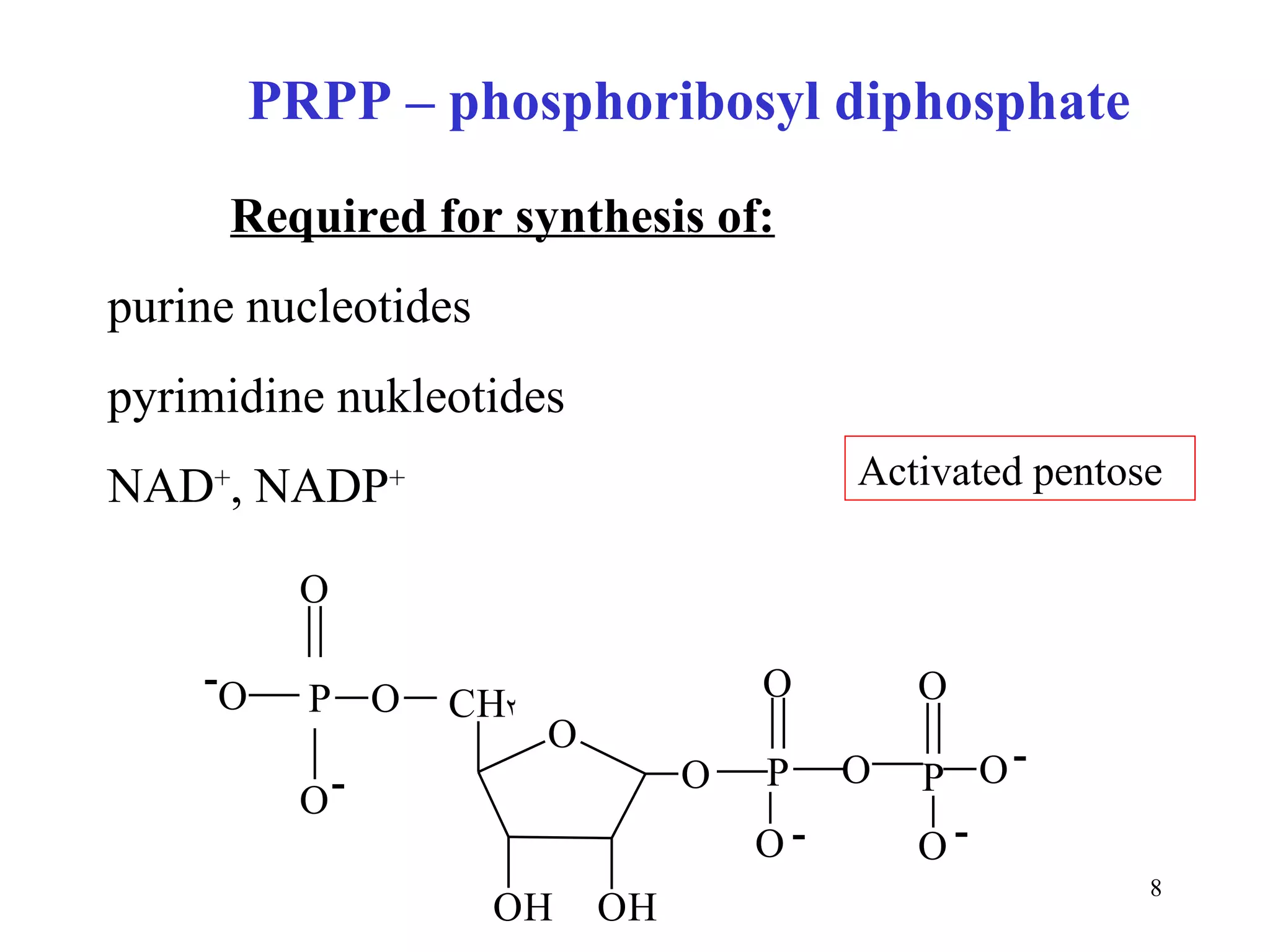
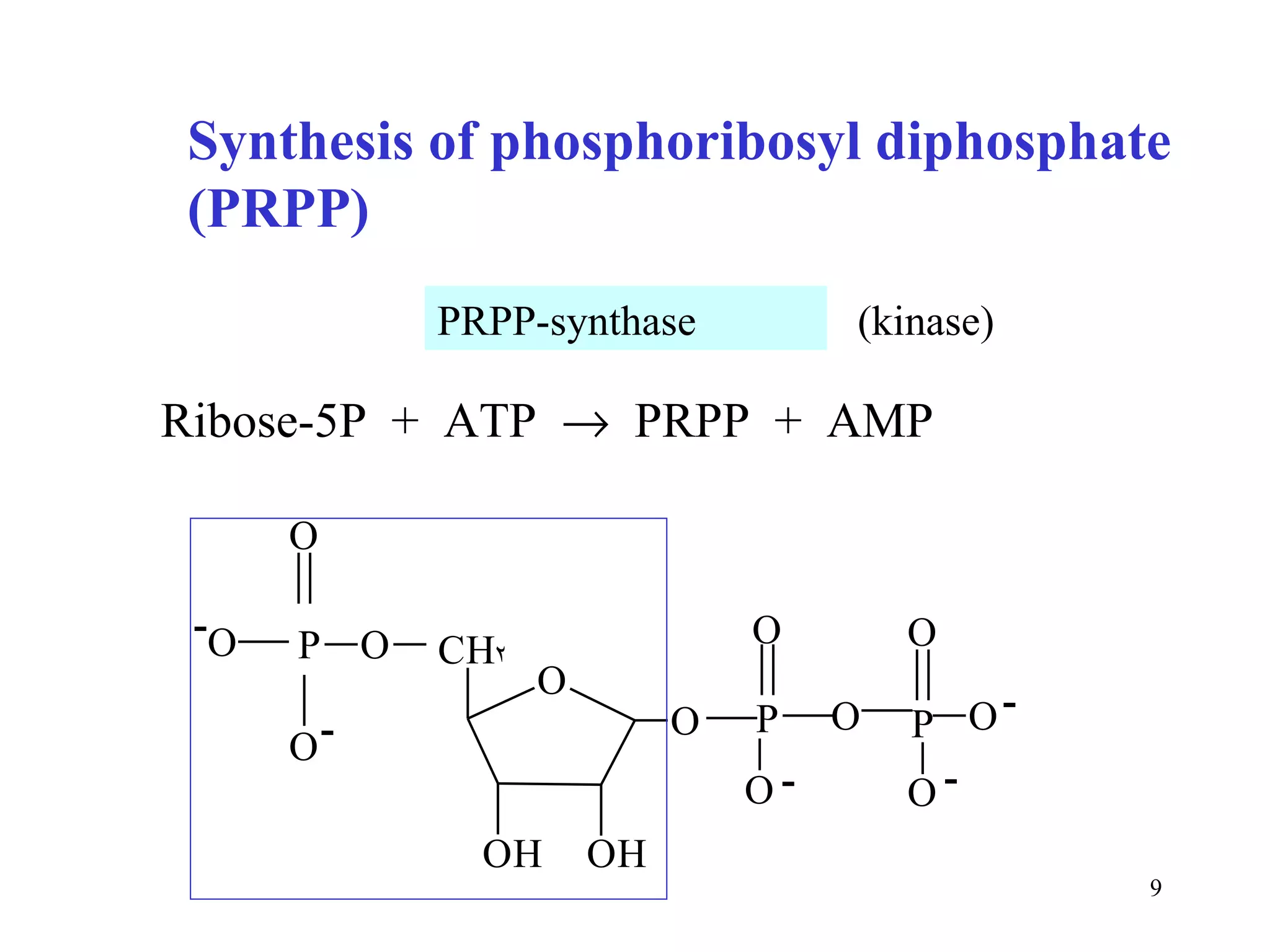
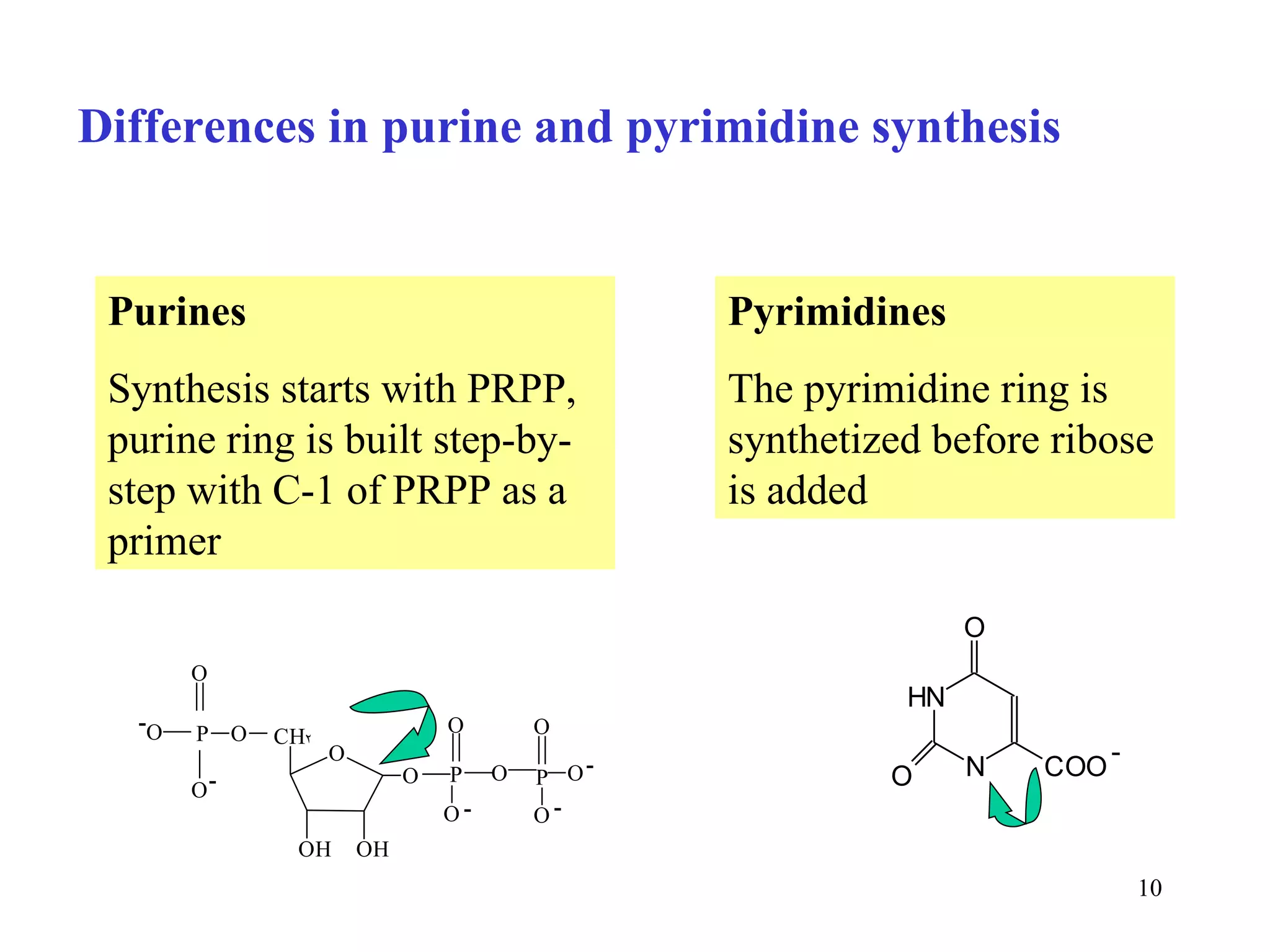
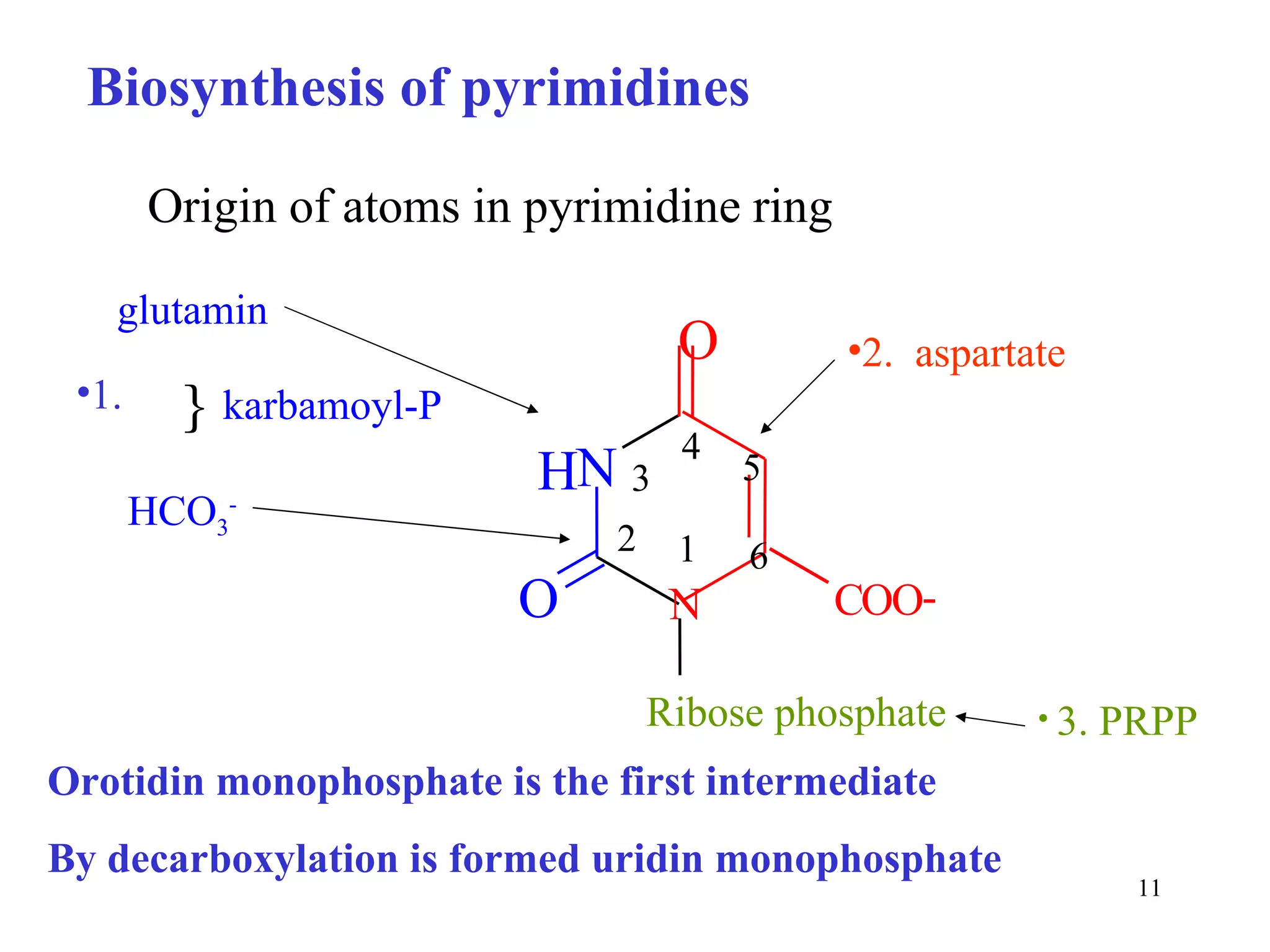
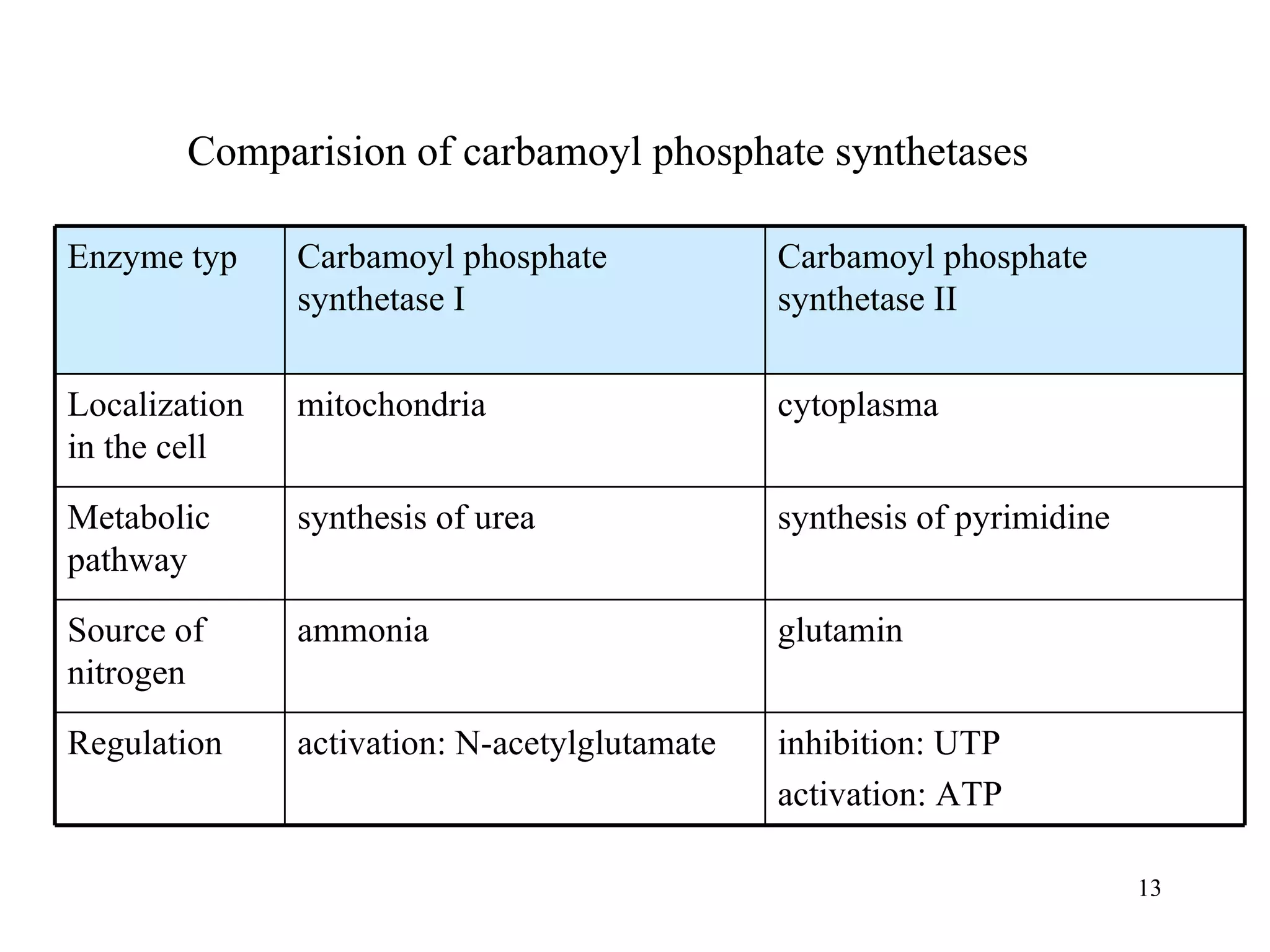
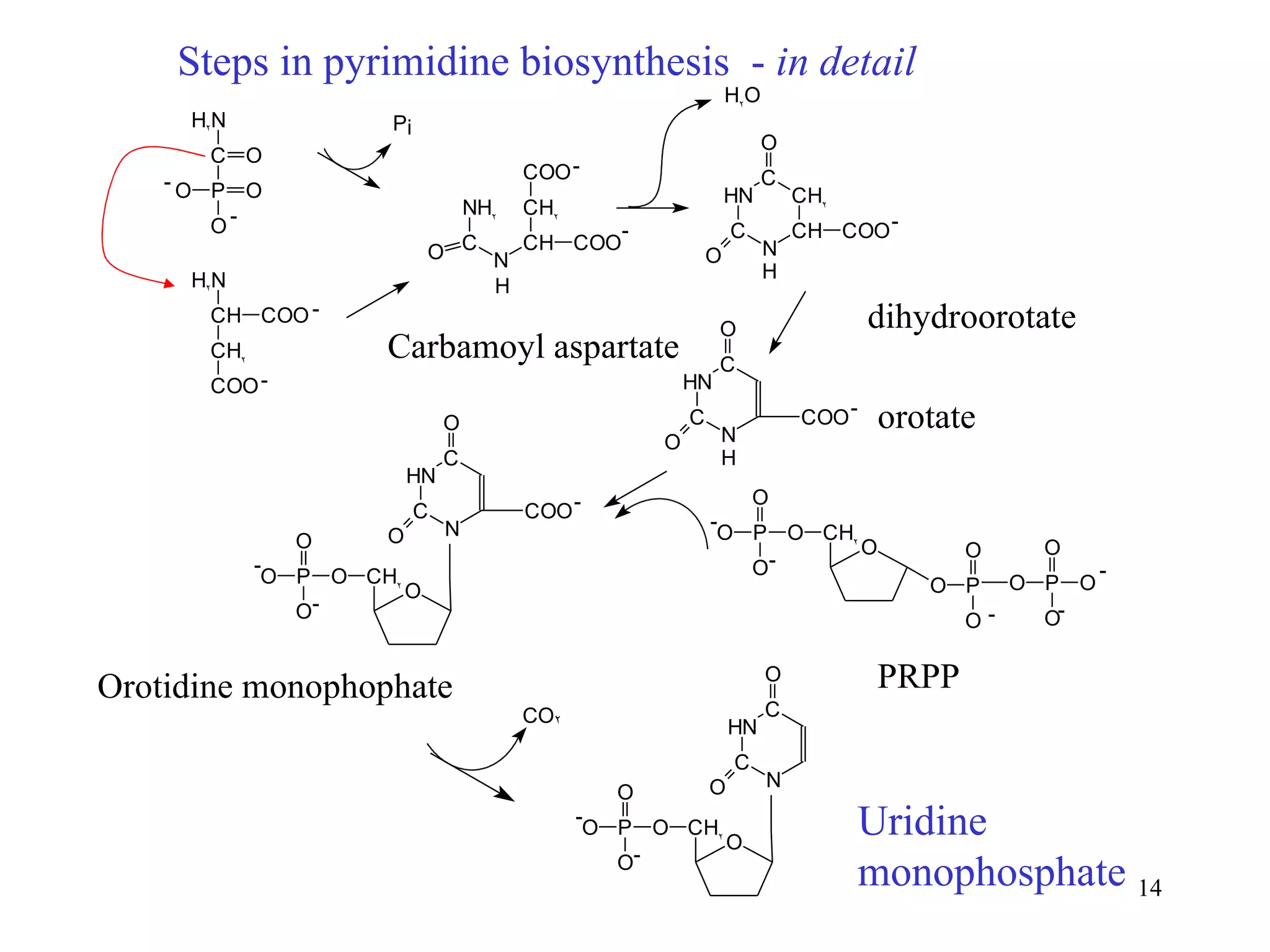
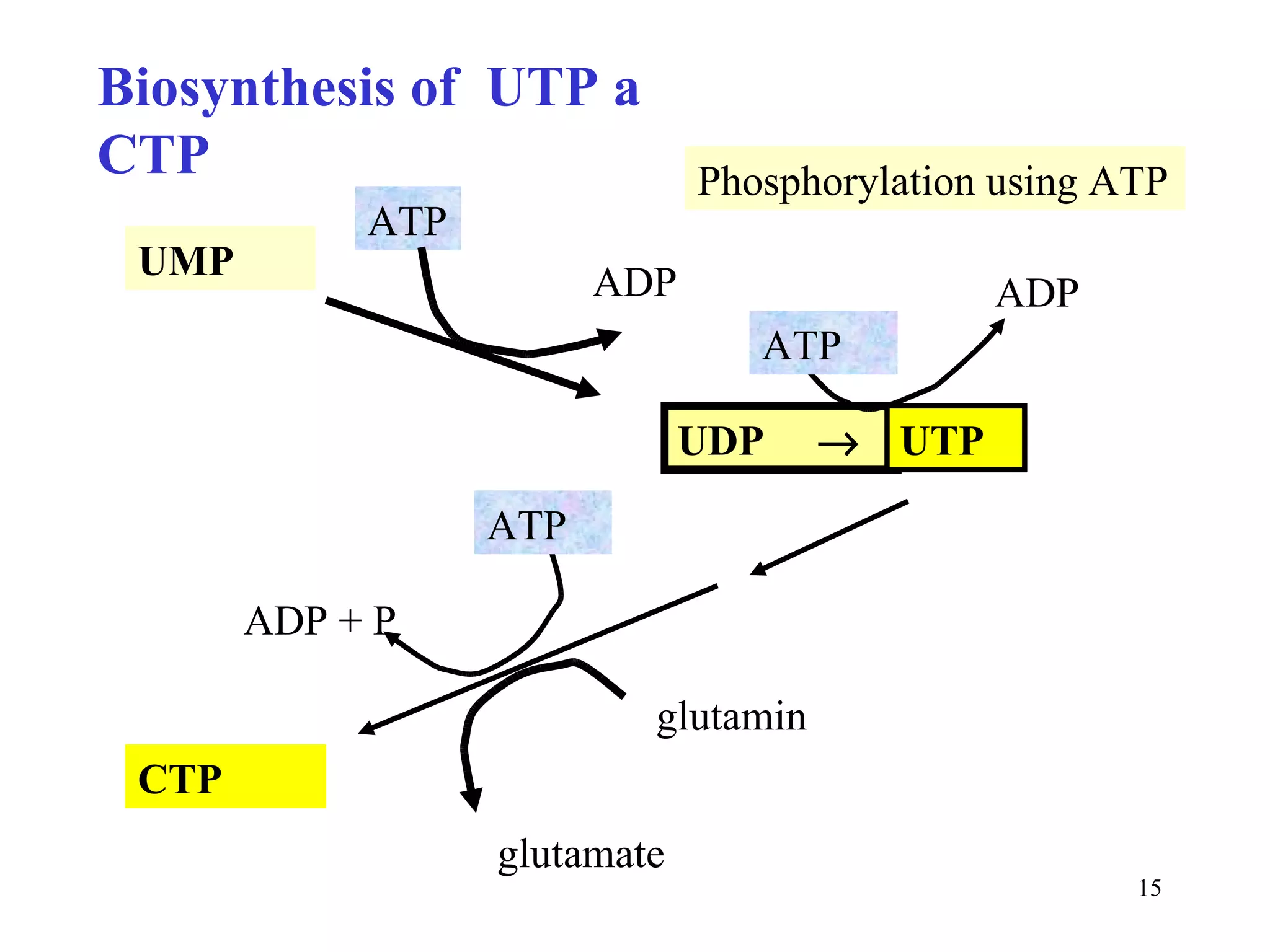
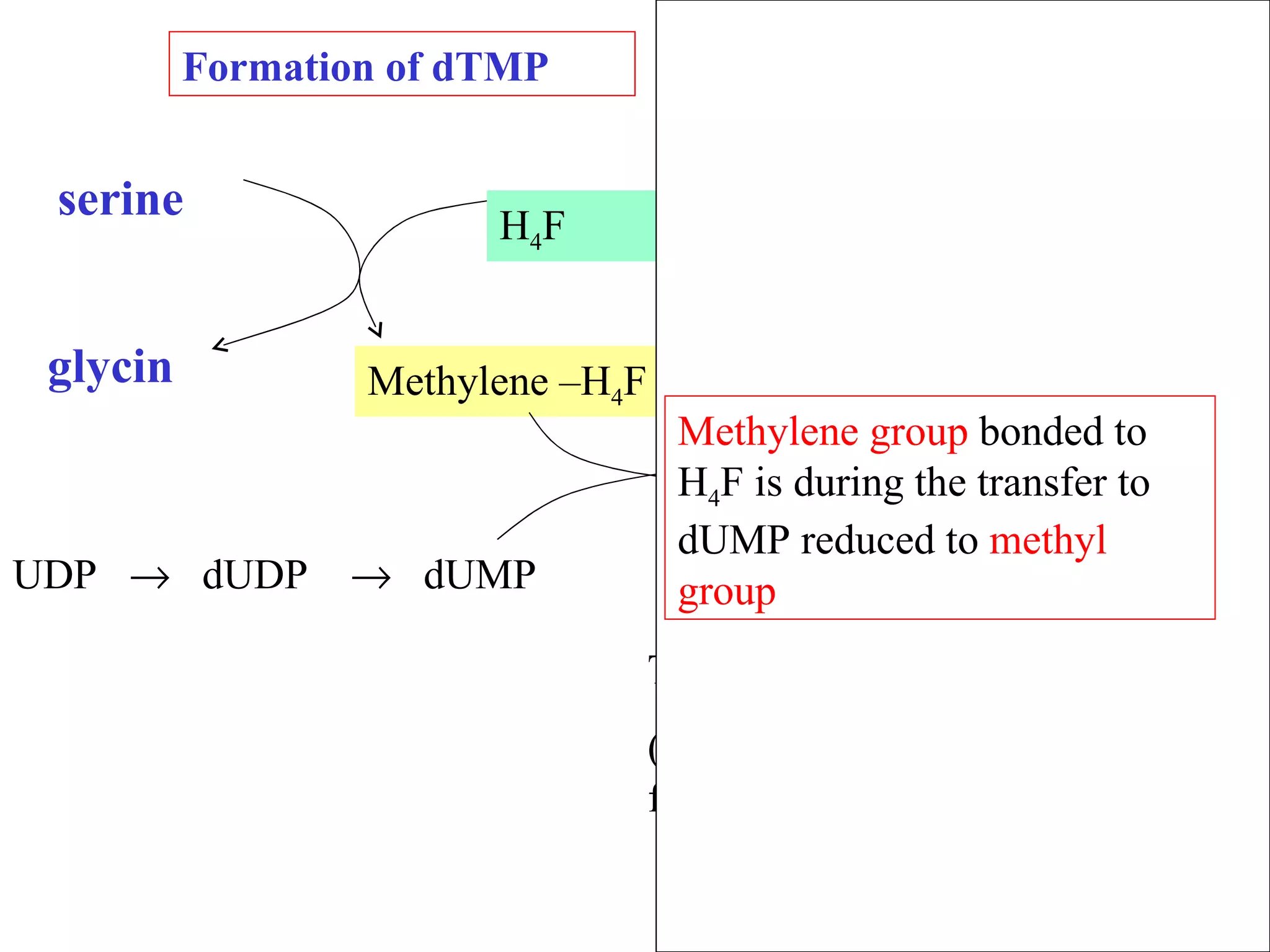
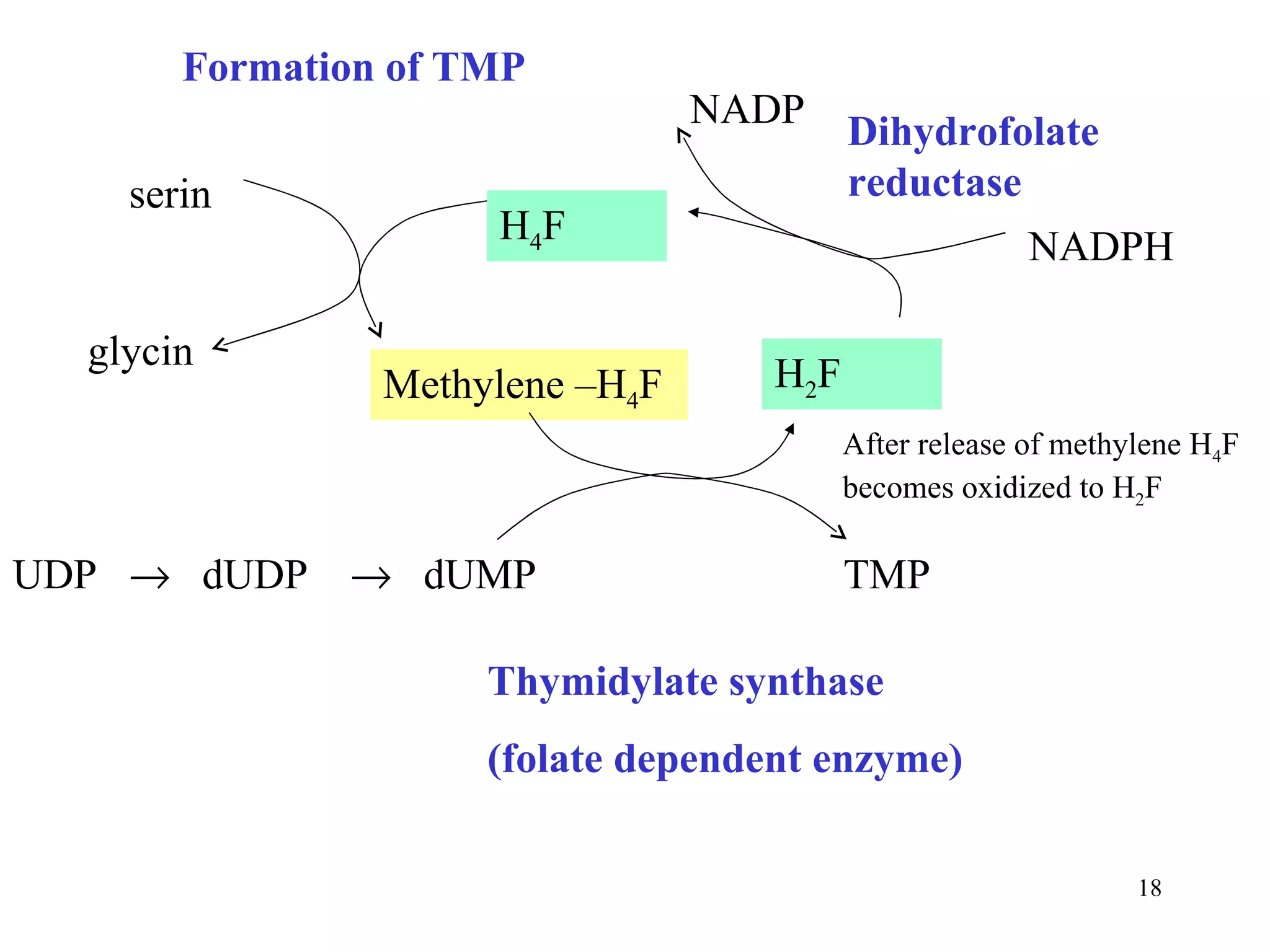
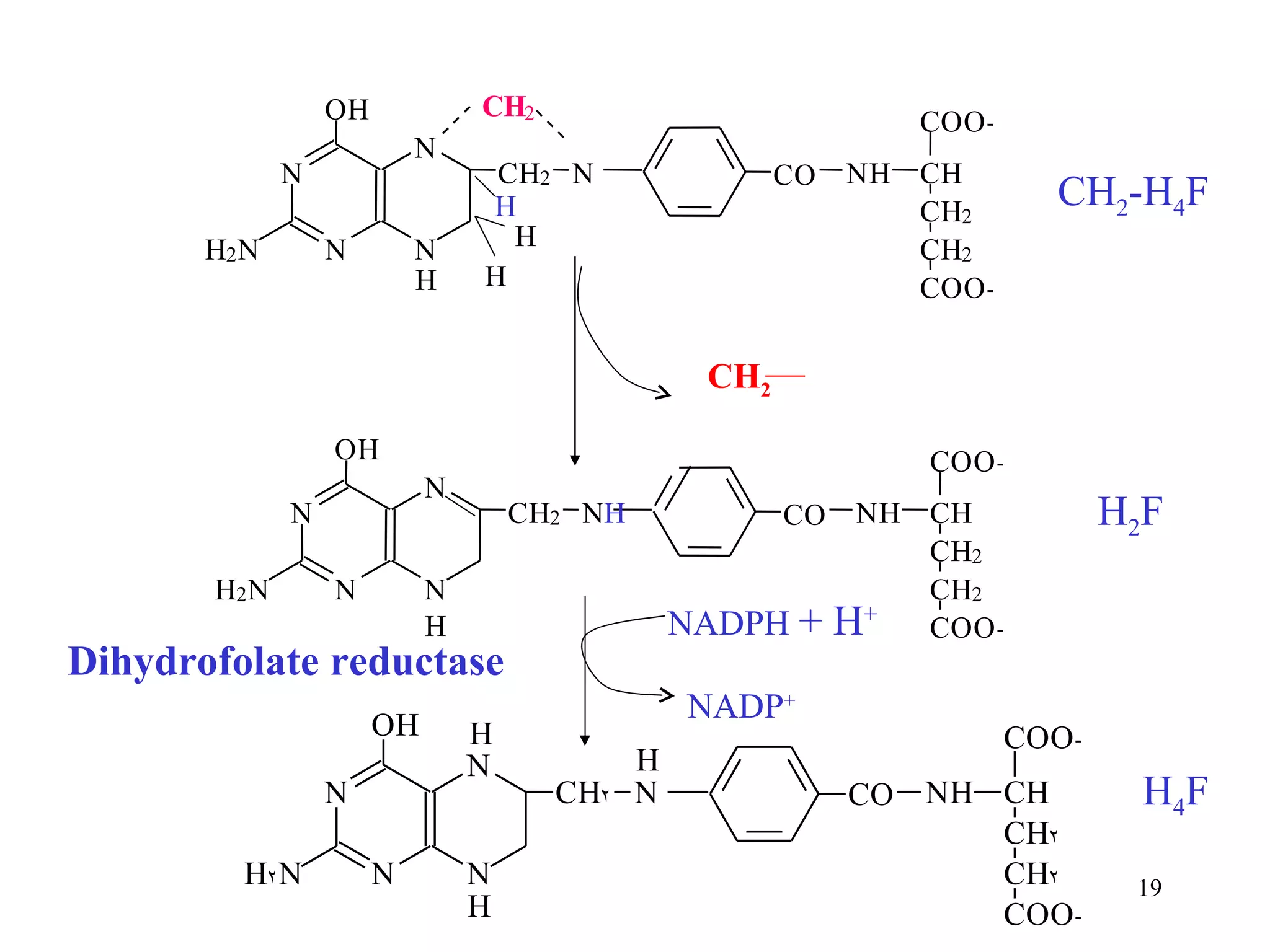
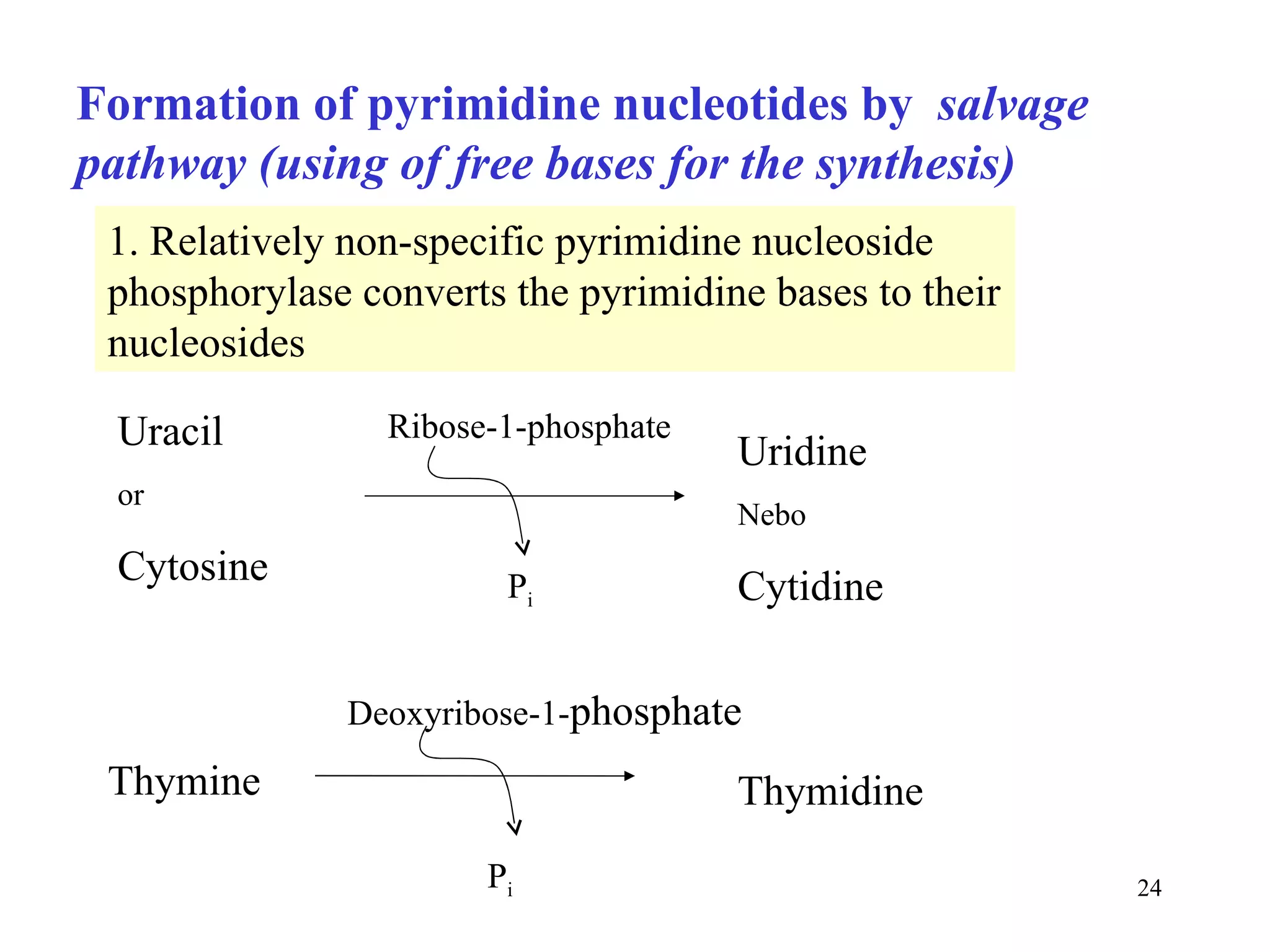
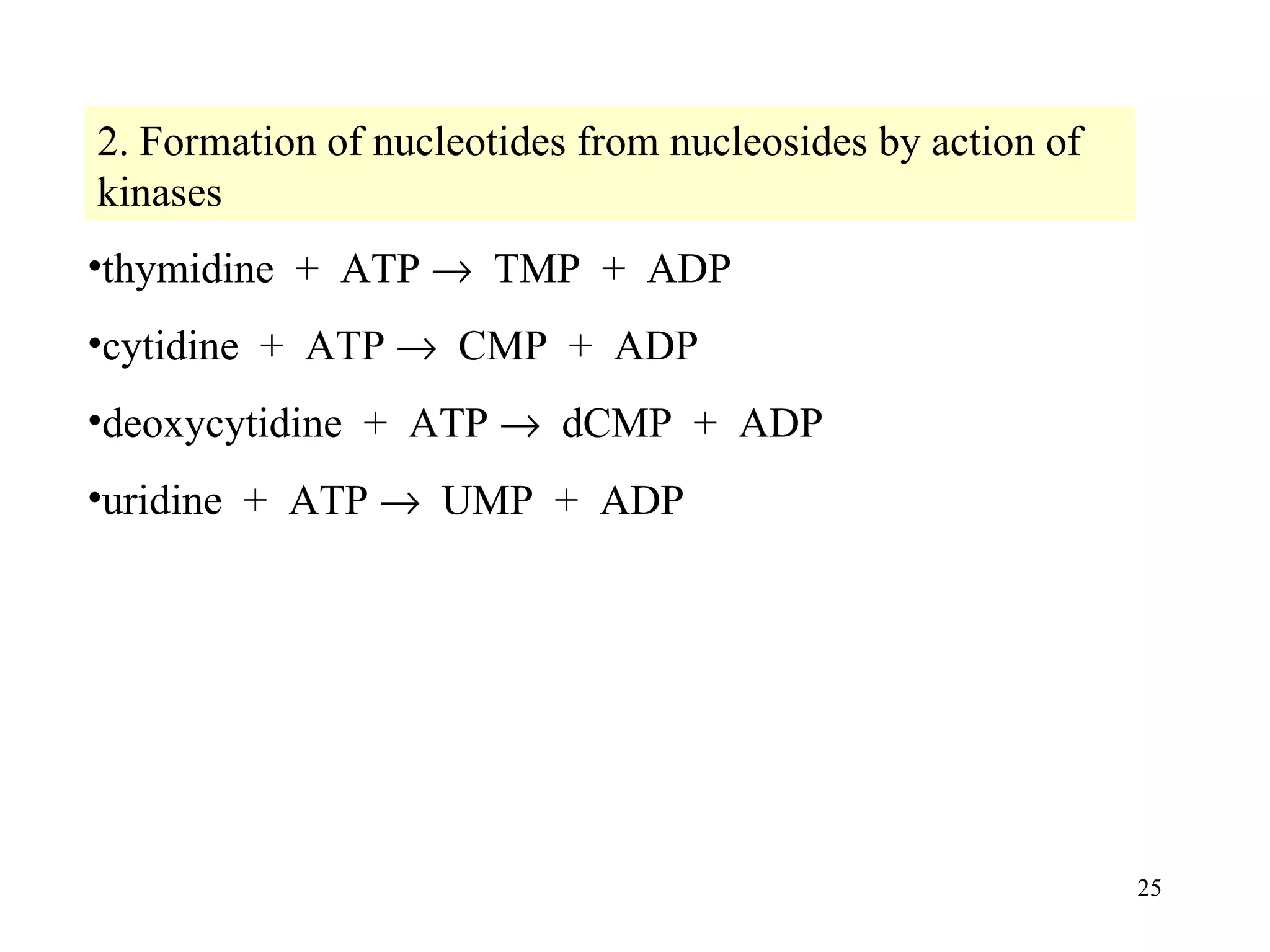
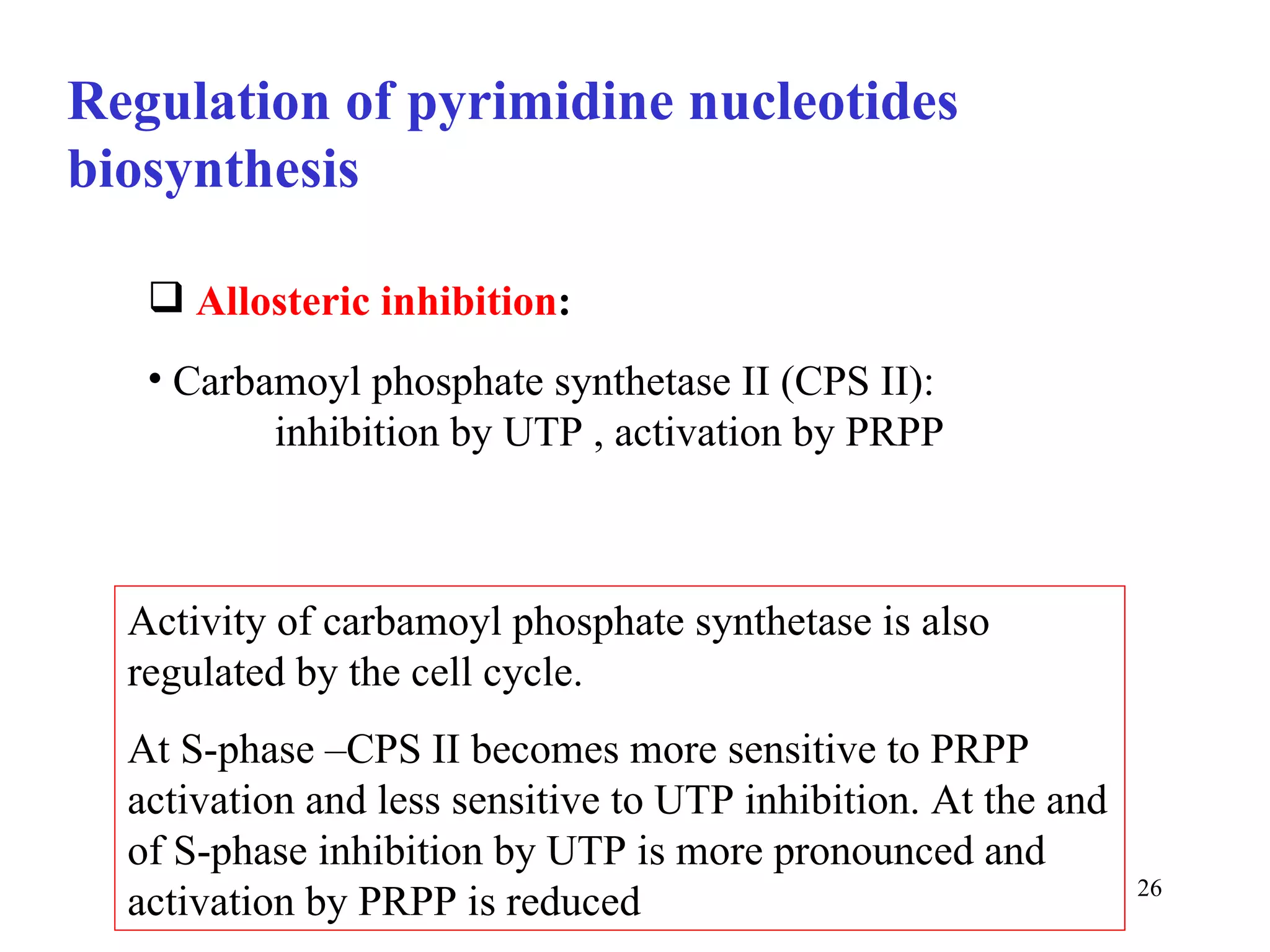
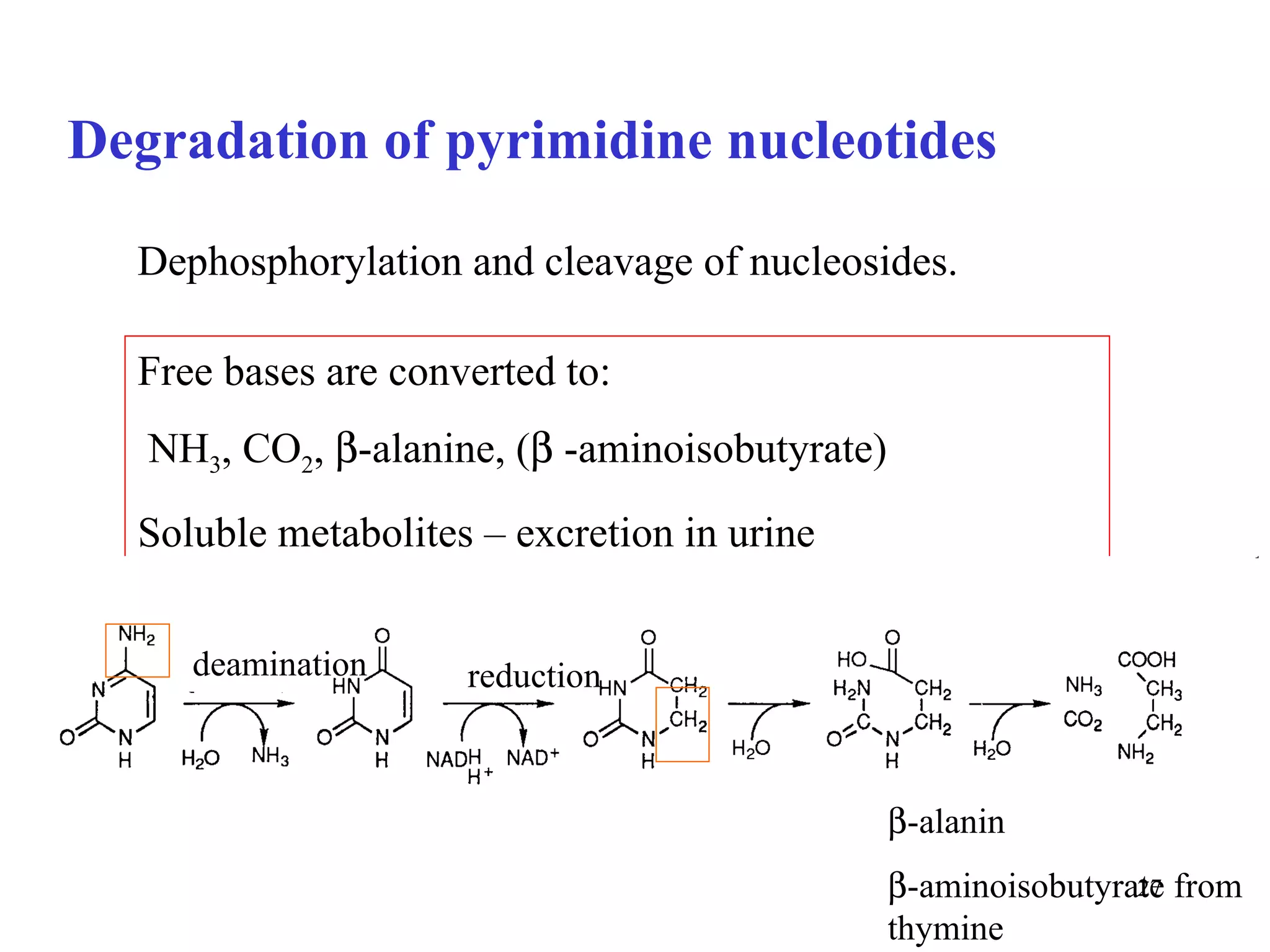
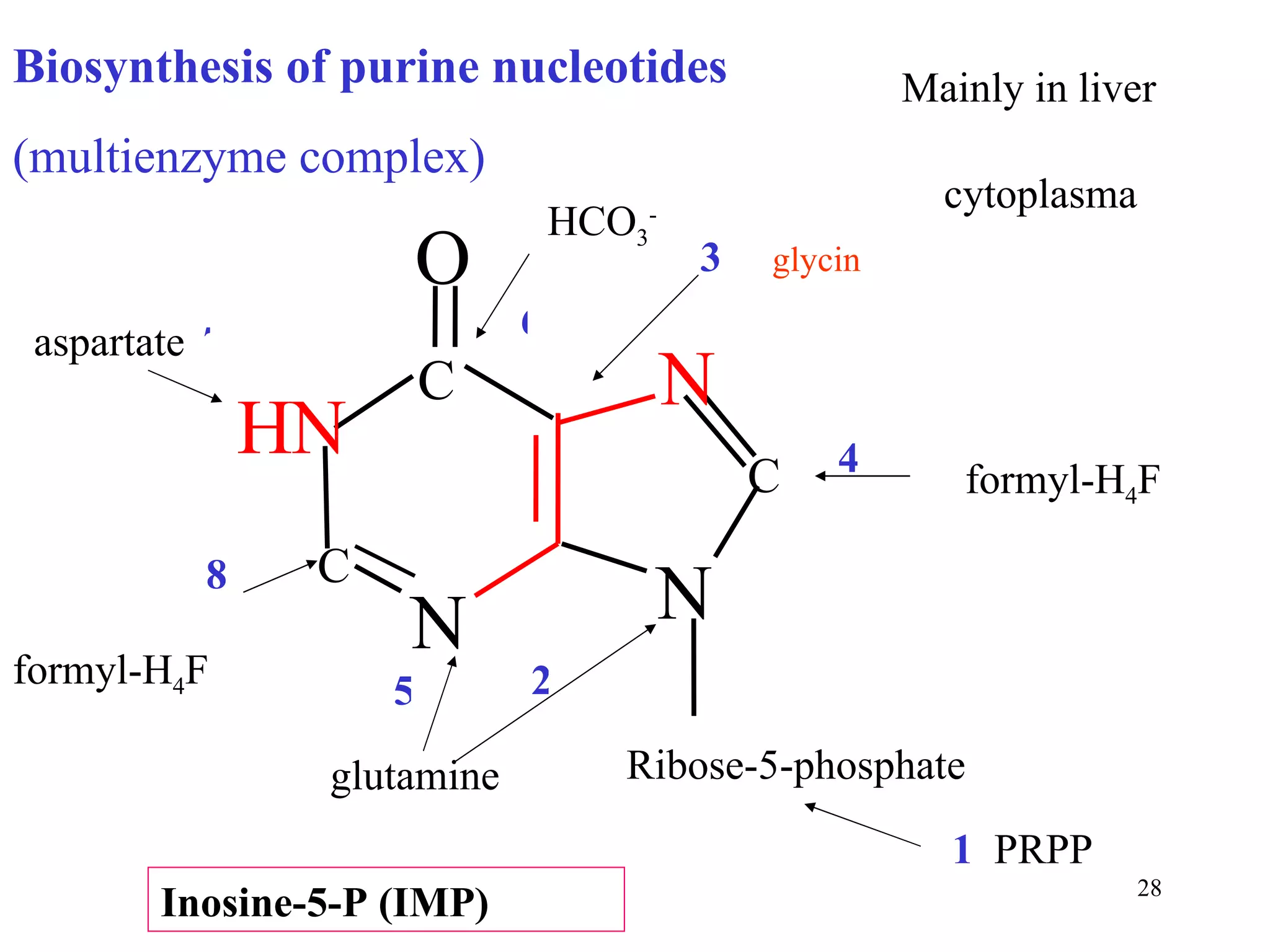
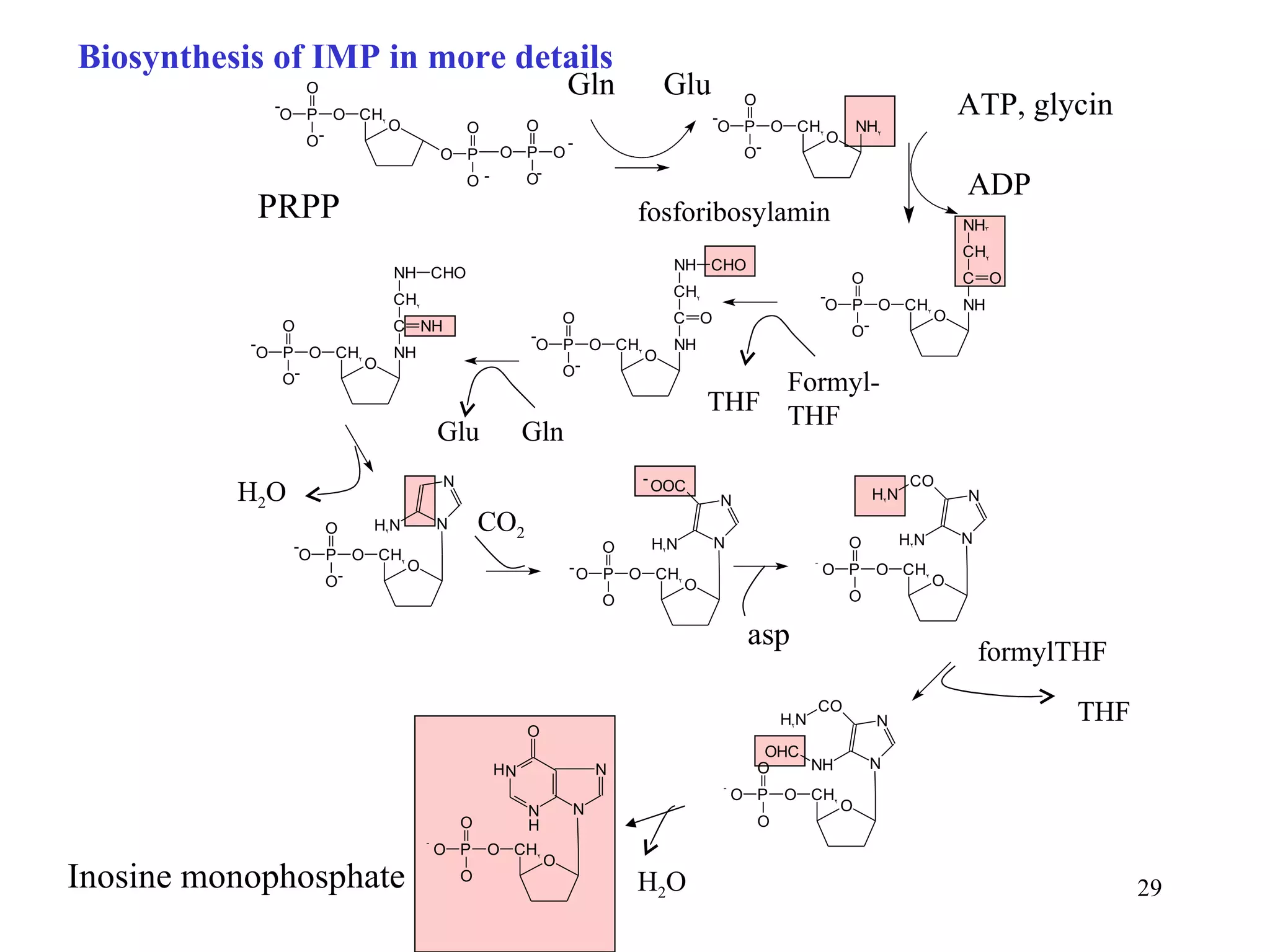
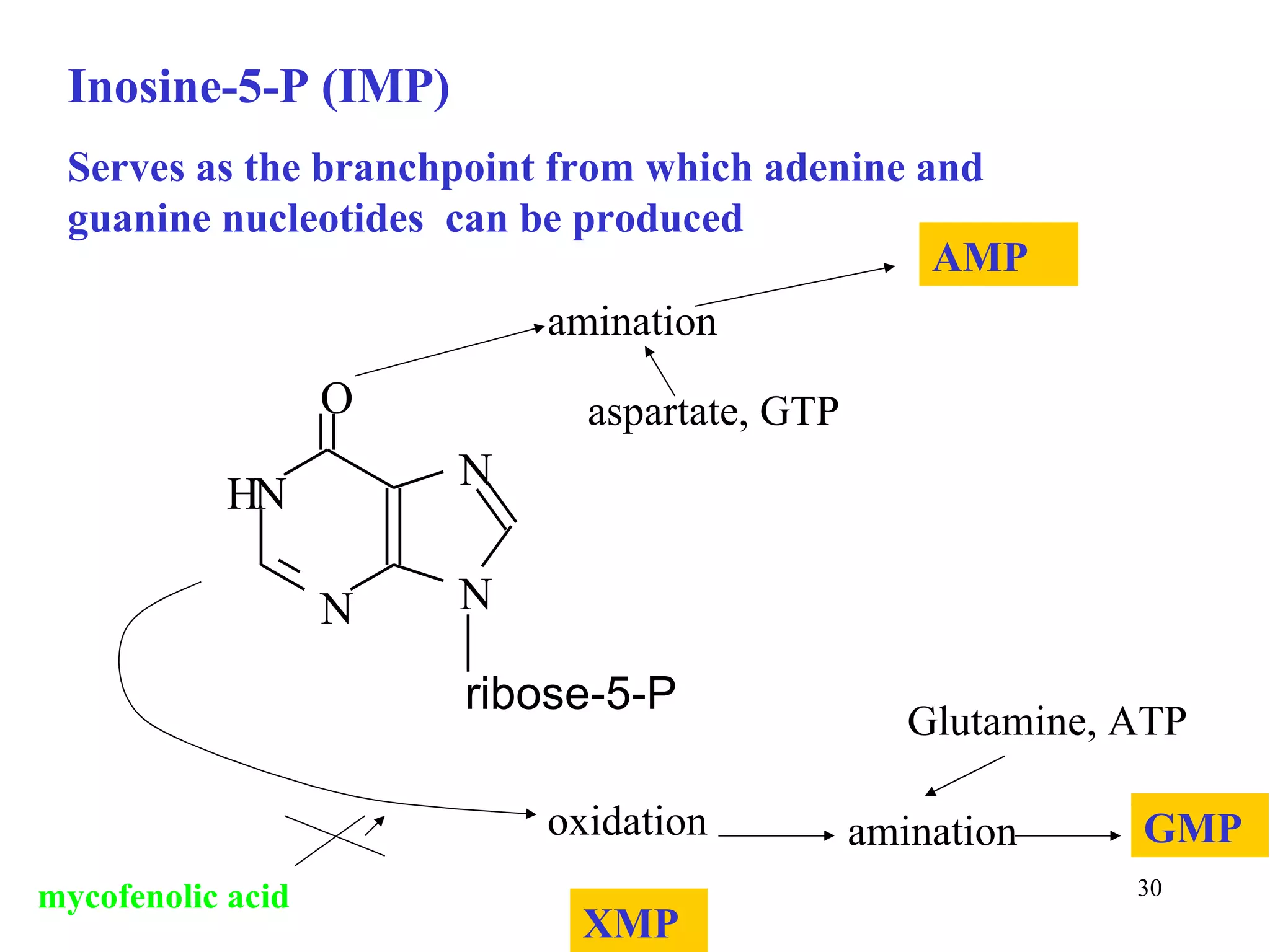
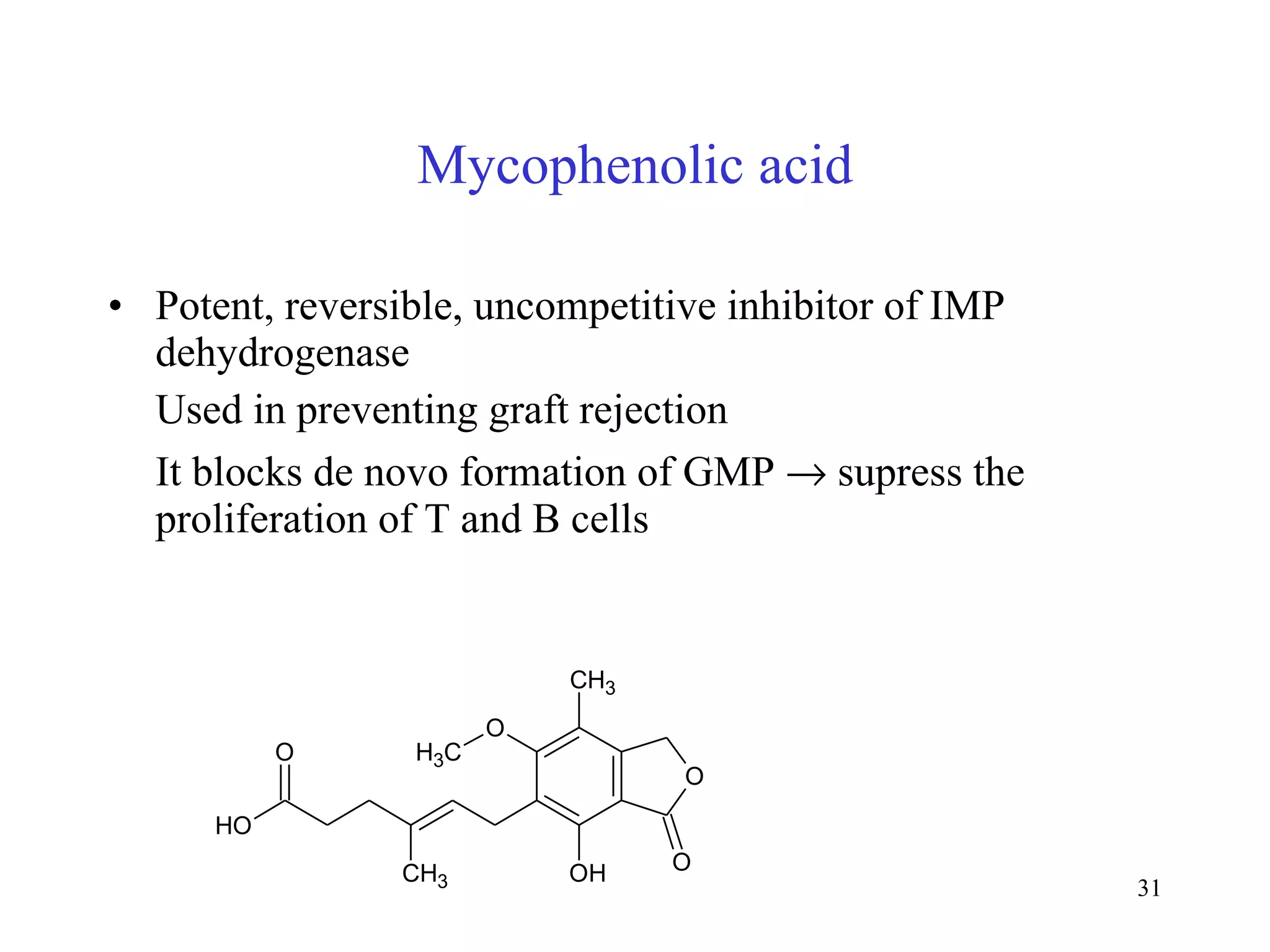
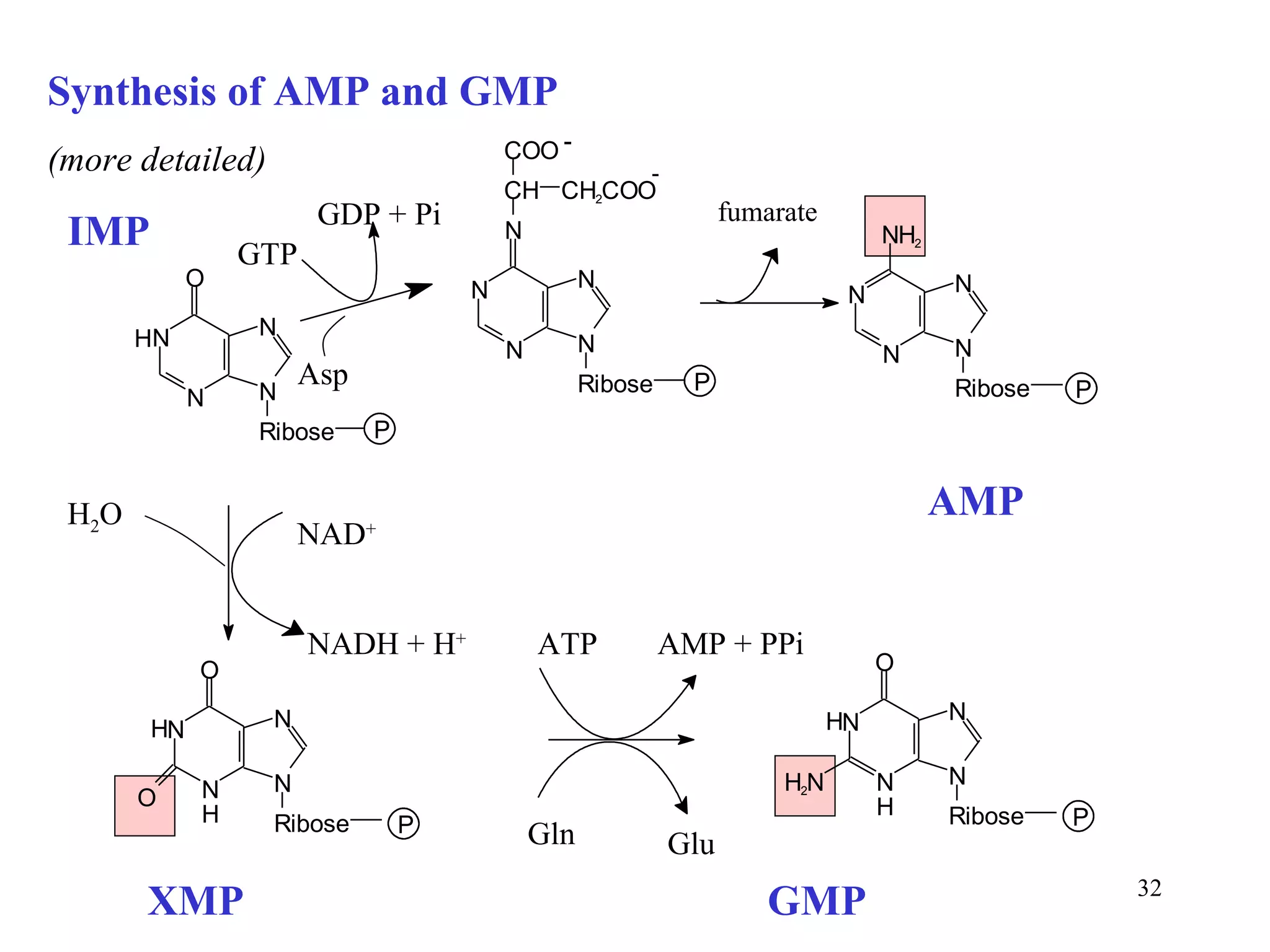
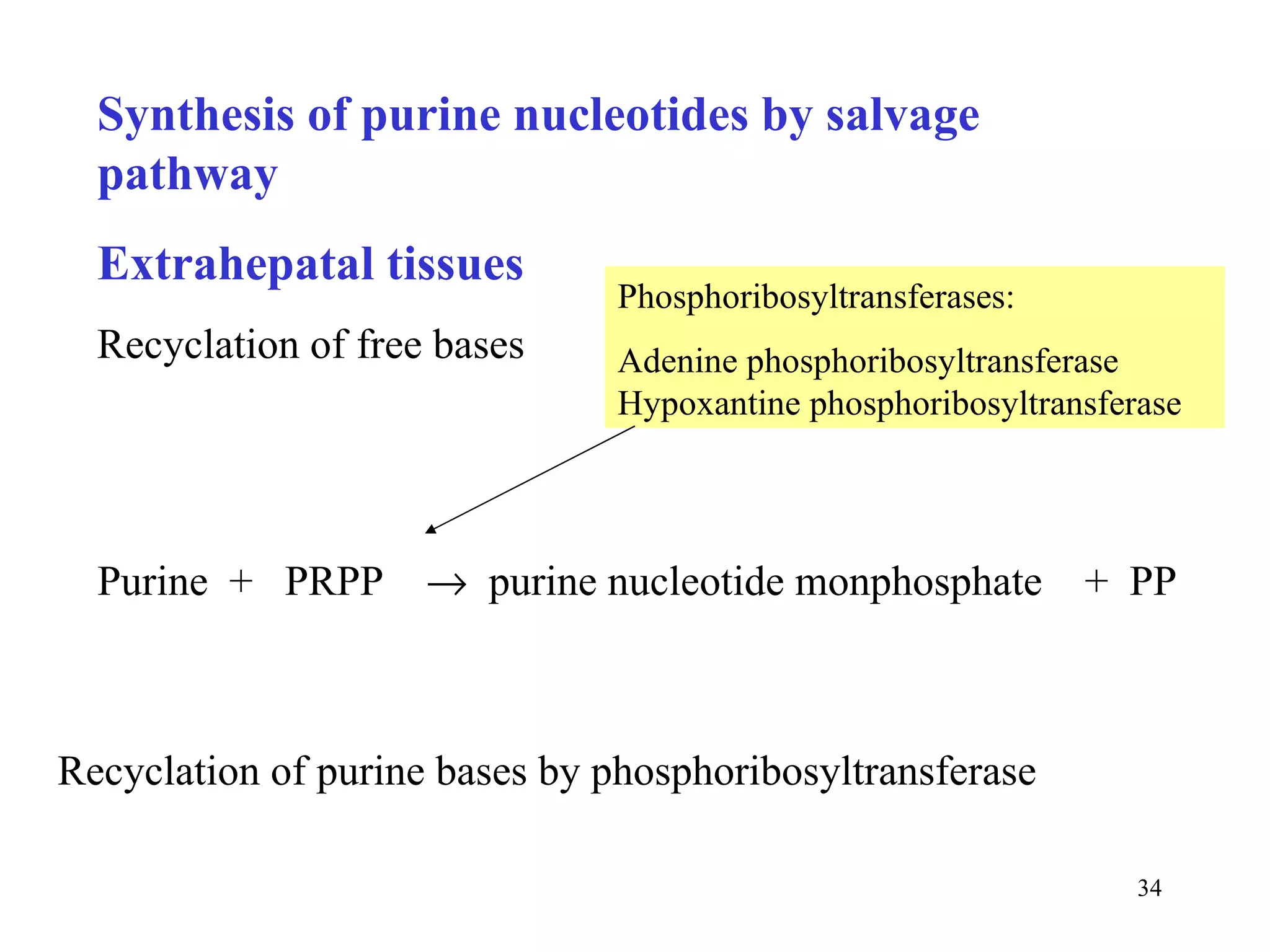
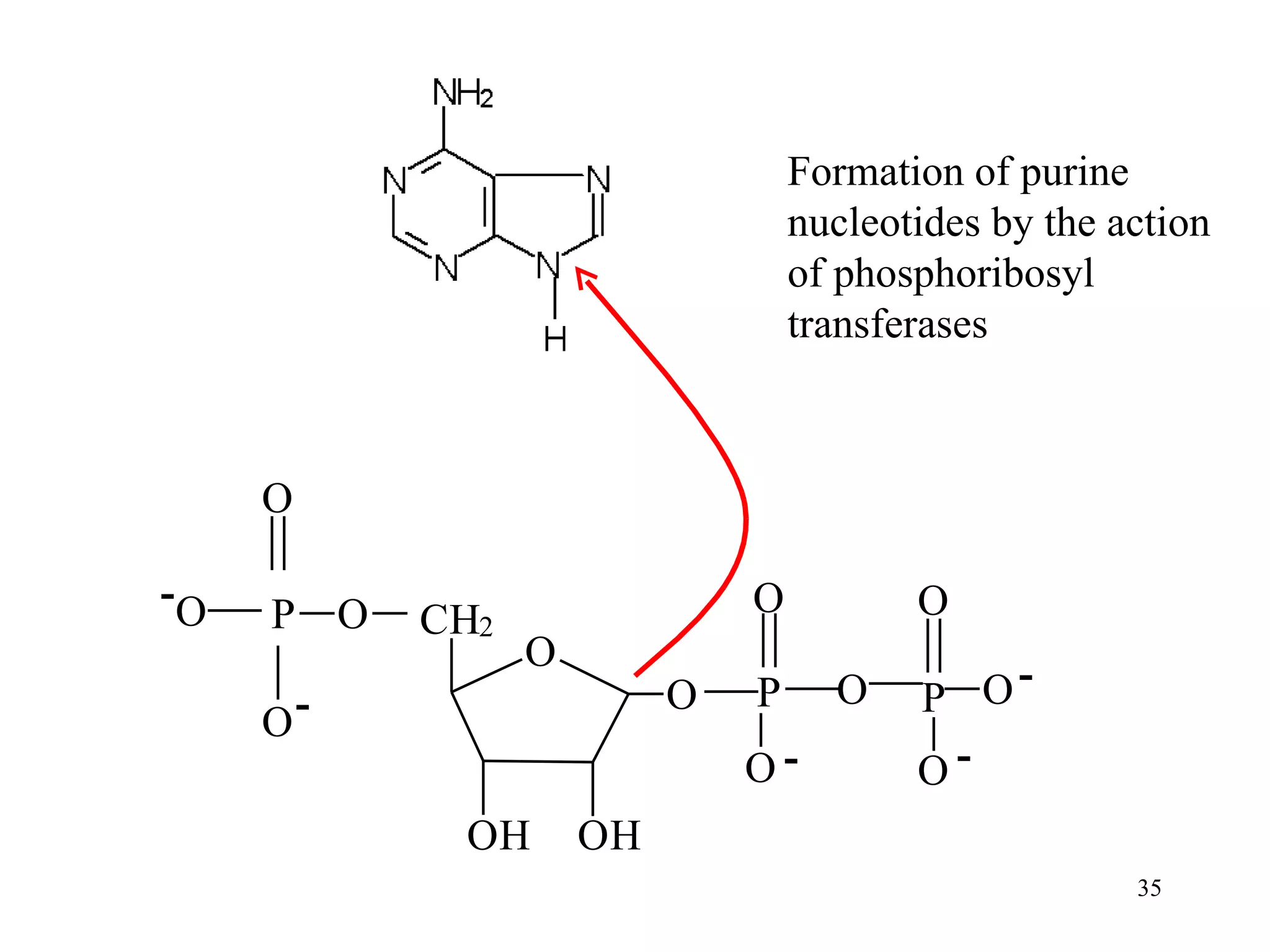
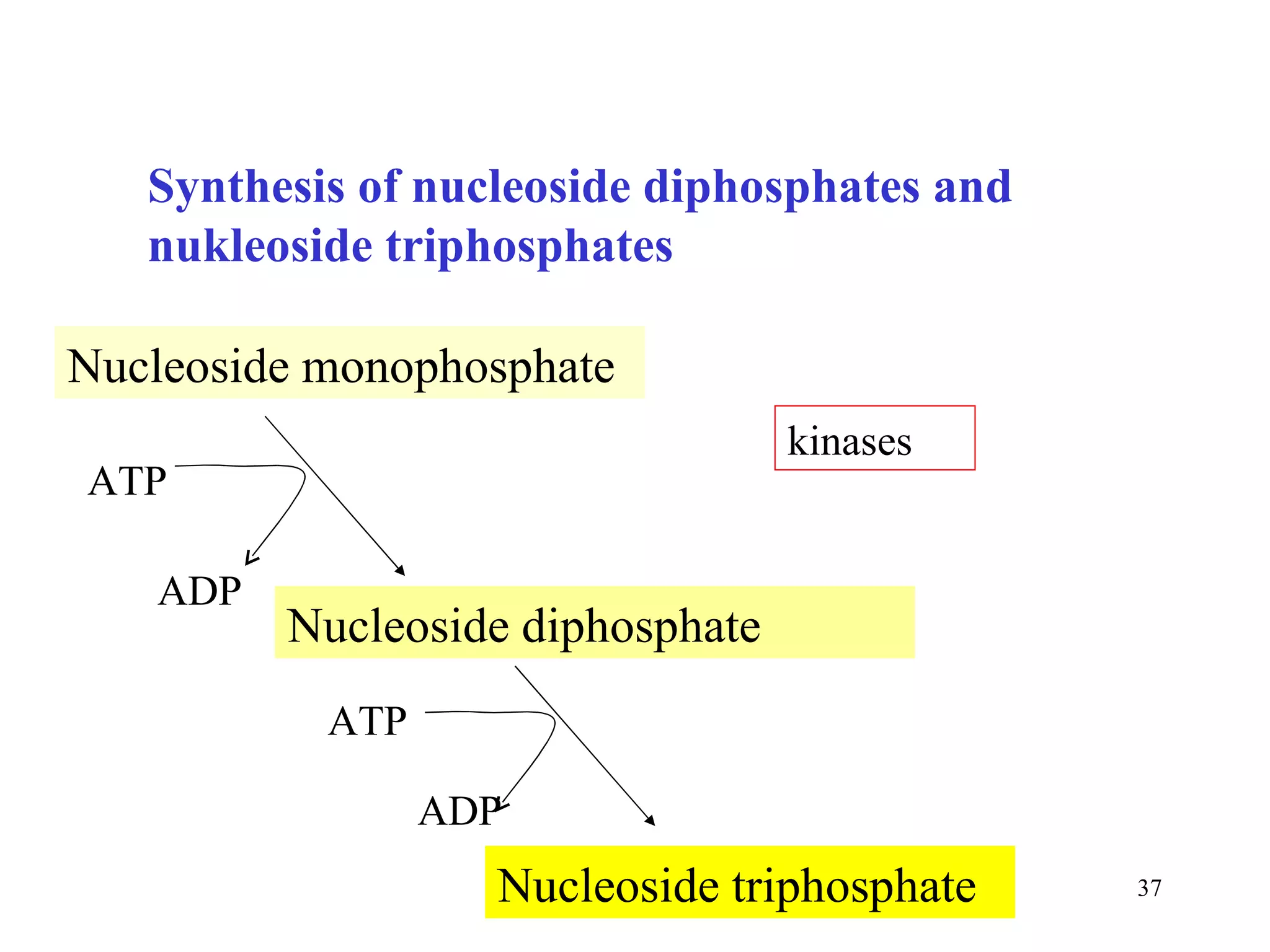
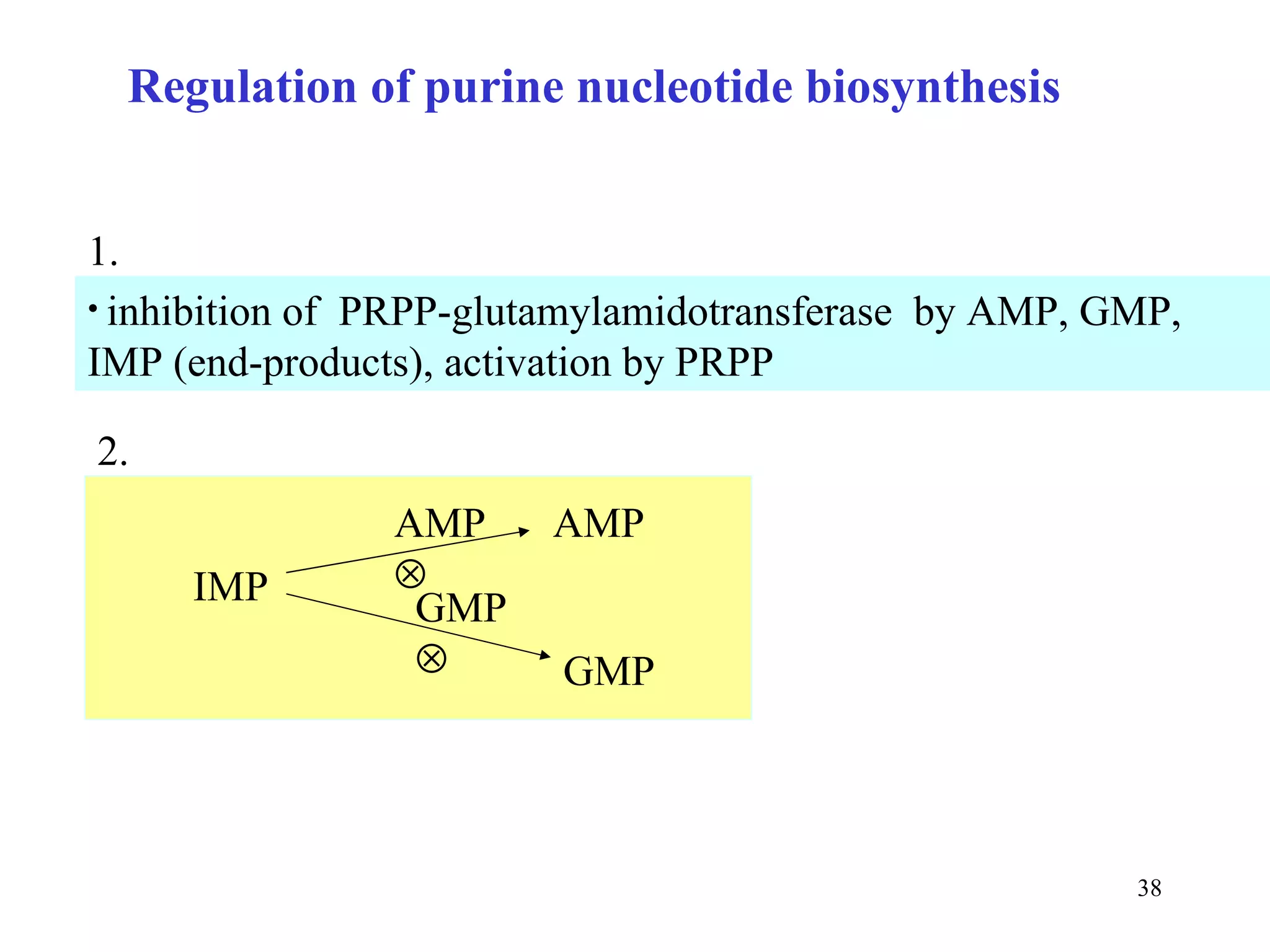
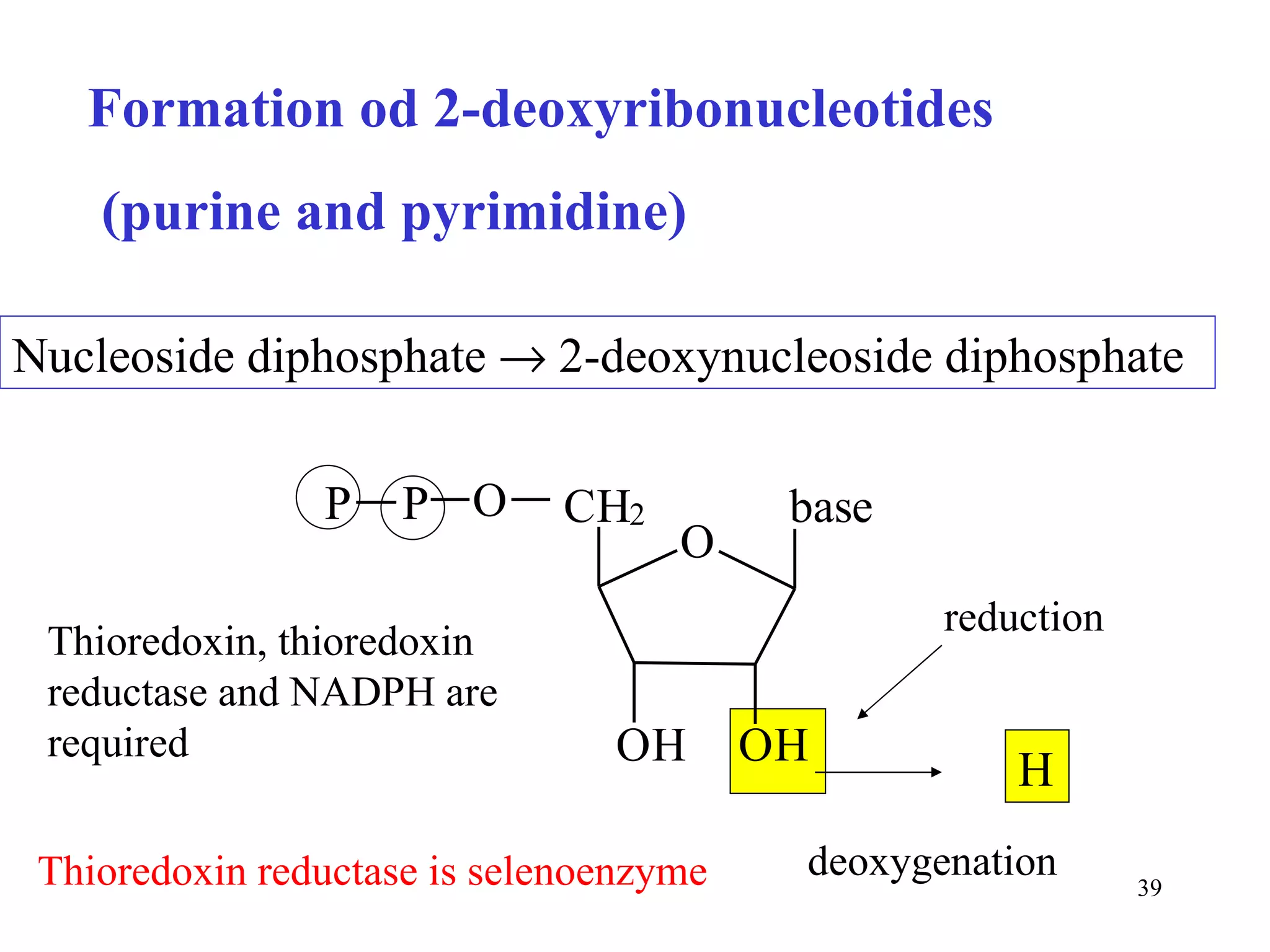
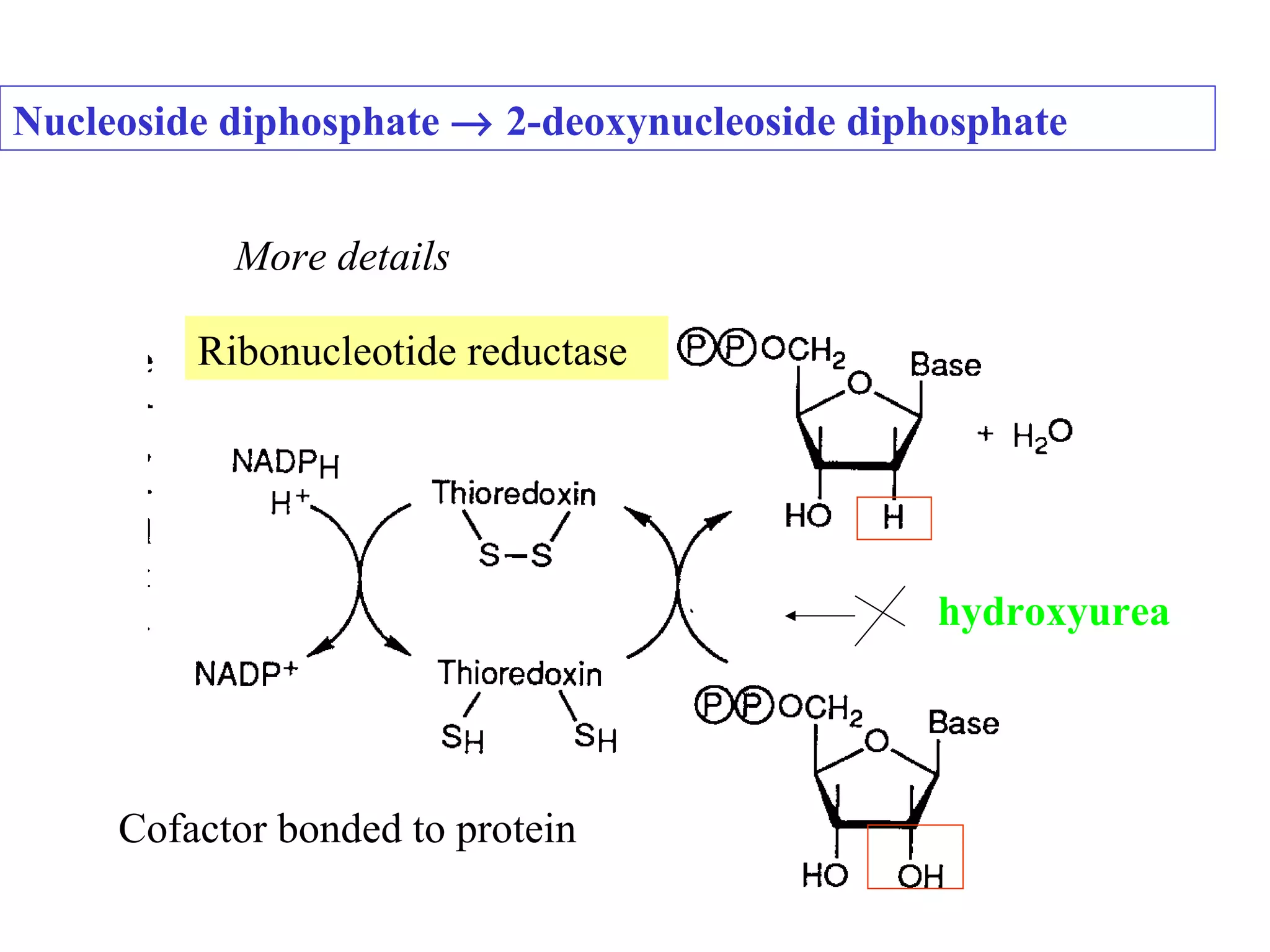
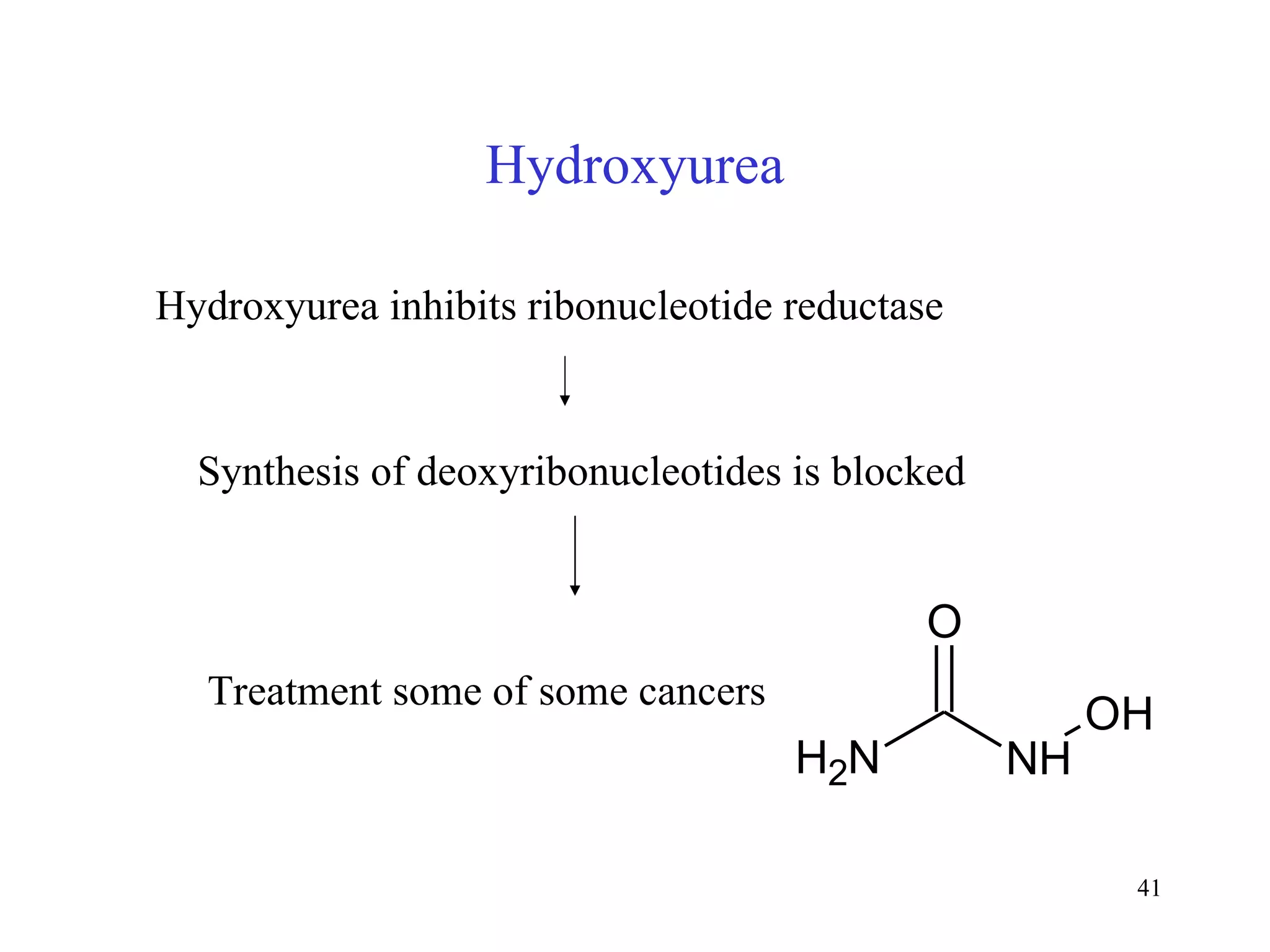
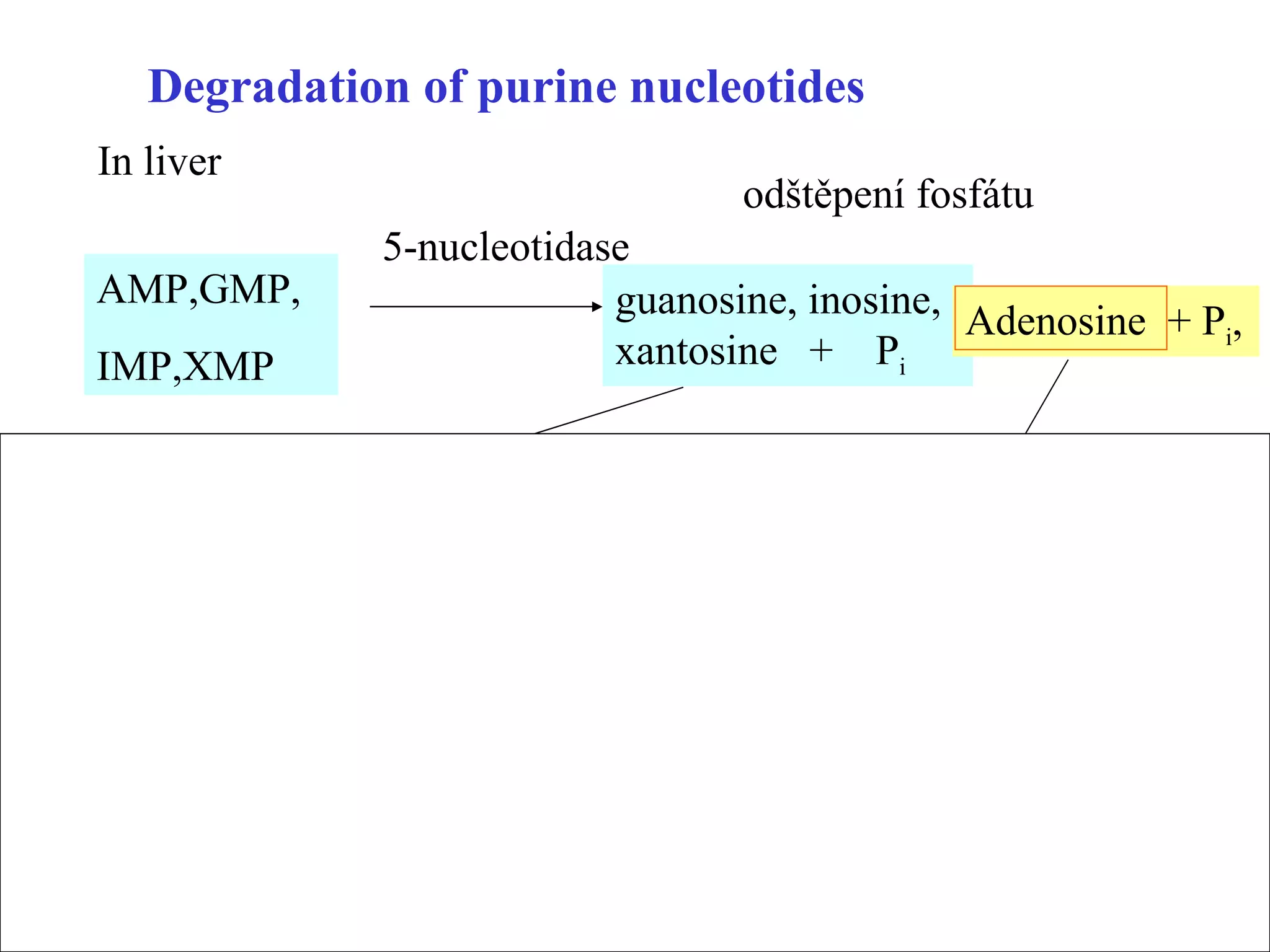
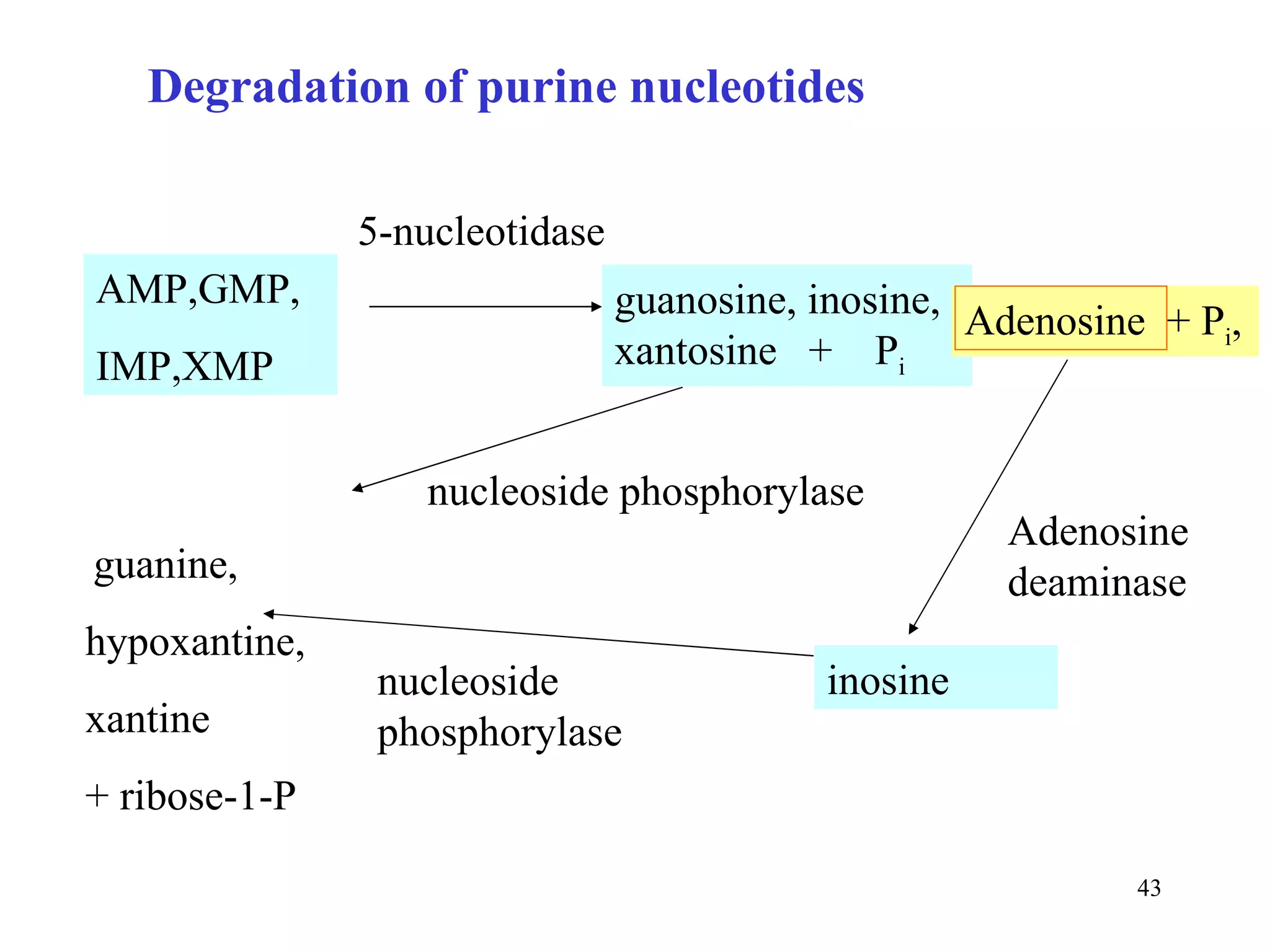
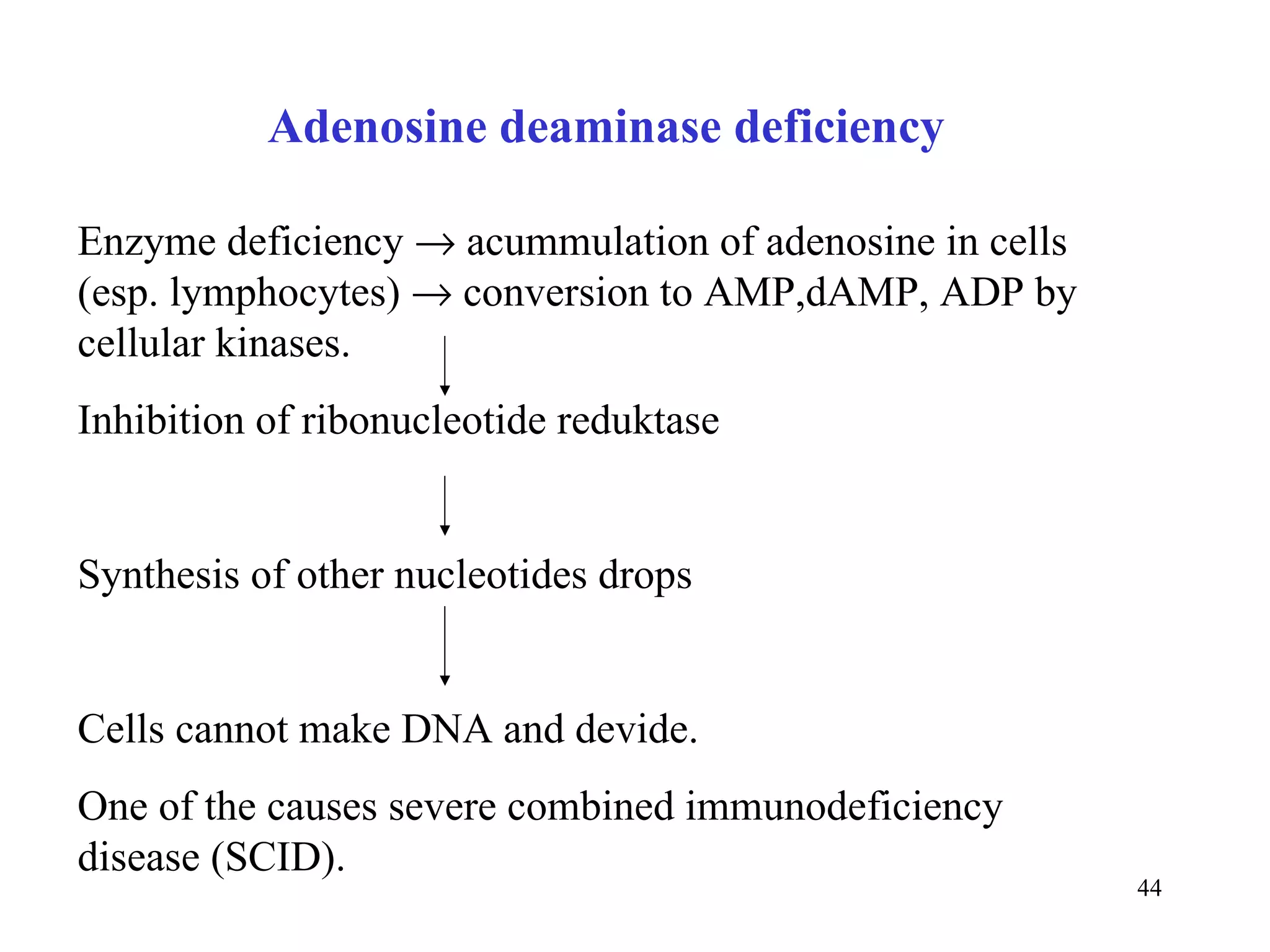
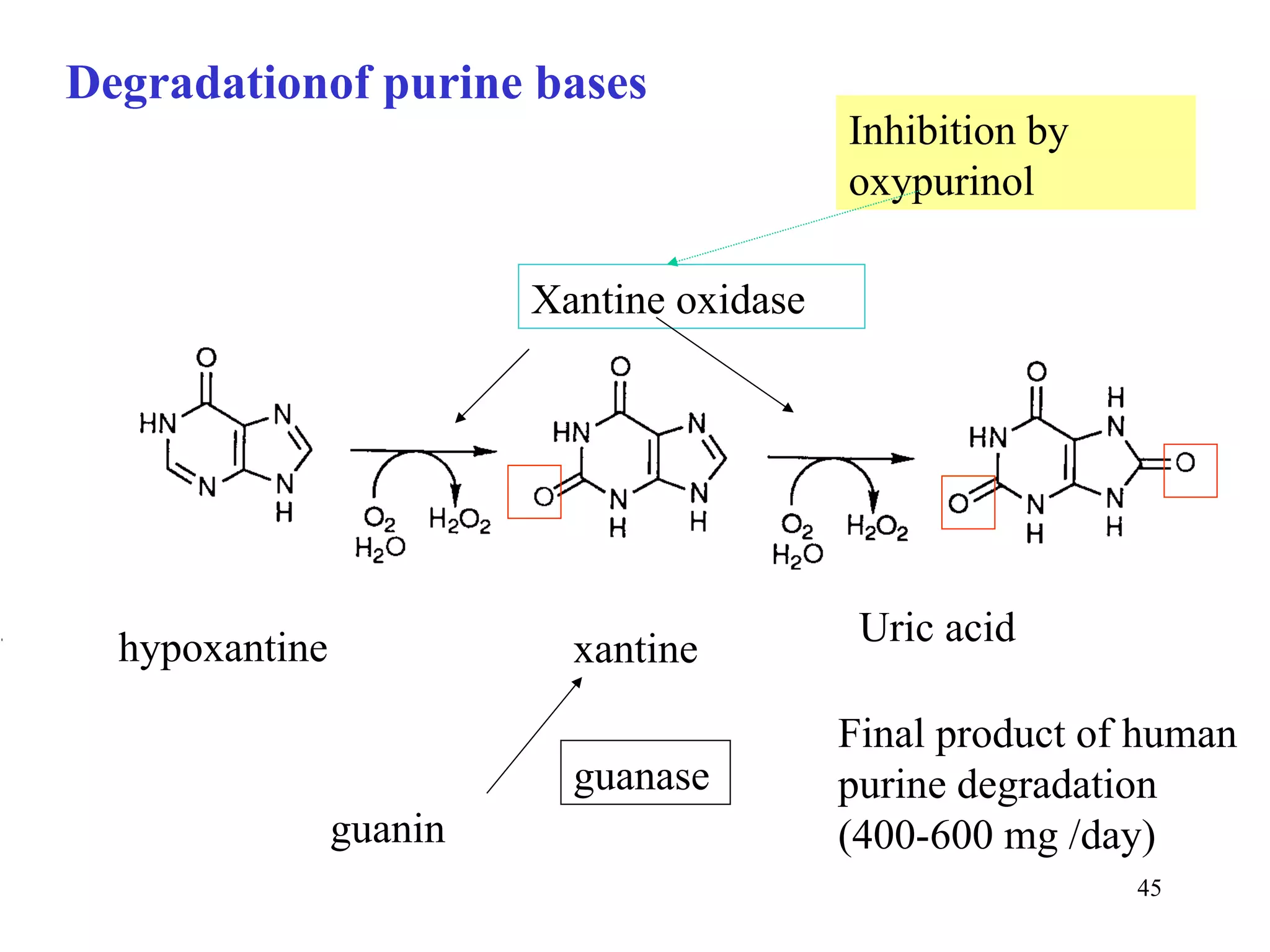
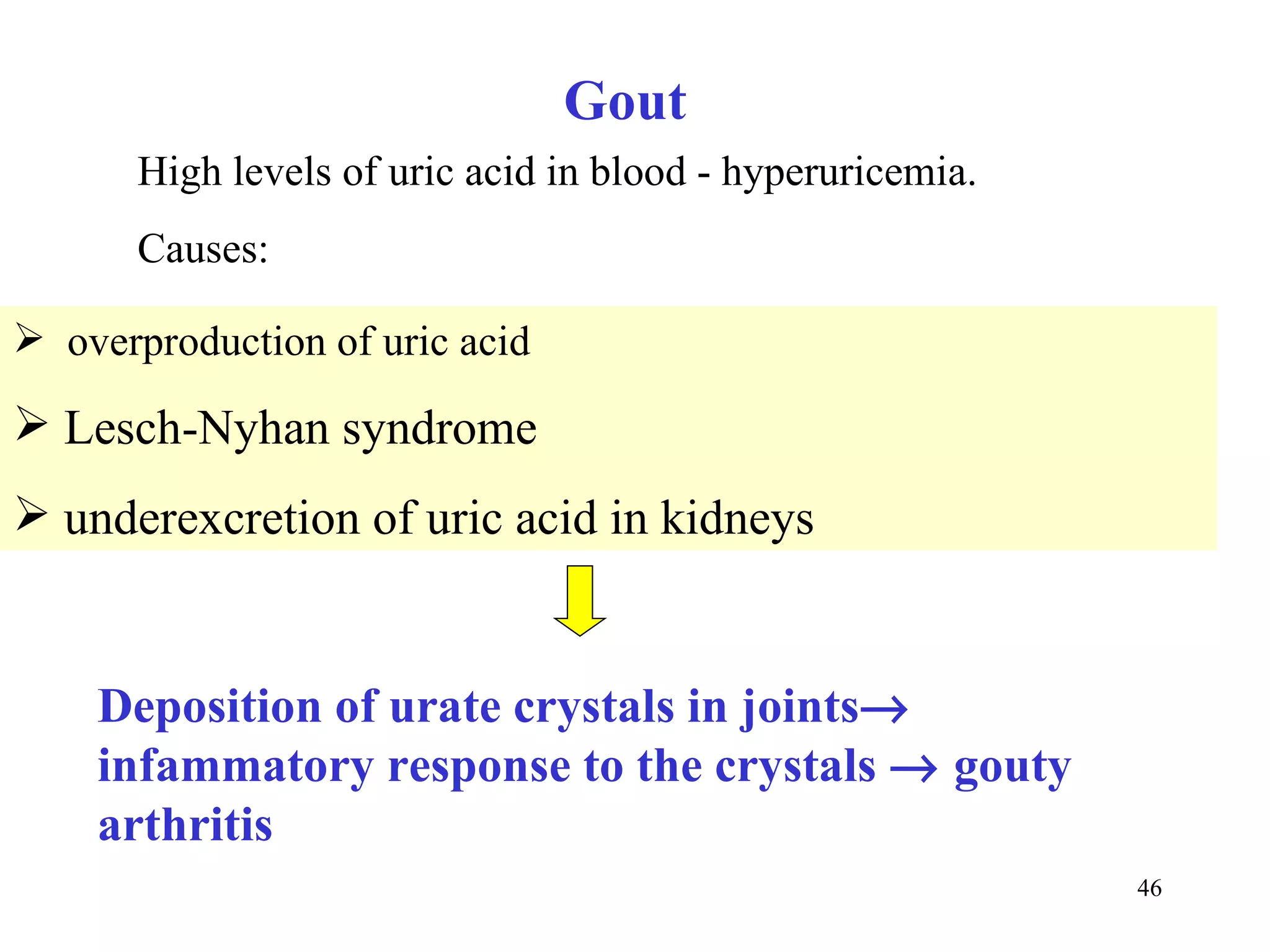
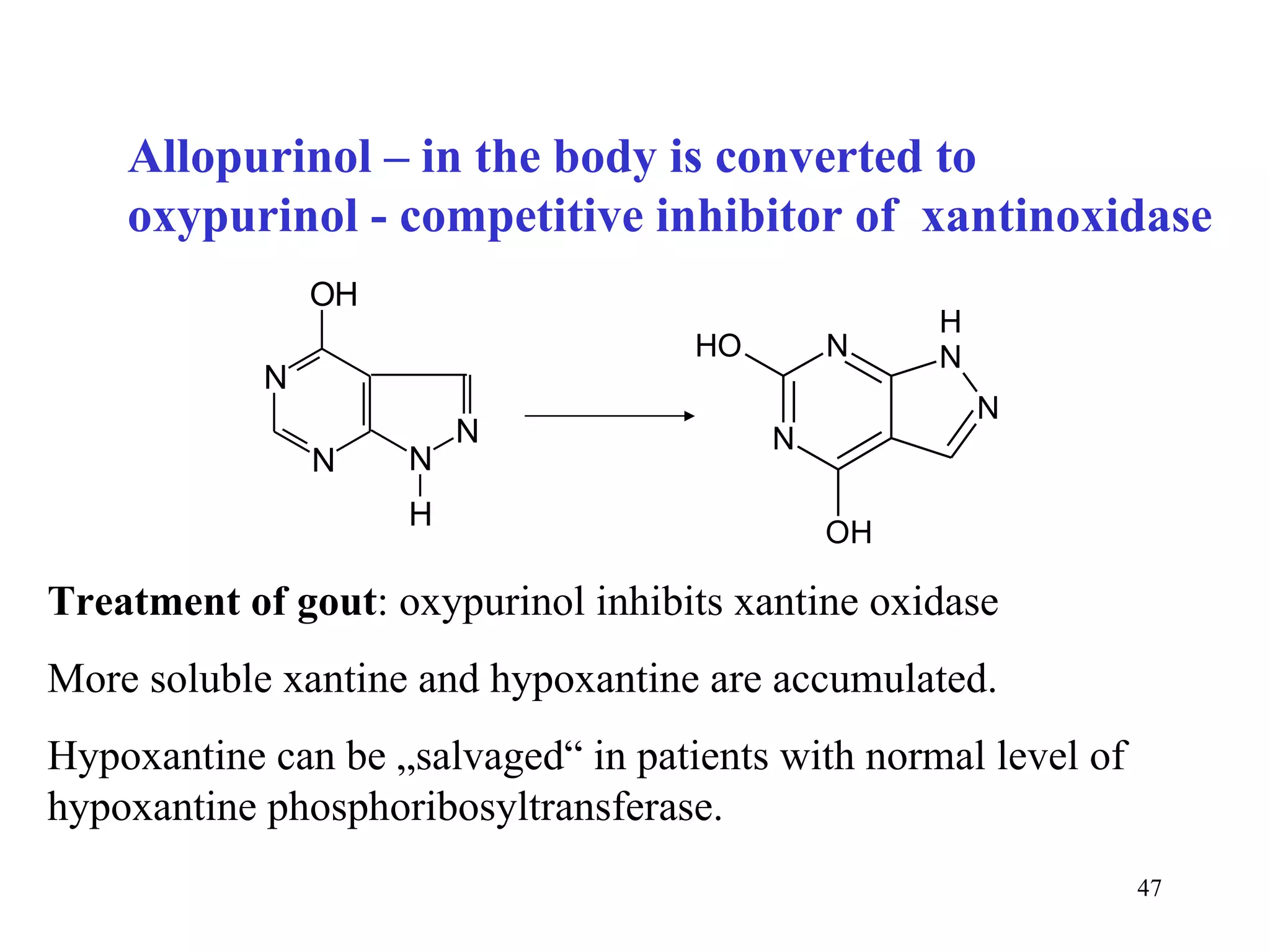
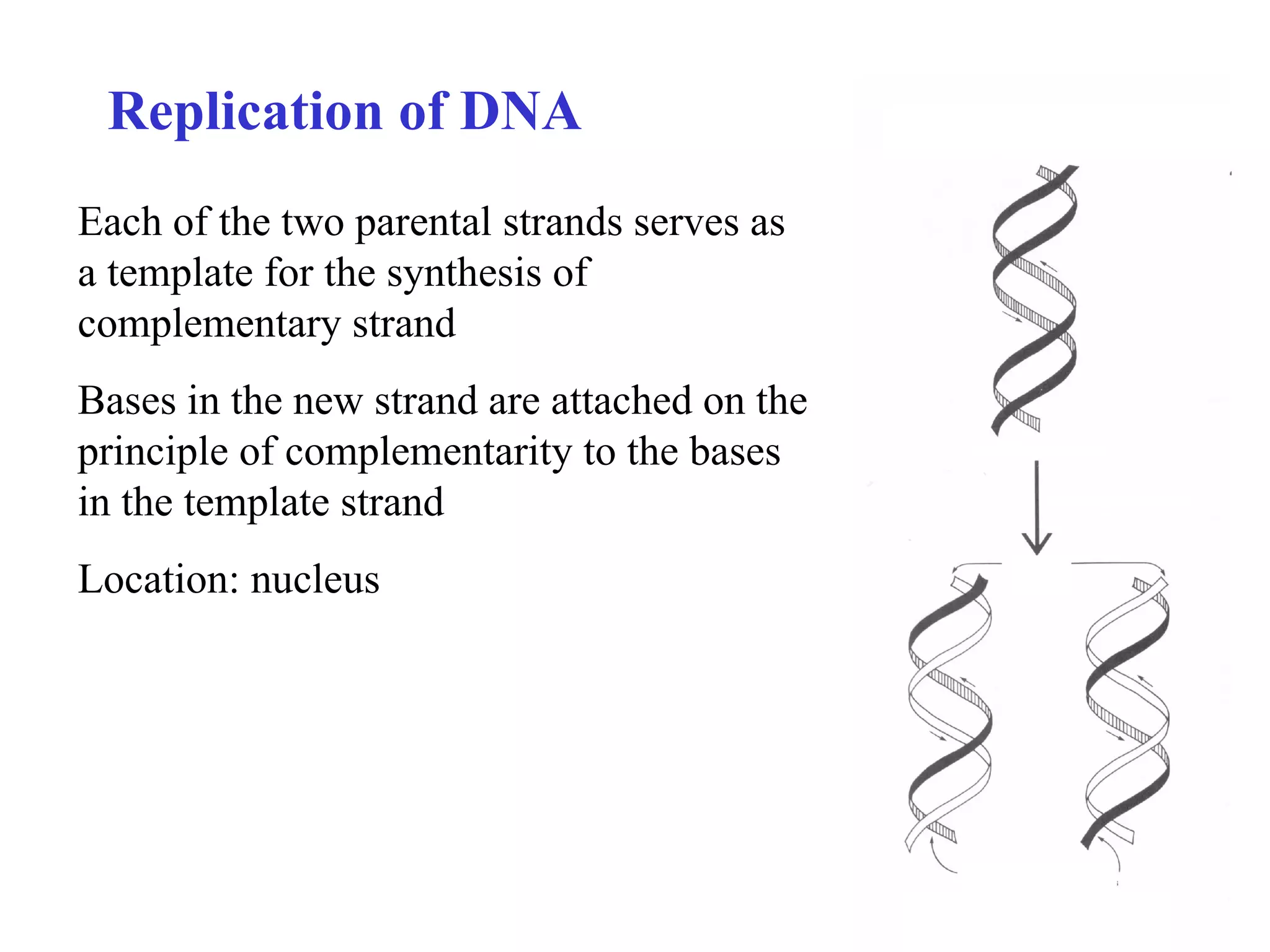
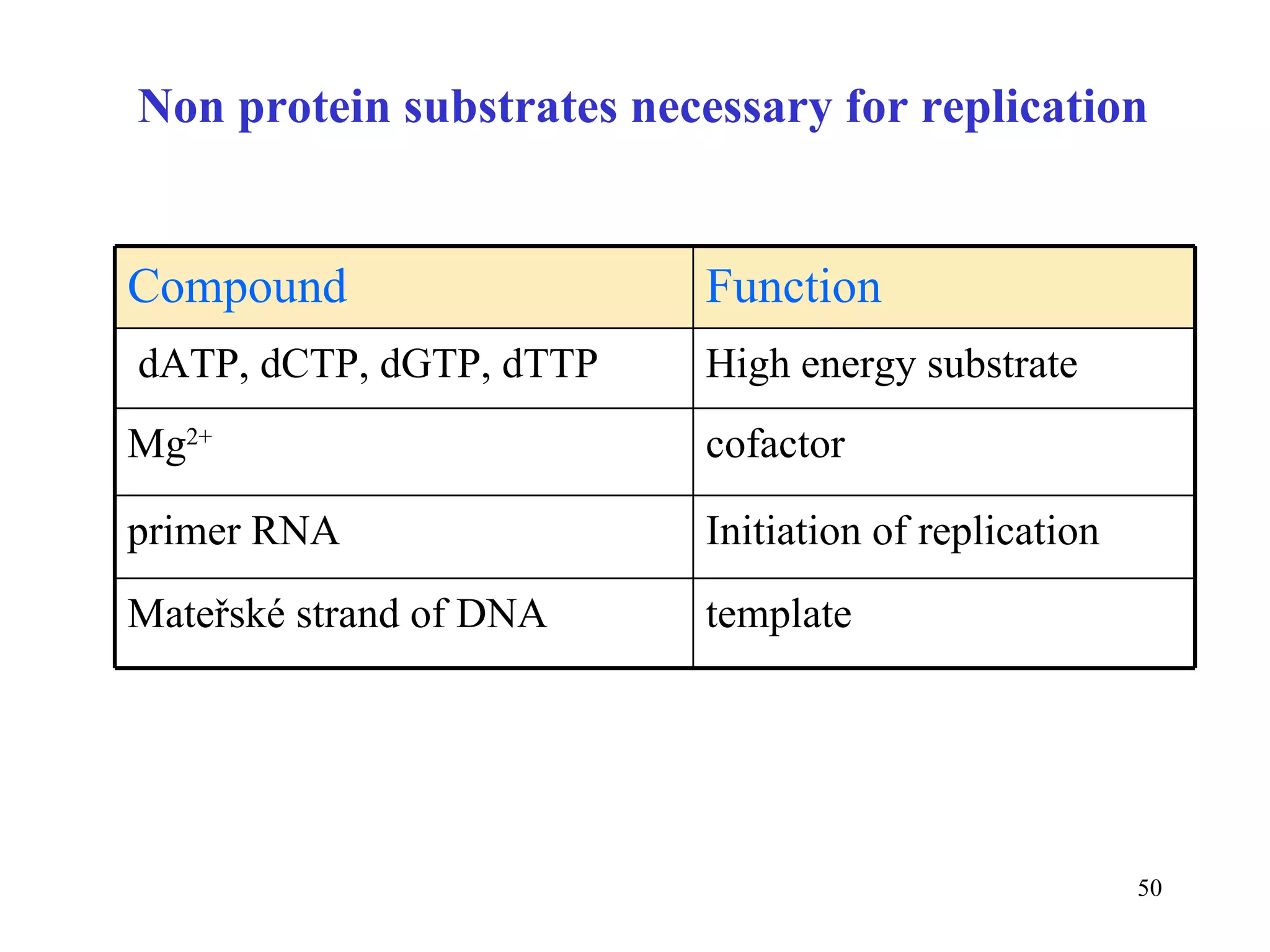
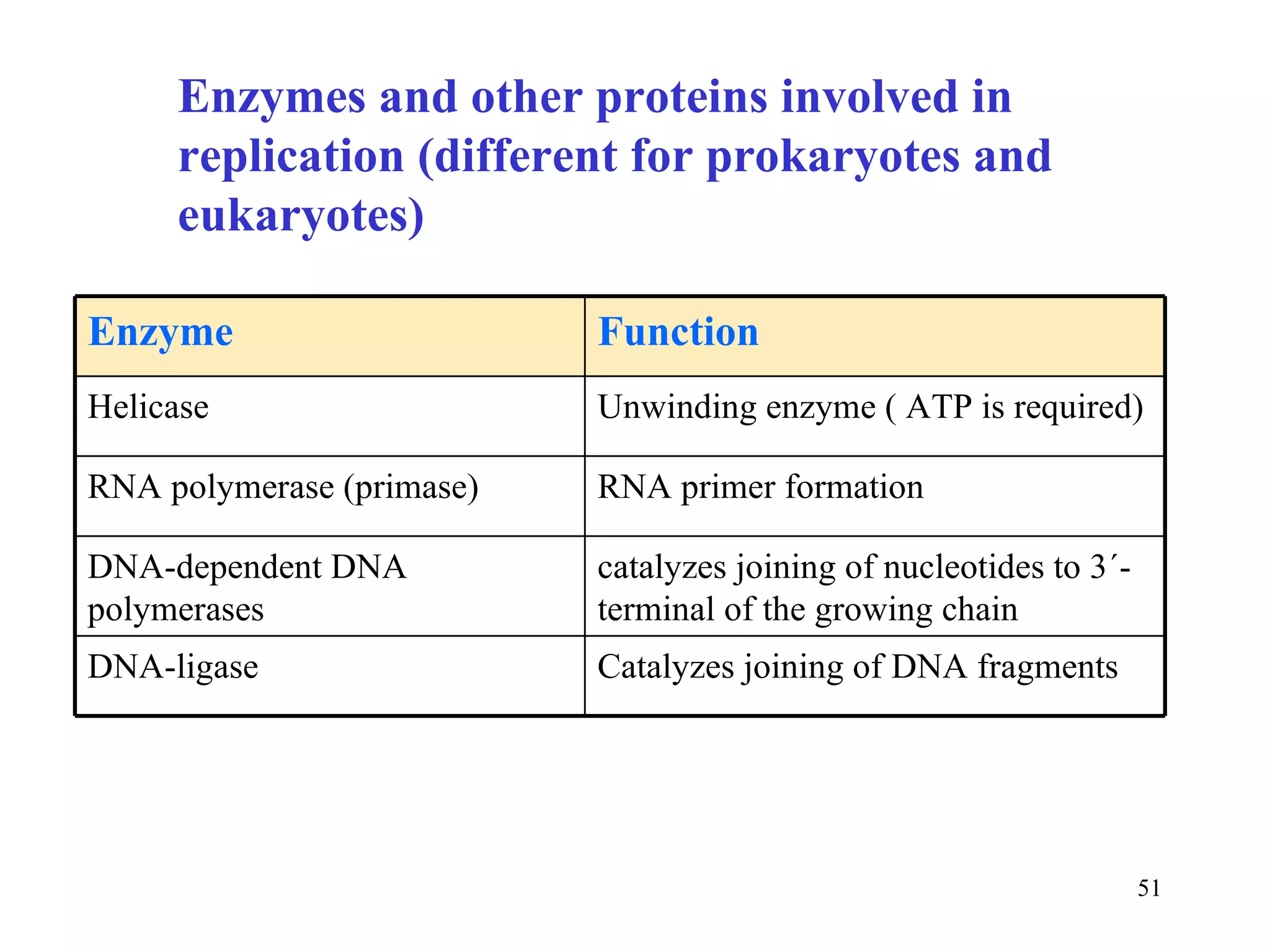
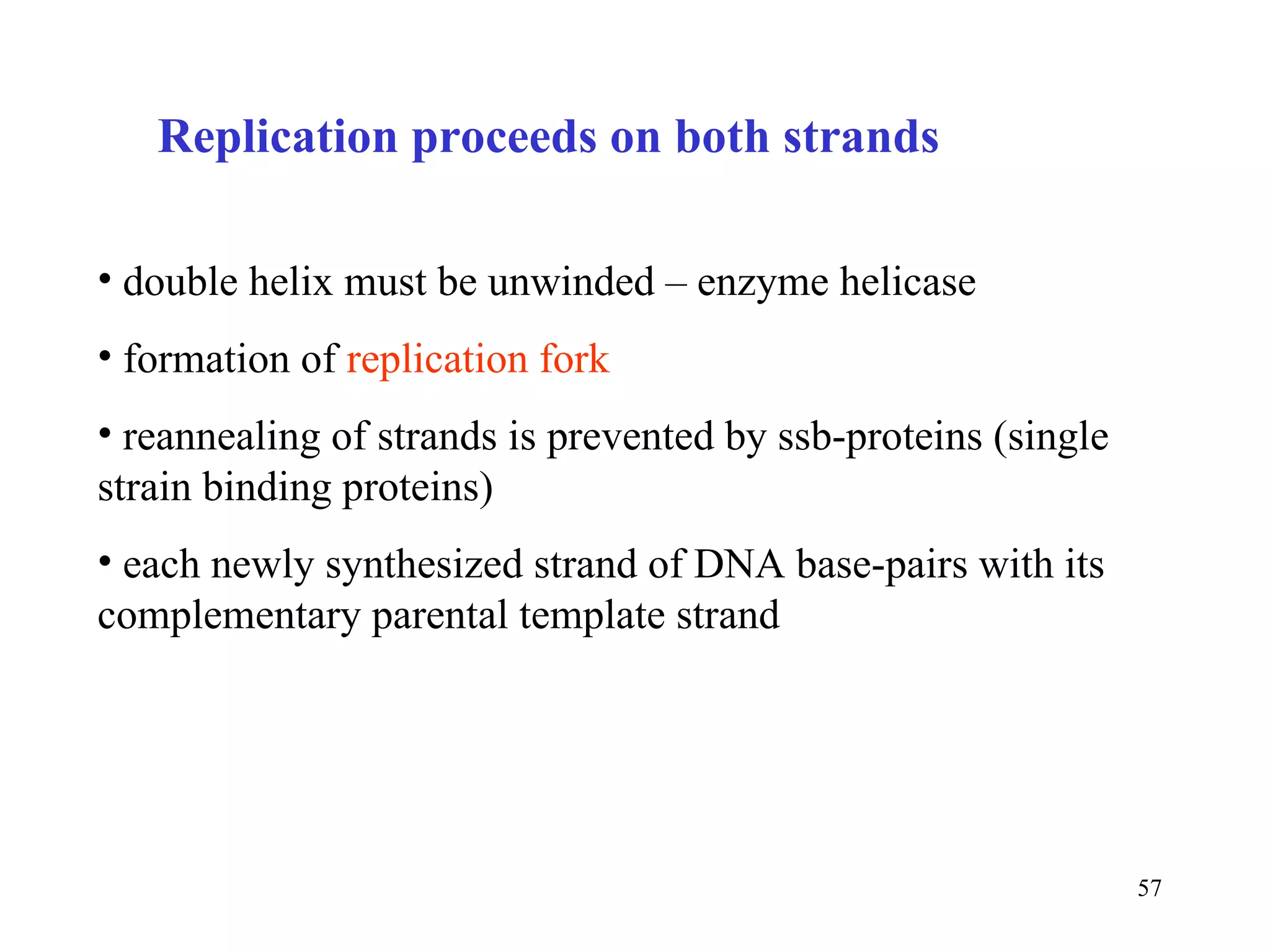
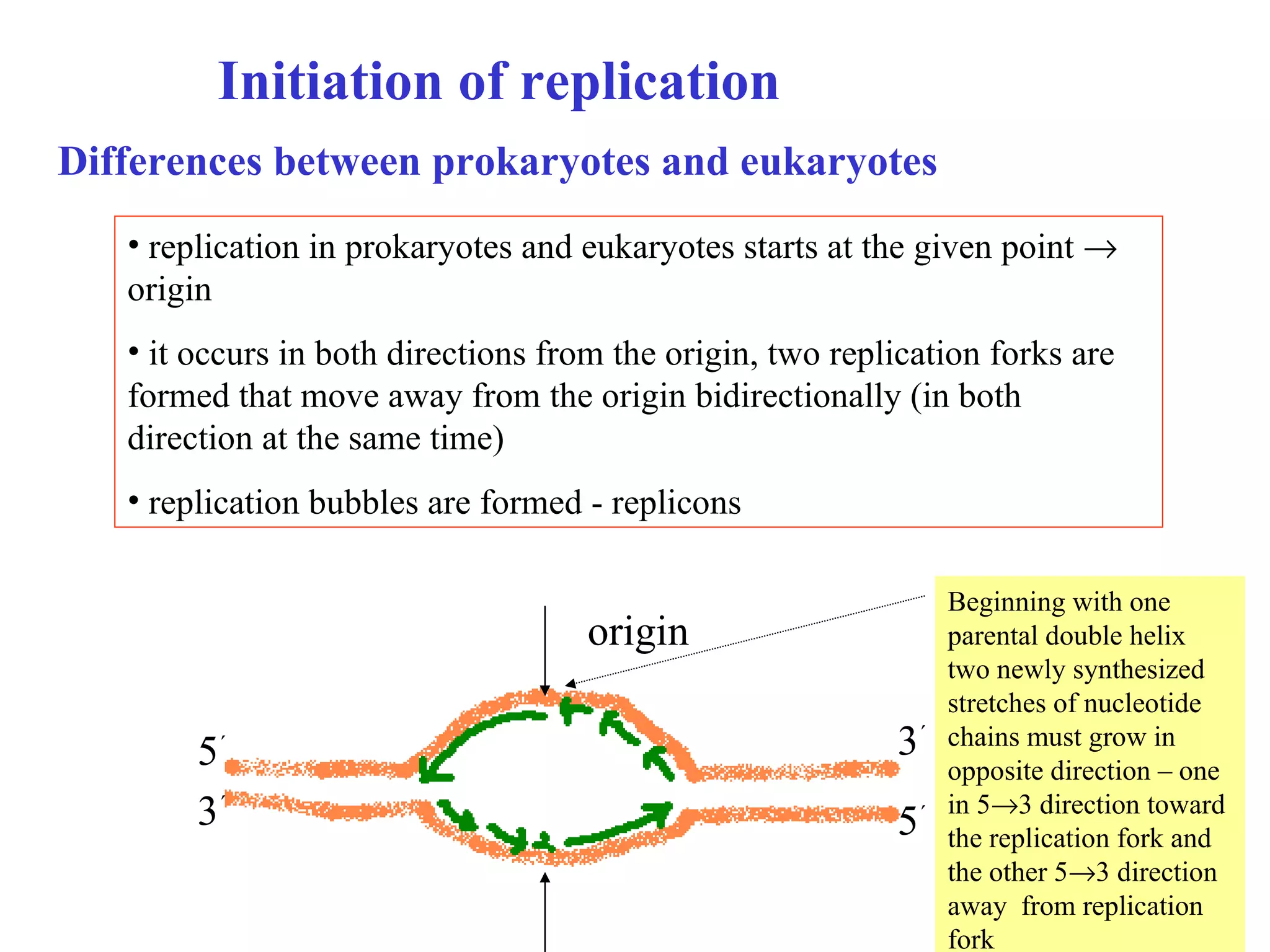
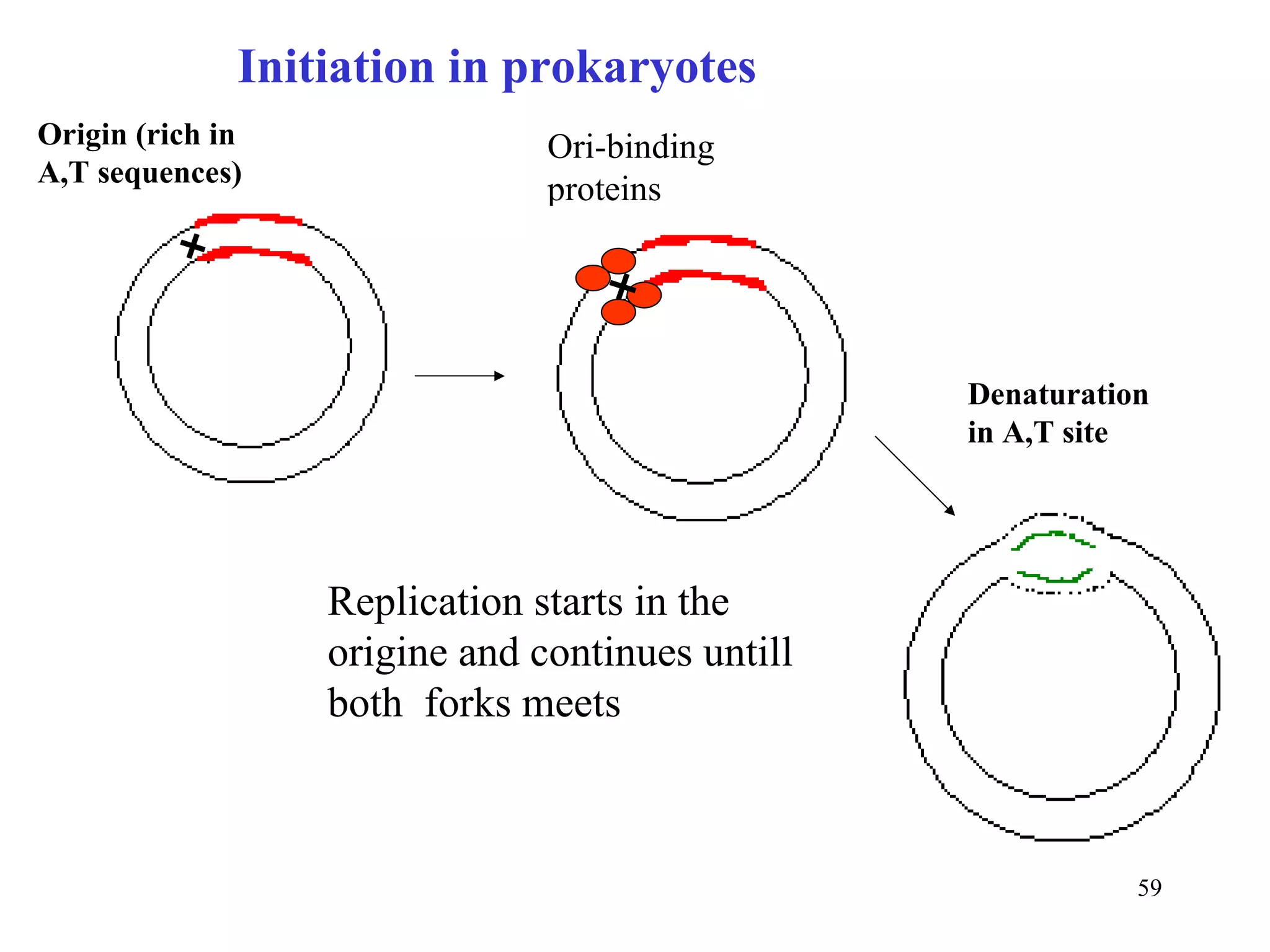
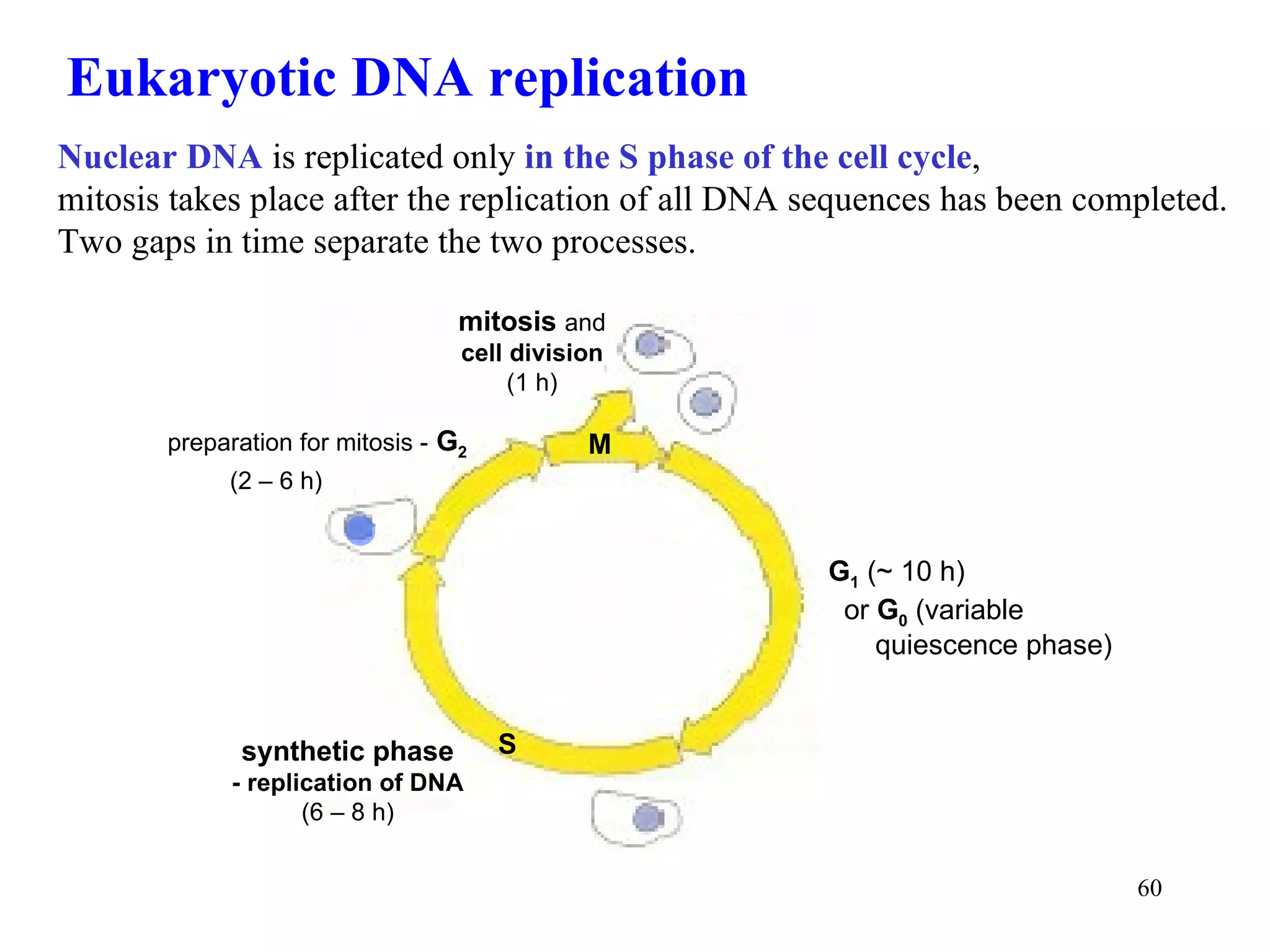
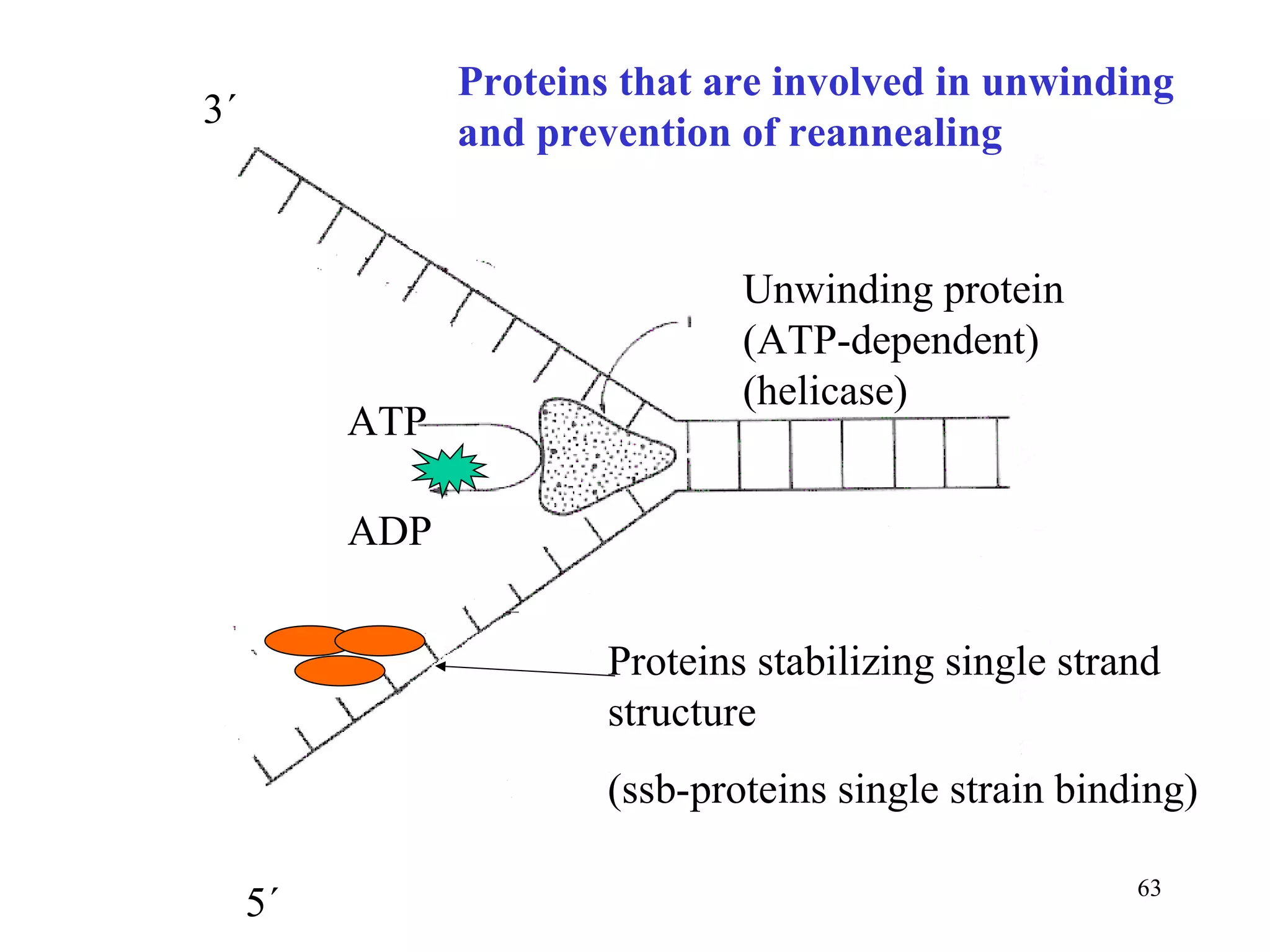
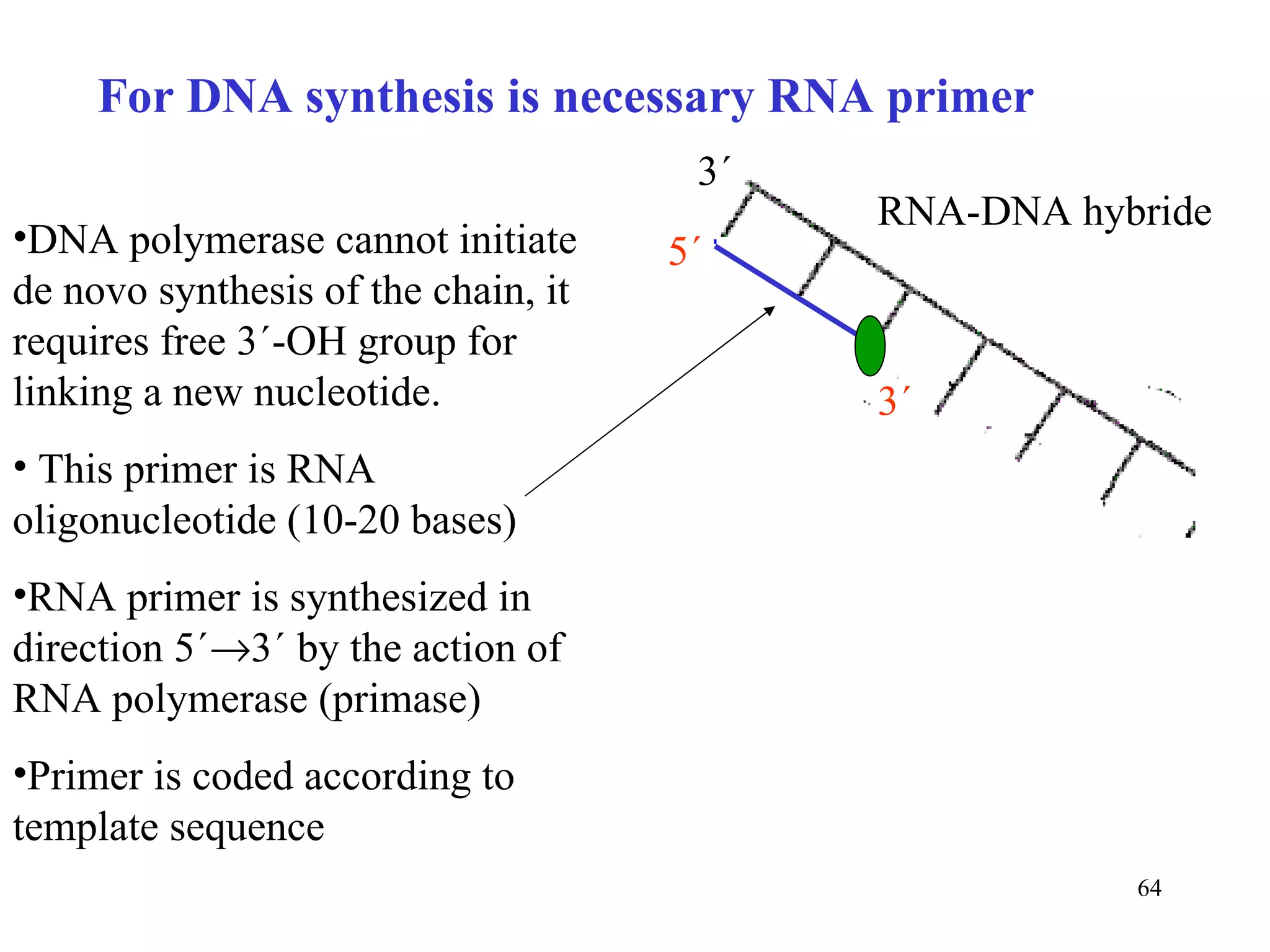
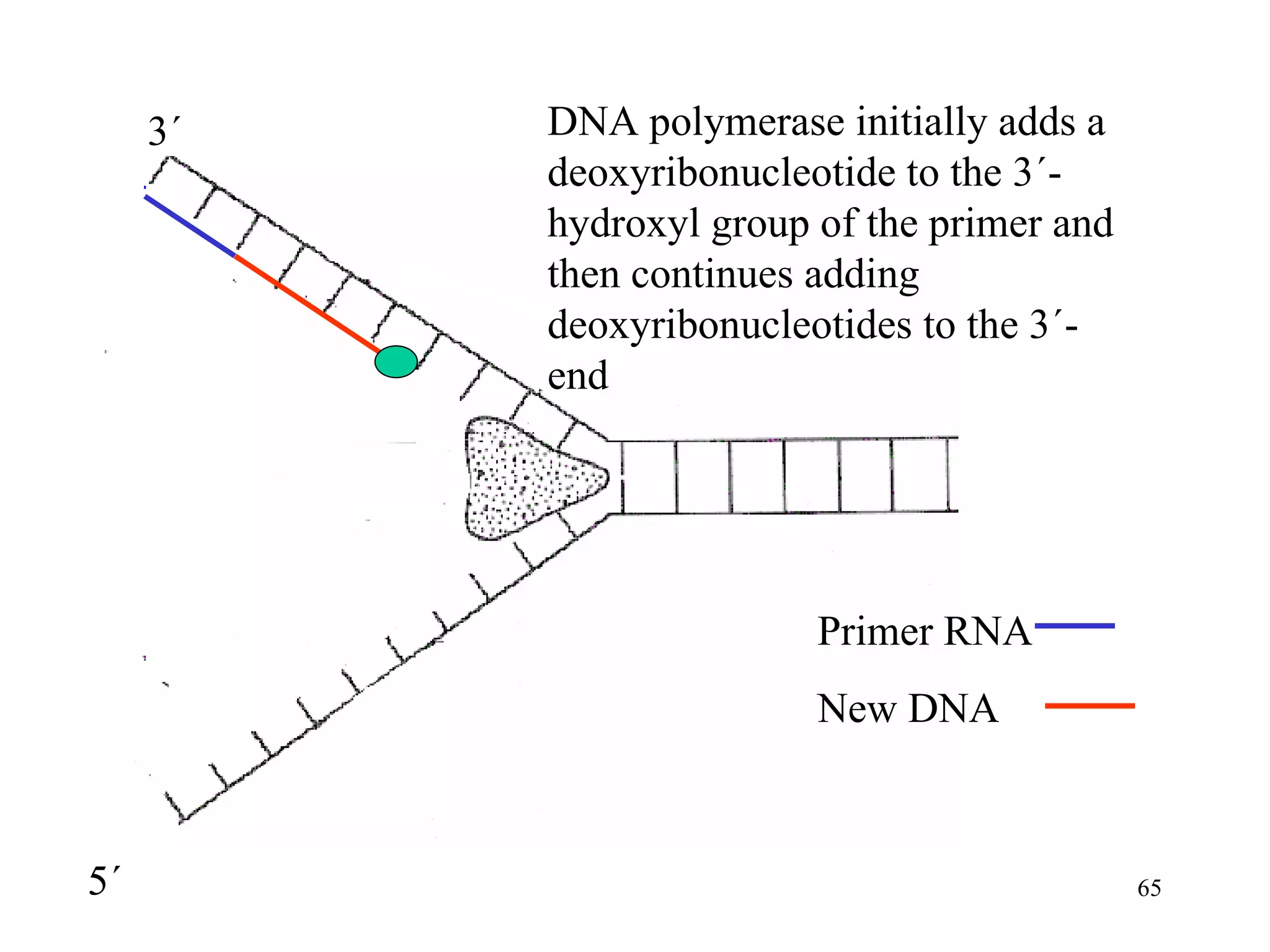
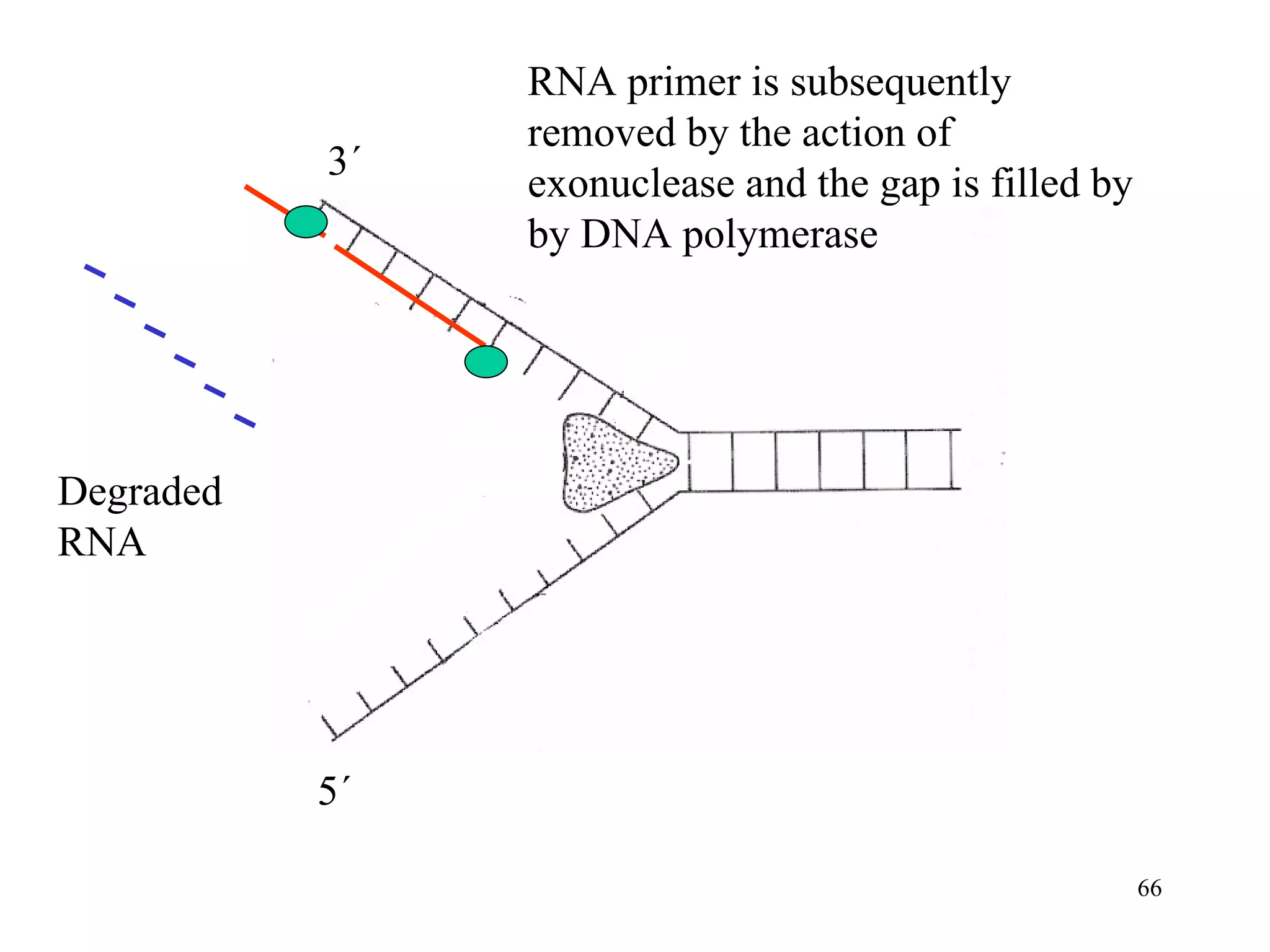
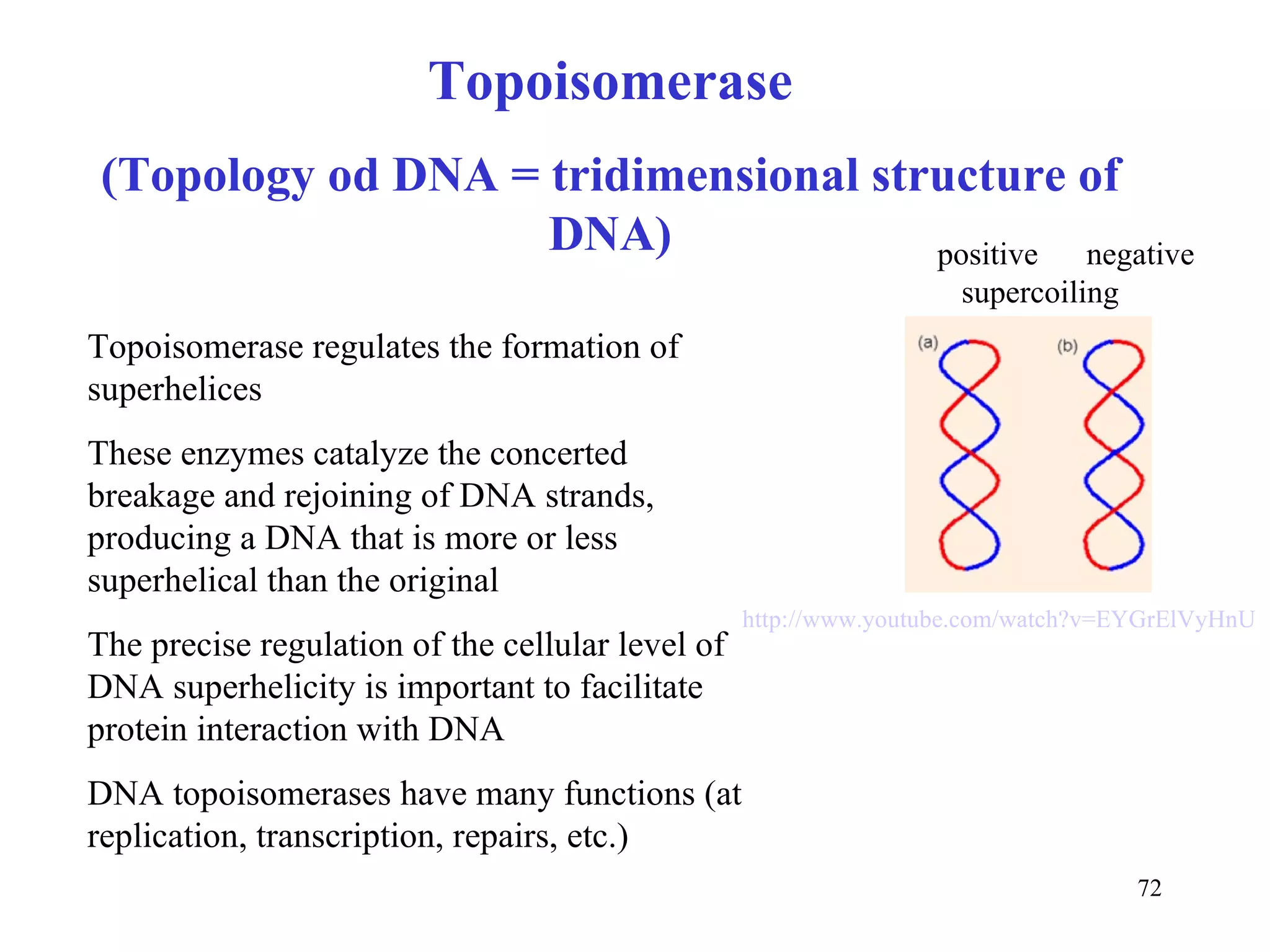
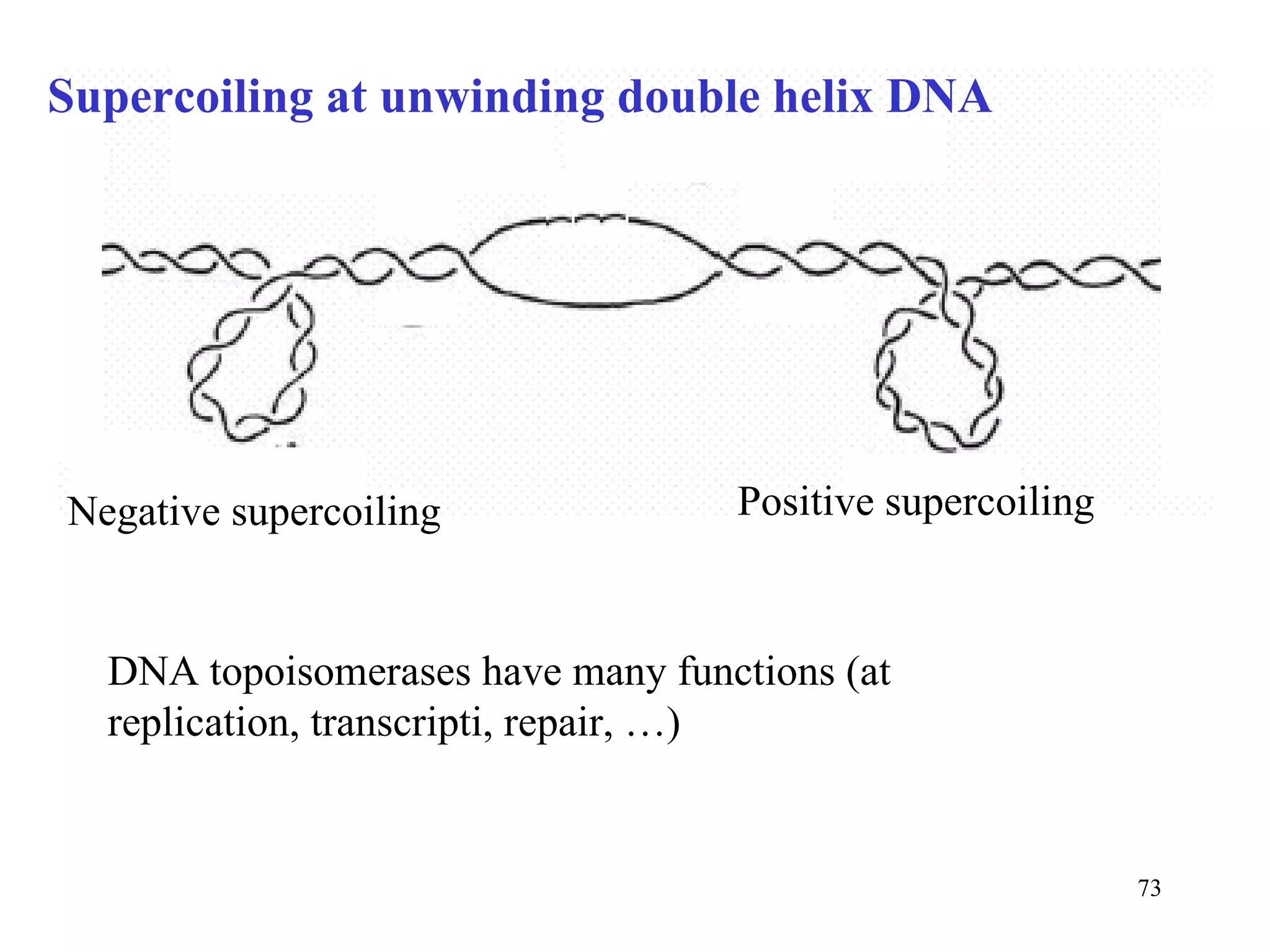
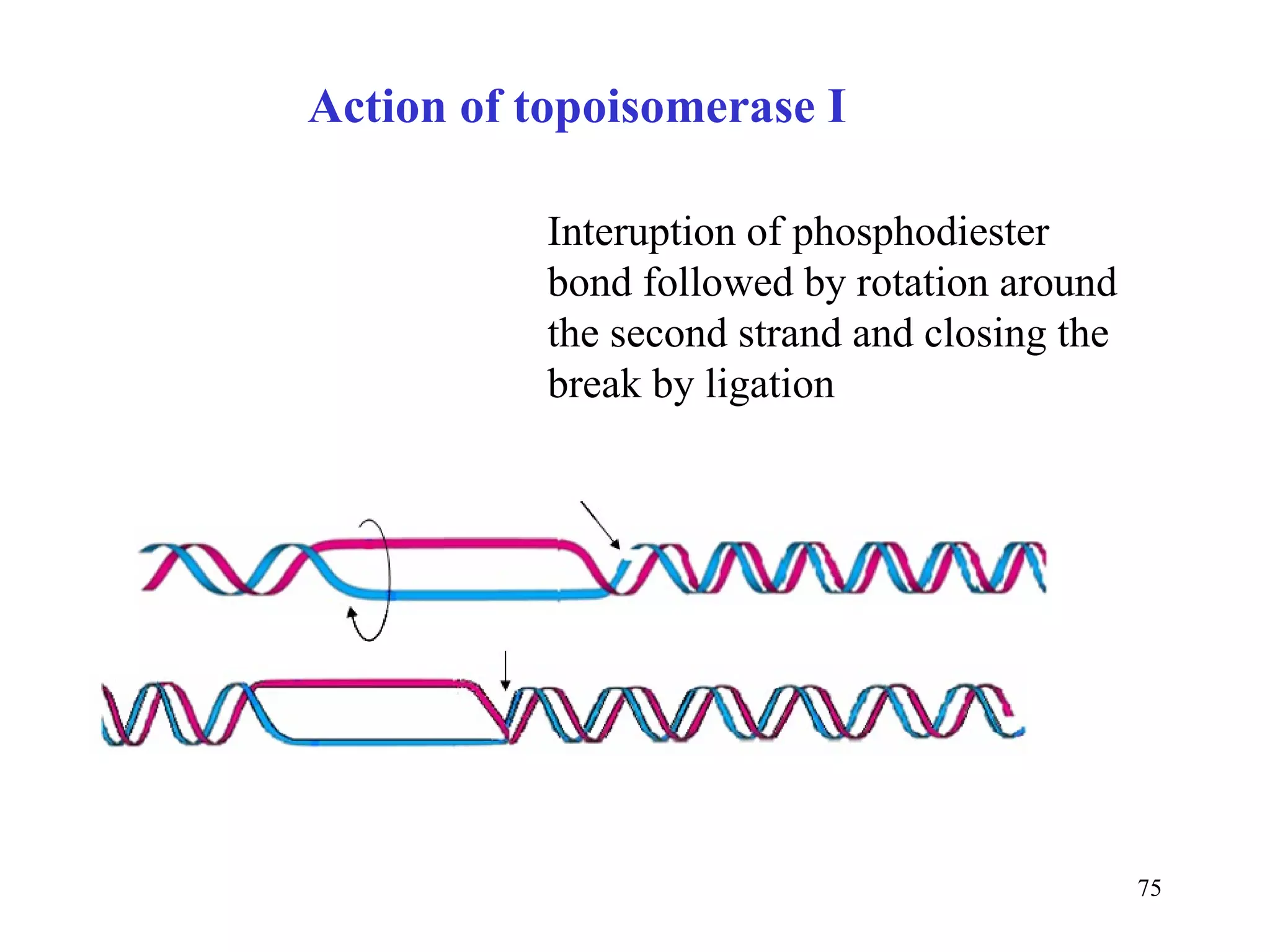
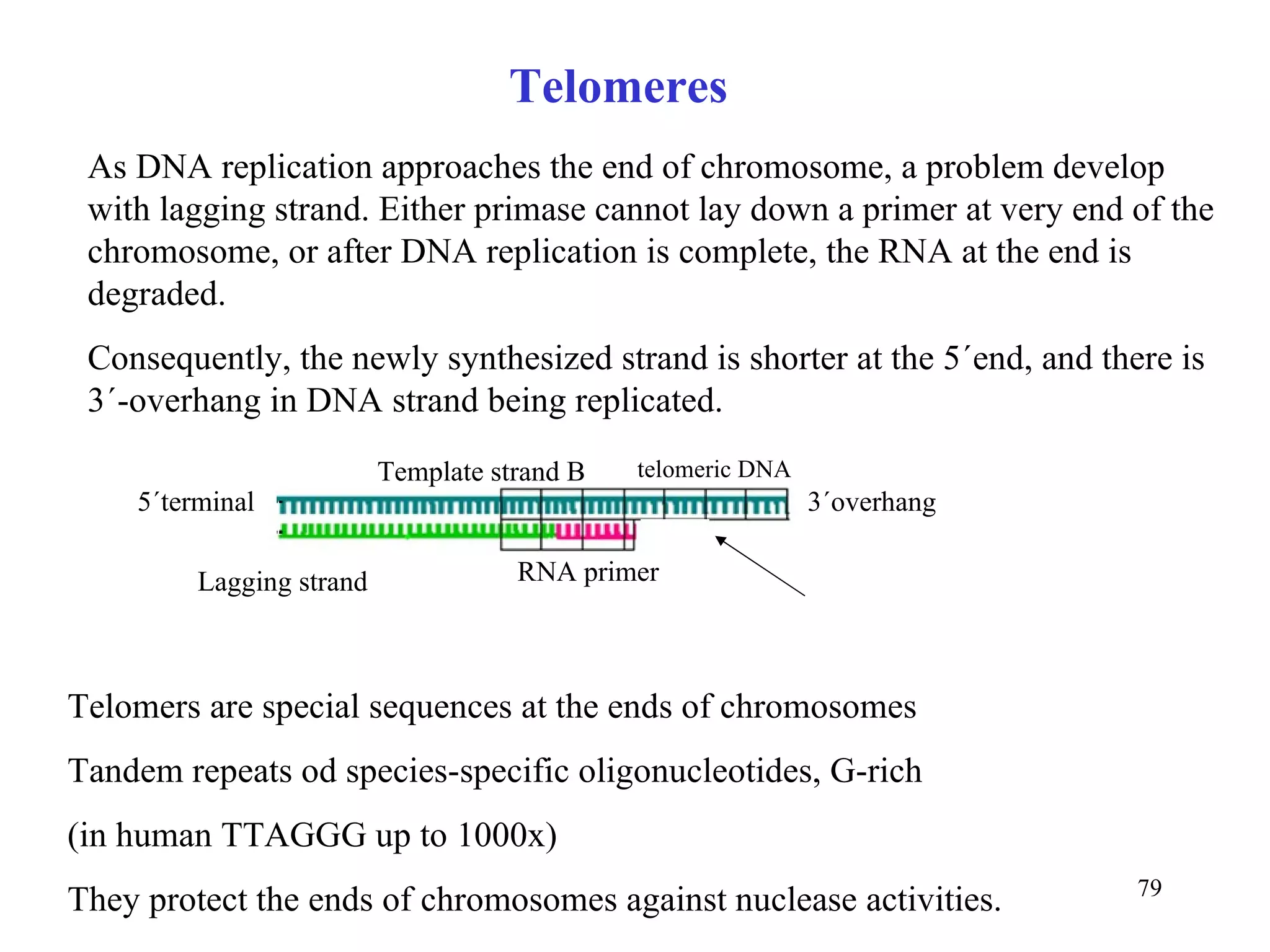
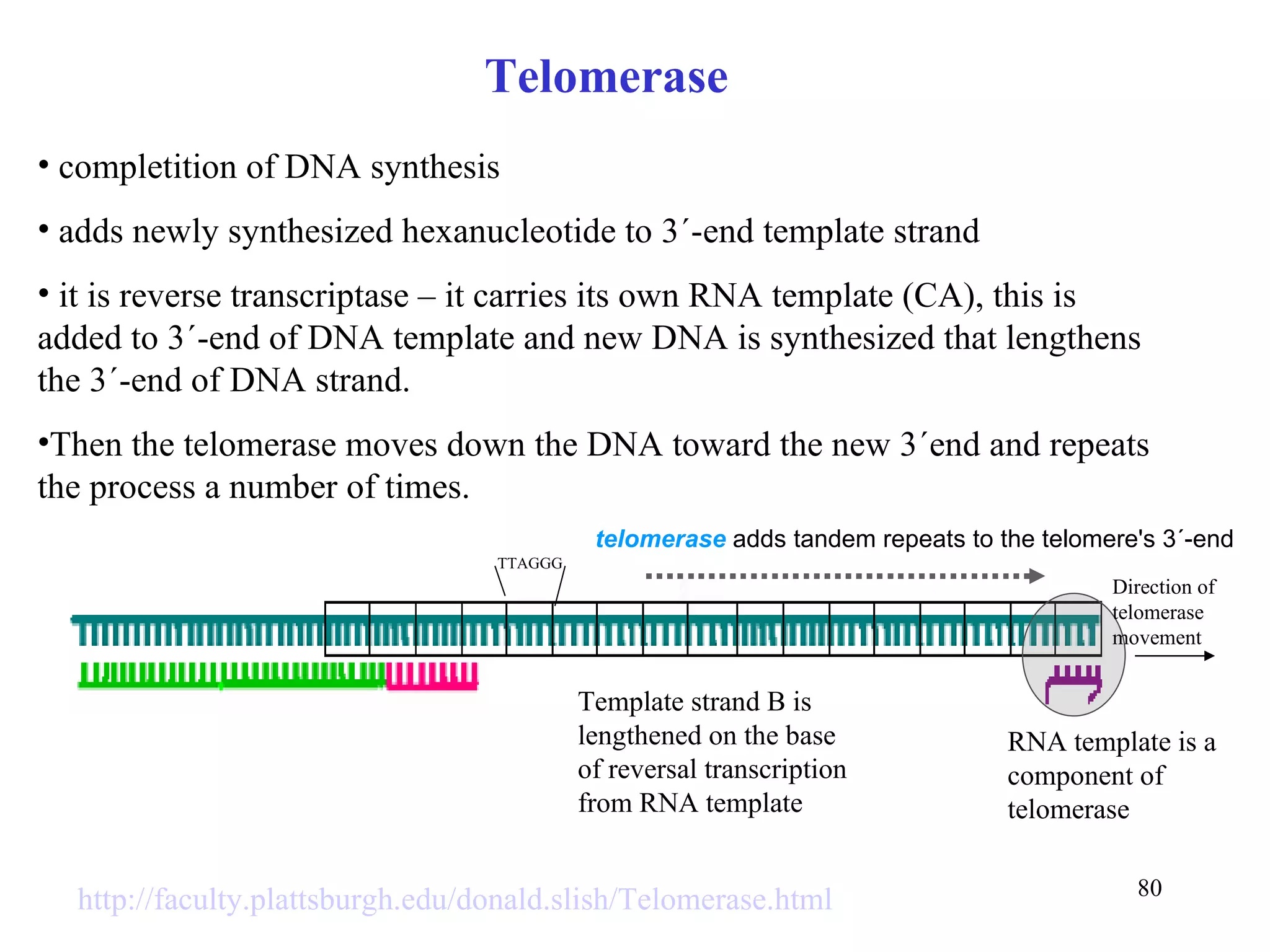
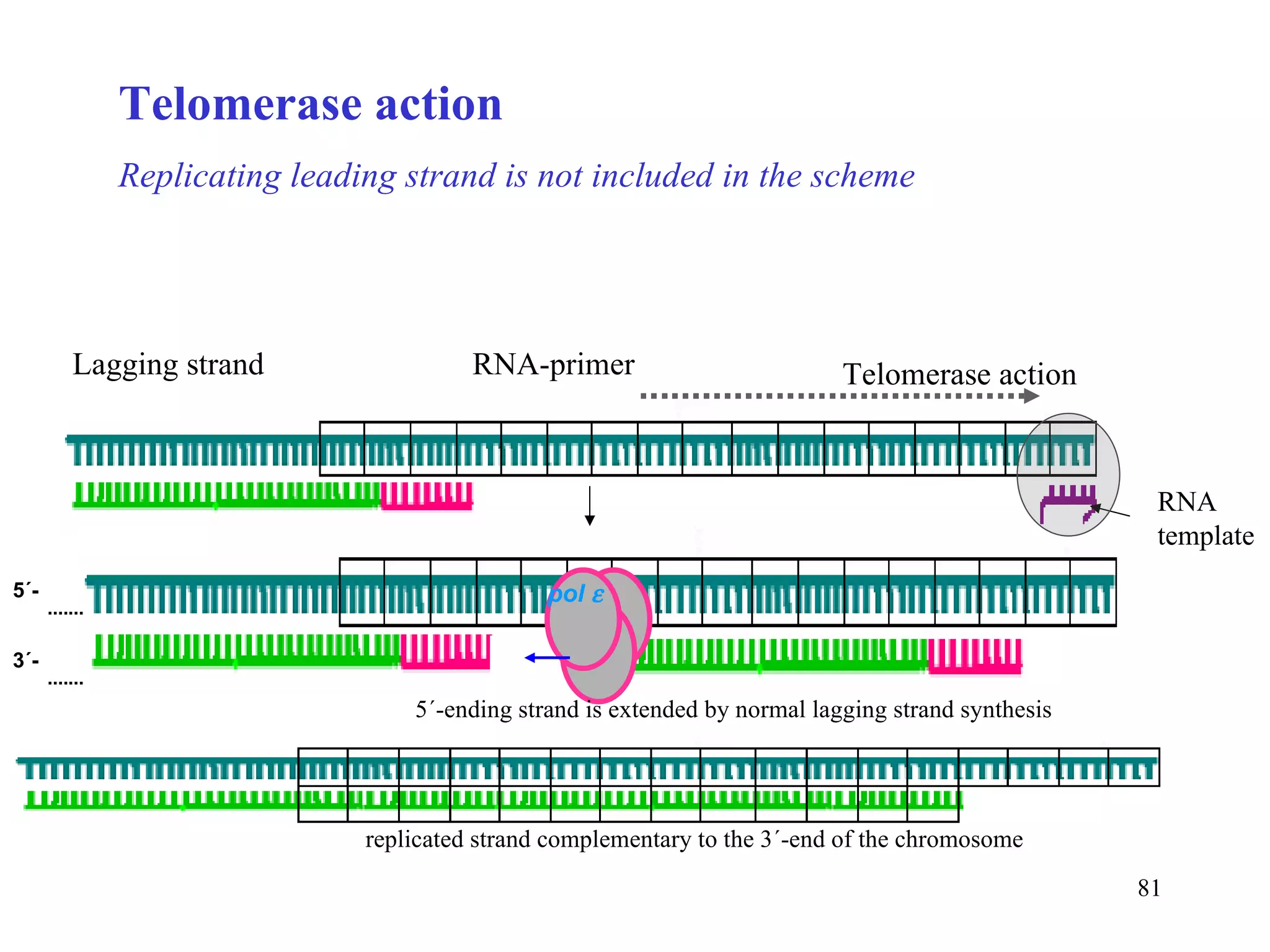
- The document summarizes purine and pyrimidine nucleotide metabolism. It describes the biosynthesis and degradation pathways of purines and pyrimidines, and their regulation. Key enzymes and cofactors like tetrahydrofolate and PRPP are discussed.
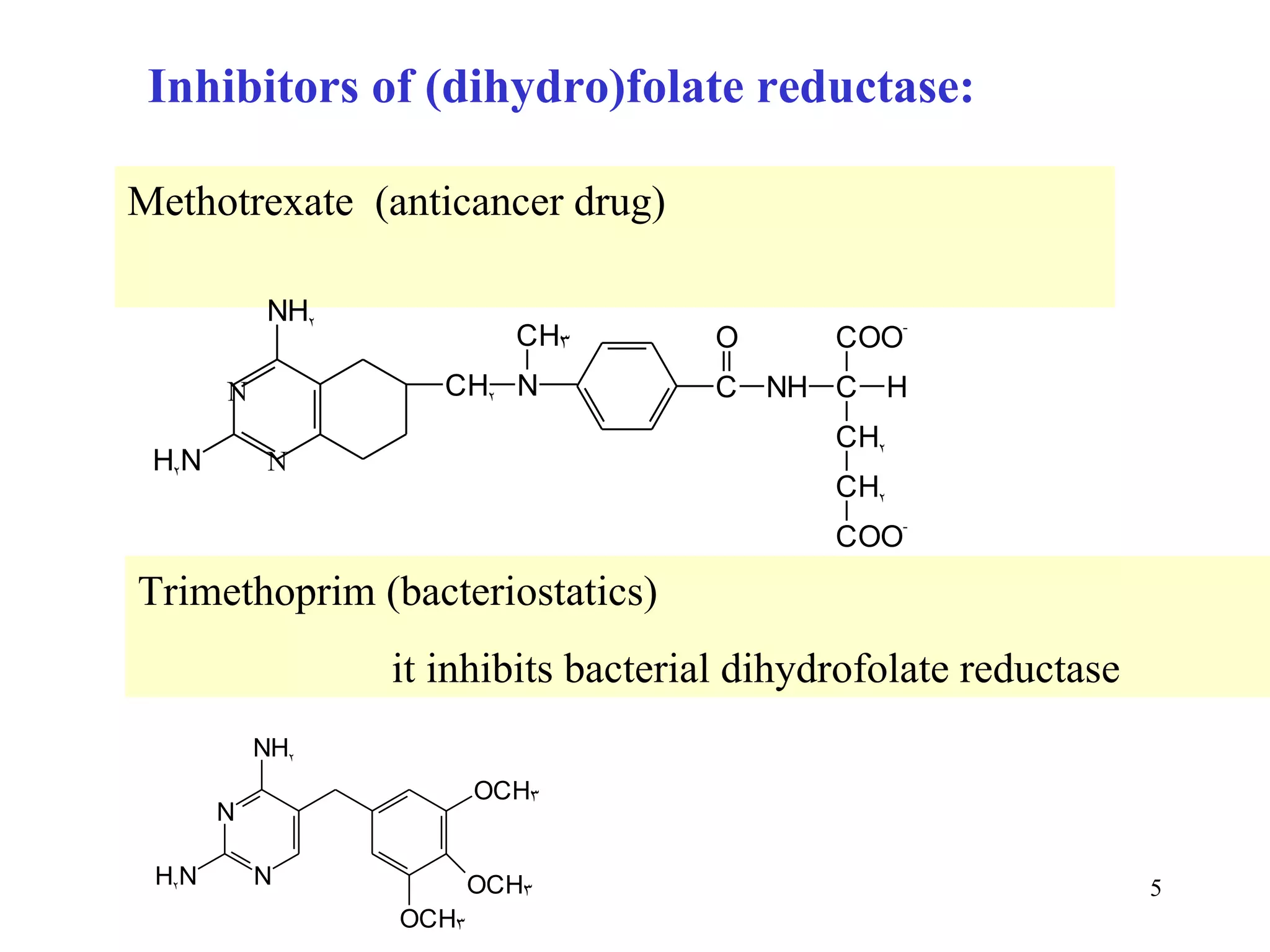
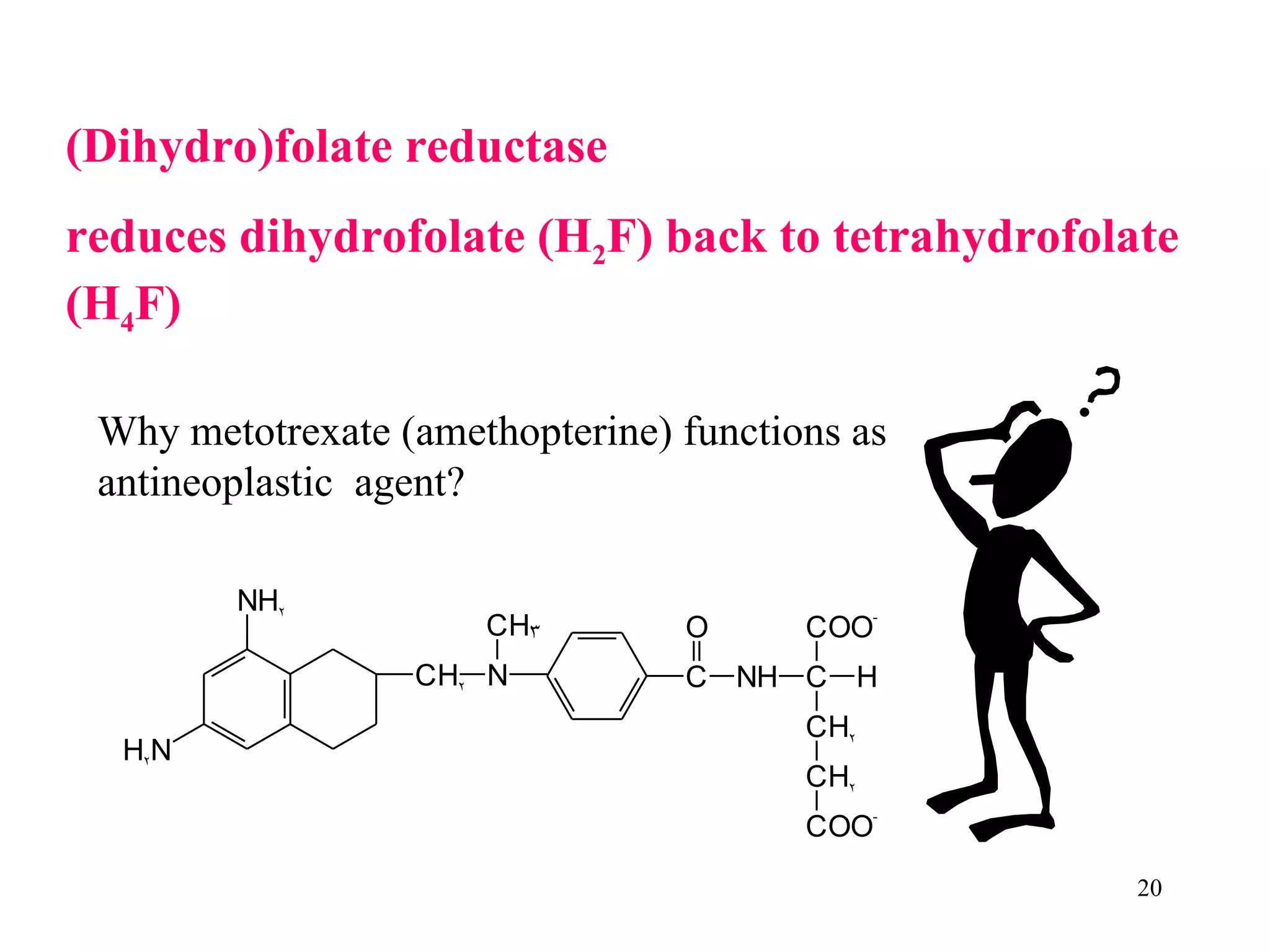
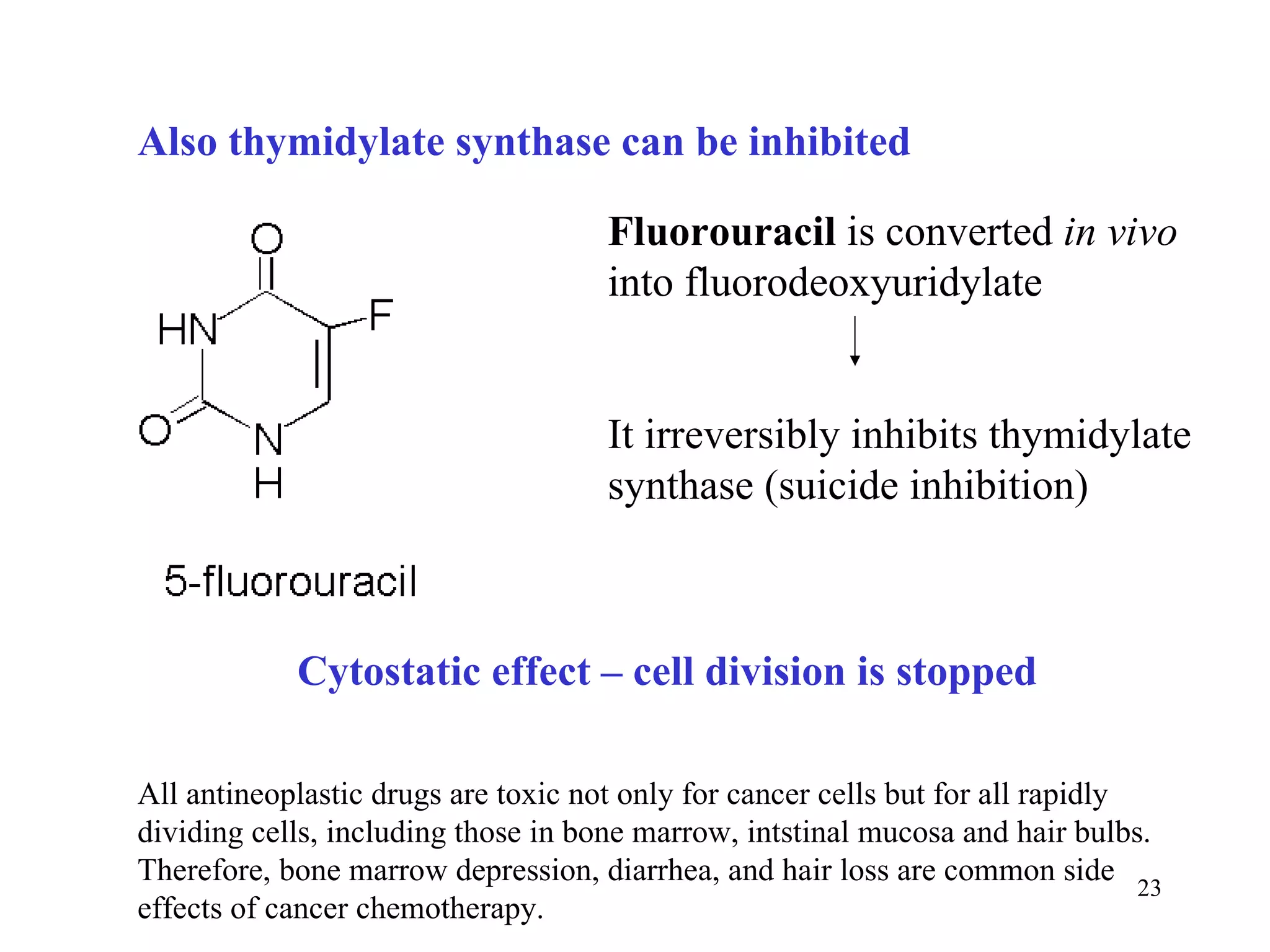
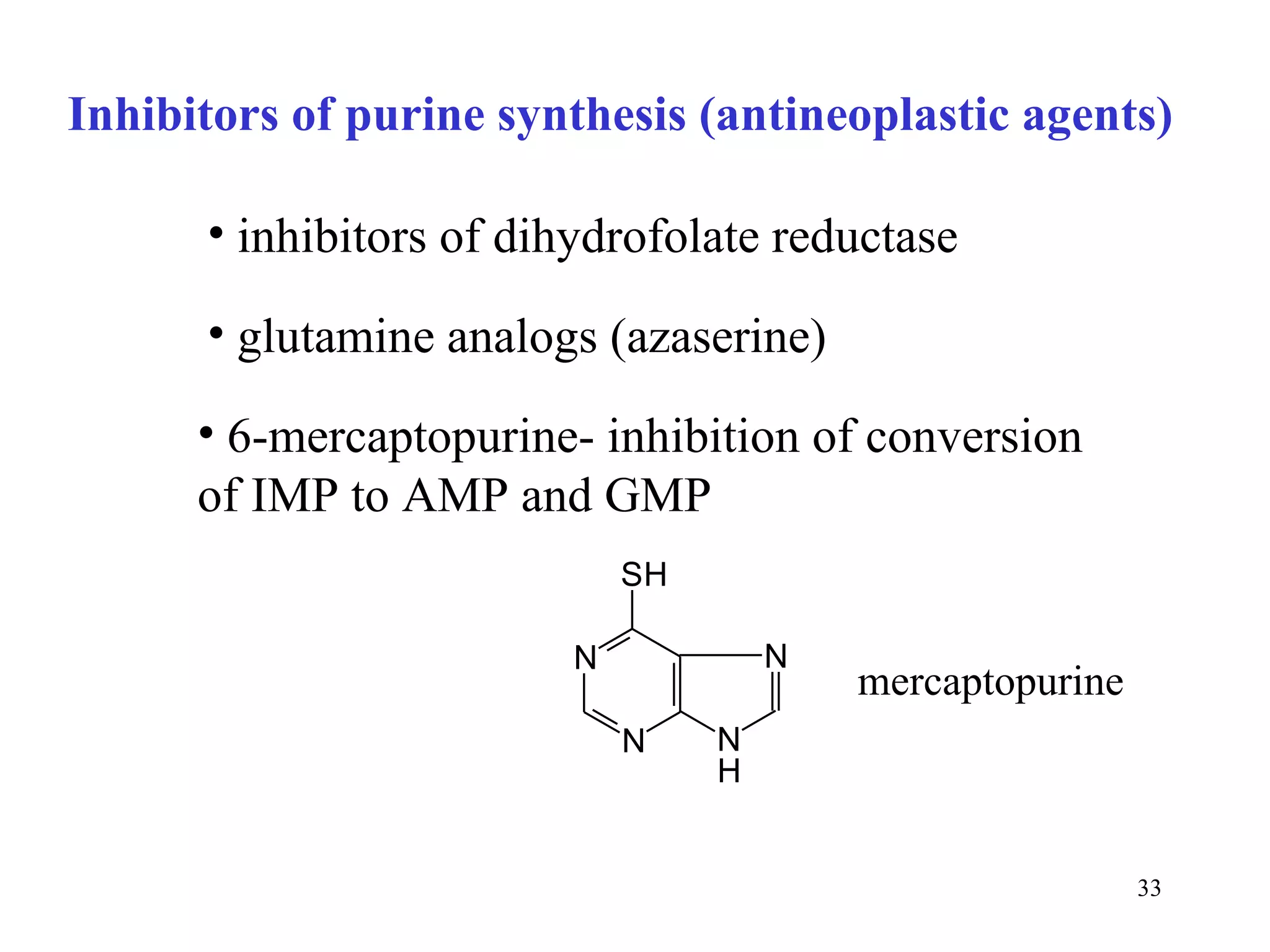
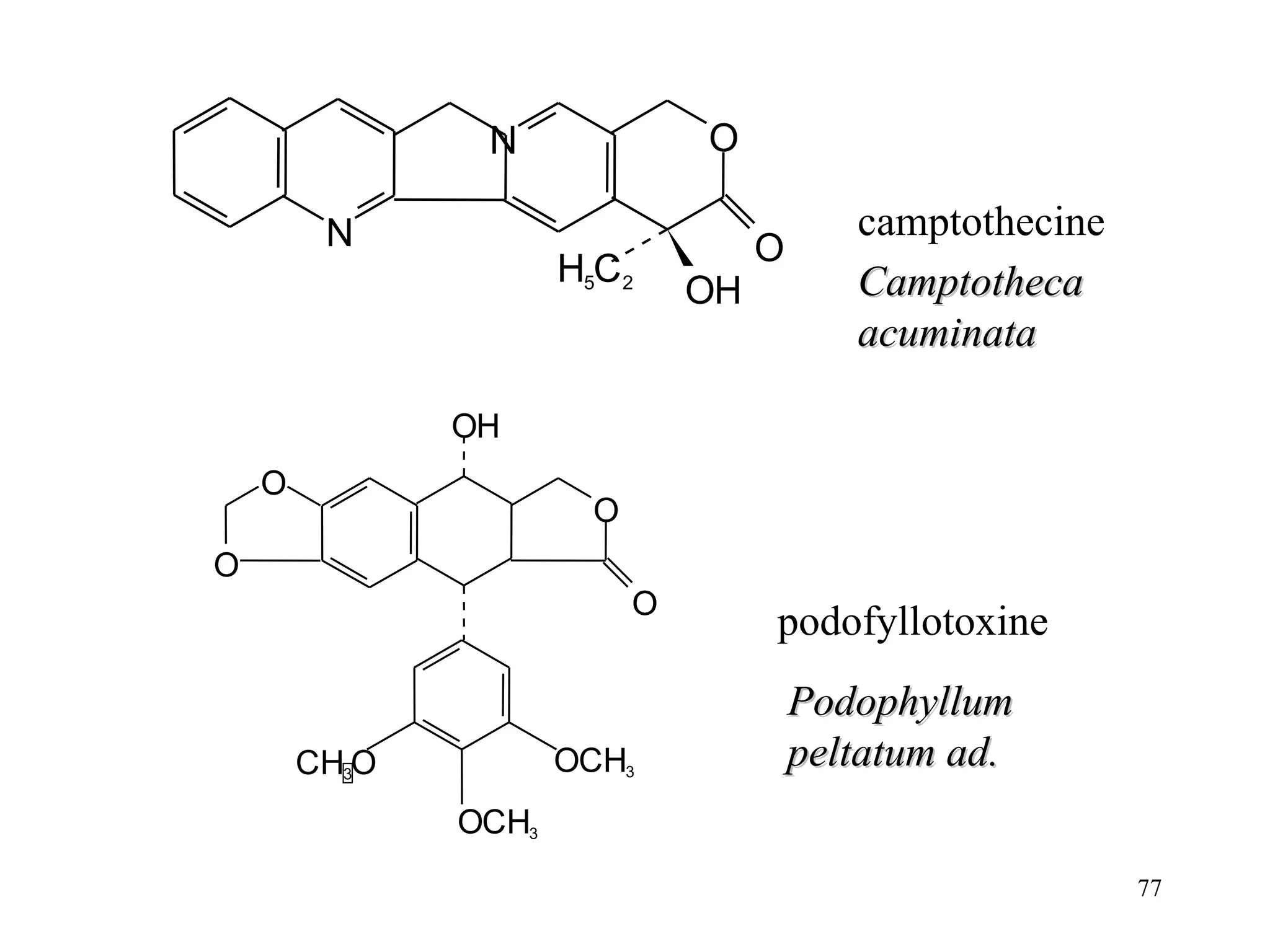
- Inhibitors of nucleotide metabolism are important targets for cancer chemotherapy drugs. Drugs like methotrexate and fluorouracil inhibit key enzymes to selectively target rapidly dividing cancer cells.
- The metabolism of purines and pyrimidines provides the essential building blocks for nucleic acid synthesis and is tightly regulated through feedback inhibition at multiple steps in the pathways. Proper regulation is crucial as nucleotides are required for cell growth and proliferation.