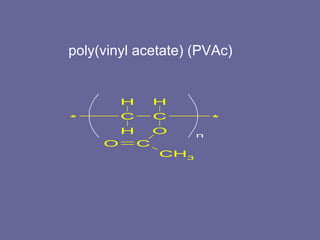
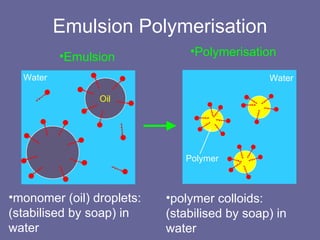
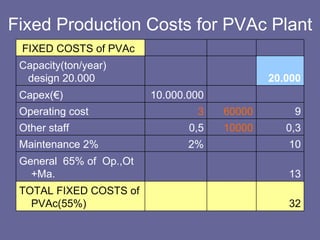
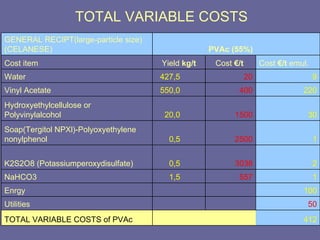
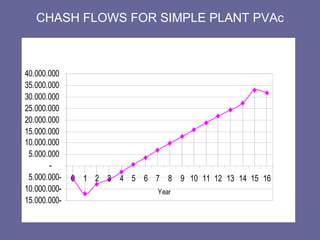
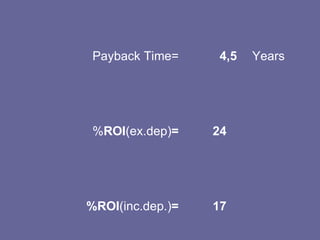
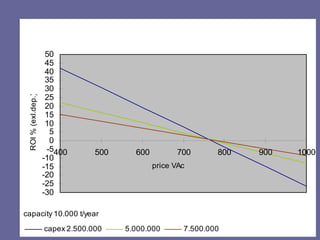
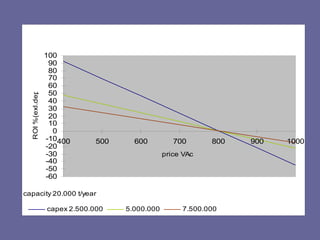
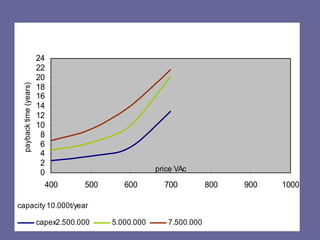
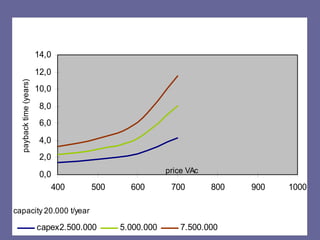
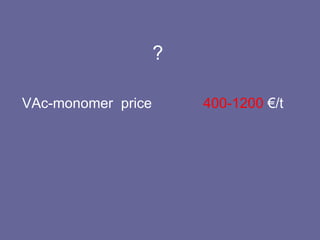This document discusses research proposals for the production of polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) emulsions. It aims to analyze the composition of Mowilith resins, how they are made, production processes and costs. The document outlines the polymerization of PVAc and economic analysis. It also provides details on the emulsion polymerization process, raw material requirements, production cost estimates and a project cash flow analysis for a proposed PVAc plant with an initial capacity of 20,000 tons per year and investment of 10 million euros.



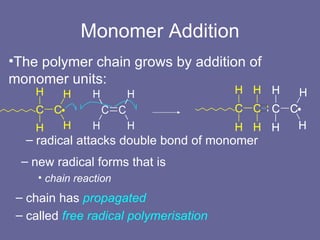
![Initiation From where does the first unpaired electron come? Generated by an initiator e.g. hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) has O–O bond (easy to break) generates 2 OH • radicals usually don’t use H 2 O 2 but other peroxides, e.g.: potassium persulfate persulfate ion is: [O 3 S–O–O–SO 3 ] 2– O–O- bond breaks readily at 60 o C to initiate reaction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pvac-120202122925-phpapp02/85/PVAc-5-320.jpg)